Abstract
Optogenetics has advanced our understanding of the neural basis of simple behaviors in rodents and small animals. In primates, however, for which more sophisticated behavioral assays exist, optogenetic manipulations of behavior have been unsuccessful. Here, we report that monkeys reliably shift their gaze toward the receptive field of optically driven channelrhodopsin–2–expressing V1 neurons. This result establishes optogenetics as a viable tool for the causal analysis of behavior in primate brain.
In 2007, Aravanis and colleagues pioneered an optogenetic approach to control the behavior of an experimental animal 1. They expressed channelrhodopsin–2 (ChR2) in the vibrissal motor cortex of the mouse and demonstrated that activation of ChR2 by blue light evoked whisker deflections. Since then, this approach has found numerous applications in the study of the neural circuitry underlying simple behaviors in rodents and lower animals 2, 3. These successes bode well for the use of optogenetics in the analysis of more complex behaviors, cognition, and their disorders 4. A key step towards this goal is to adapt this technology to non–human primates, both as a tool for analyzing neural function in more sophisticated models of behavior and as a stepping–stone toward clinical applications. Light–sensitive proteins have been used to influence neural activity in the primate brain 5-7, and ChR2-mediated activity has been shown to reduce saccade latency 8. Here we demonstrate the first use of optogenetics to evoke a behavioral response in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta).
We expressed channelrhodopsin–2 (ChR2) in a small region of the primary visual cortex (V1) of two monkeys, and asked whether ChR2–mediated neuronal activation produced a visual sensation at the location of the neurons’ receptive fields (RFs). The ChR2 gene was delivered with an AAV vector (rAAV1–hSyn– ChR2(H134R)–mCherry) which was pressure injected at multiple depths, ~300 μm apart, spanning the thickness of the cortex. Five to seven weeks later, we placed an optical fiber just above the dura mater near the site of injection and shined pulses of blue light to stimulate V1 neurons. This “optical stimulation” (as opposed to “visual stimulation”, which would be through the eyes) reliably modulated single– and multi–unit activity. The effectiveness of optical stimulation was specific to the site of injection (data not shown).
A key question was whether ChR2–mediated activation of V1 neurons was sufficient to engage visuomotor behavior. To answer this question, we used a behavioral paradigm developed by Tehovnik and colleagues 9 that exploits monkeys’ natural tendency to orient toward flashed stimuli. The task consisted of two randomly interleaved trial types, ‘Fix’ and ‘Tar’. On Fix trials, monkeys fixated a central fixation point (FP) for 500–1000 ms and received liquid reward immediately after FP was extinguished (Fig. 1a). Unbeknownst to the monkeys, on a random half of the Fix trials, we applied optical stimulation 130 ms after the disappearance of FP (‘Fix+Op’; Fig. 1b). In both Fix and Fix+Op trials, monkeys received reward for maintaining fixation, and not for their oculomotor behavior after the disappearance of FP (Fig. 1a,b top). On Tar trials, monkeys received reward for making a saccade to a visual target that appeared 100 ms after FP was extinguished (Fig. S1). The optical stimulation was also applied in a random half of the Tar trials (‘Tar+Op’).
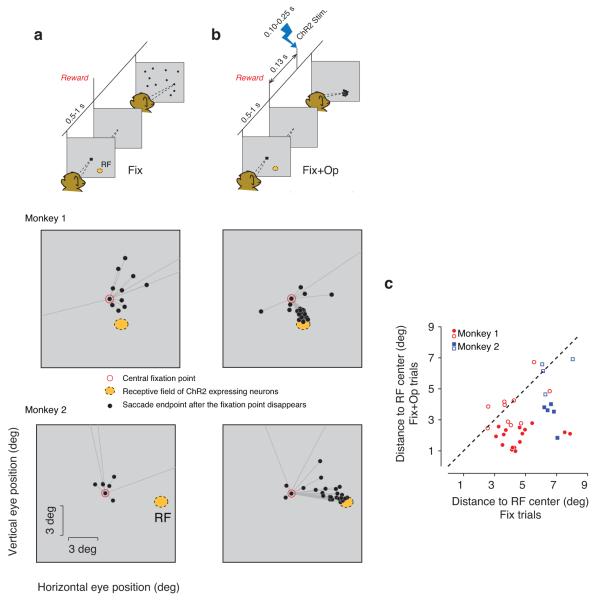
Figure 1.
Task description and distributions of saccade endpoints in Fix trials. Schematics in (a) and (b) show task events for trials with and without optical stimulation (‘Fix’ and ‘Fix+Op’ respectively). On both Fix and Fix+Op trials, monkeys were required to maintain fixation for 0.5–1 sec on a central fixation point (FP, black square) and received liquid reward immediately after FP disappeared. On Fix+Op trials (b), the disappearance of FP was followed by optical stimulation, which consisted of light pulses of 0.1 to 0.25 sec duration. Black circles in the topmost panel of the schematic diagrams represent endpoints of spontaneous saccades made after the disappearance of FP. Middle and bottom panels show post–fixation spontaneous saccades in example experimental sessions in the two monkeys. Whereas in the Fix condition (a), saccade endpoints (black circles) were broadly distributed, in the Fix+Op condition, they were concentrated near the RF of the stimulated neurons (orange) even though no visual target was presented. In these sessions, the laser intensity was set to 50 mW for monkey 1 and 20 mW for monkey 2. (c) Comparison of saccade endpoints in trials with and without optical stimulation. For each experiment, we measured the distance of each saccade endpoint to the center of the RF of the optically stimulated neurons and computed a mean distance for the Fix and Fix+Op trials in each block. In most experiments, saccades in Fix+Op trials (ordinate) landed closer to the RF center than saccades n the Fix trials (abscissa). Red circles and blue squares correspond to data collected from monkey 1 and monkey 2, respectively. Filled symbols correspond to blocks in which the optical stimulation had a significant effect on behavior (Mann–Whitney, p<0.05).
We hypothesized that the optical stimulation would bias saccades toward the RF of the optically stimulated neurons. To test this hypothesis, we compared saccade endpoints after the disappearance of FP in different conditions. On the Fix trials, the disappearance of FP was followed by spontaneous saccades with variable directions and amplitudes (Fig. 1a). In the Fix+Op condition, saccade endpoints were indeed biased toward the RF (Fig. 1b). To quantify this observation, we compared the Euclidean distance of the saccade endpoints to the center of the RF between the Fix and Fix+Op trials. We made this measurement in 35 distinct experimental sessions that differed in the position of the electrode, optical fiber, or both. This magnitude of this optical stimulation effect varied with laser power (Fig. S2), and was significant in 21 of 35 experiments (16 of 26 in one monkey, and 5 of 9 in the other; Fig. 1c). Overall, the distance of the saccade endpoints to the center of the RF was significantly smaller when optical stimulation was applied than when it was not (Mann–Whitney; monkey 1: p<1e–10; monkey 2: p<1e–10). In the Tar and Tar+Op trials, nearly all saccades were directed toward the visual target, which was presented in the RF of the ChR2–expressing neurons (Fig. S1).
We also compared saccade latencies across conditions (Fig. S3). The median latency of the first saccade after the disappearance of FP was 0.29, 0.24 and 0.26 sec in the Fix+Op, Tar and Tar+Op conditions, respectively. The saccade latency in the Fix+Op and Tar+Op conditions was significantly longer that those in the Tar condition (Mann–Whitney; Tar versus Tar+Op: p<1e–10; Tar versus Fix+Op: p<1e–4).
The retinotopic specificity of saccades in the Fix+Op condition suggests that optical stimulation evoked a spatially localized visual sensation. However, it is also possible that this spatial specificity was established indirectly in the course of Tar+Op trials, in which visually guided saccades toward the RF of the optically stimulated neurons were rewarded. In other words, the repeated pairing of optical stimulation and the reward given for RF–directed saccades in the Tar+Op condition could have conferred retinotopic specificity to an otherwise nonspecific stimulation effect. Under this alternative explanation, the location of the saccade endpoints in the Fix+Op trials is determined by the location of the visual target and not by the RF of the ChR2–expressing neurons. To test this possibility, we examined saccade endpoints in blocks of trials in which the saccade target was presented in the hemifield opposite to the RF of the ChR2–expressing neurons (Fig. S4). In these blocks of trials, eye movements toward the RF of the ChR2–expressing neurons were never rewarded. Nevertheless, the monkeys continued to make saccades into the RF of the optically stimulated neurons, indicating that ChR2–mediated activity produced a localized visual sensation near the RF of the stimulated neurons.
We also compared the pattern of activity evoked by optogenetic and visual stimulation of V1 neurons. As expected, V1 activity was unmodulated in the absence of visual or optical stimulation (Fig. 2a), and usually increased in response to a visual target in the RF (Fig. 2b). In contrast, ChR2–mediated activity was inconsistent between recording sites (Fig. 2c). At some sites, optical stimulation produced sustained excitation as expected by the biophysical properties of ChR2 (Fig. 2c, bottom row). At other sites, the effect was either suppression (Fig. 2c, top row) or excitation followed by sustained suppression. On average, there was no significant correlation between visually–evoked and optically–induced activity across recording sites (Pearson correlation, p>0.25).
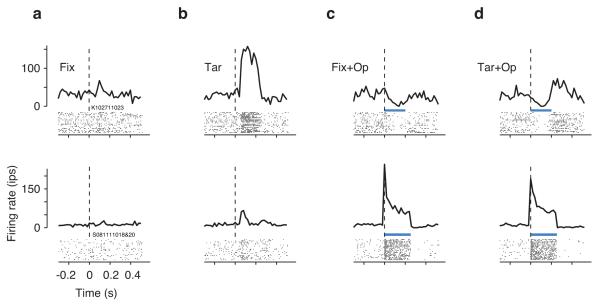
Figure 2.
V1 activity associated with the four experimental conditions. Each row corresponds to multiunit activity recorded at a different V1 site. In each panel, the raster plot shows spiking times (black ticks) of individual trials (rows), and the PSTH shows the average firing rates (bin width = 20 ms). (a) Spikes times and the corresponding PSTHs for the Fix conditions were aligned to the time when the fixation point disappeared. (b) In the Tar condition, spikes were aligned to the time of the onset of the visual target. In the Fix+Op (c) and Tar+Op (d) conditions, trials were aligned to the onset of optical stimulation (laser power: 50 mW). The top and bottom rows show PSTHs at recording sites approximately 450 and 525 μm from the cortical surface respectively. At both sites, Tar+Op responses (d) were more similar to Fix+Op responses (b) than to Tar responses (c). The blue bar indicates the duration of optical stimulation.
In light of the dissociation between patterns of activity evoked by the optical and visual stimulation, we asked which of the two was more effective in driving responses in the Tar+Op trials, in which both types of stimuli were delivered. As shown by the two examples in Fig. 2d, in the Tar+Op condition, responses were invariably dominated by the activity associated with optical stimulation. To quantify this effect across recording sites, we constructed a model in which the firing rates in Tar+Op trials ( RTar+Op ) were modeled as a linear sum of the firing rates in the Fix+Op ( RFix+p ) and Tar ( RTar ) conditions with regression coefficients β1 and β2 respectively, plus an independent constant term, β3:
The model, which predicted responses in the Tar+Op condition well (r2=0.96, p<0.001) suggested that the combined effect of optical stimulation and visual target presentation on firing rates was better predicted by the effect of optical stimulation alone (β1 =1.02, CI=[0.74 1.30]; β2 =–0.19, CI=[–4.14 3.76]).
At the end of the experiments, we used standard histological techniques to examine the pattern of ChR2 expression. A fluorescence micrograph of an unstained coronal section (Fig. 3a, left) illustrates the level of expression we observed near the injection site. Transduced cells were distributed densely in a band nearly 1 mm from the pial surface. The pattern of ChR2 expression fell off with distance from the injection site (radius ~2 mm), but no ChR2–positive cells were observed at the injection site, presumably due to tissue damage from the injection procedure. Confocal fluorescence imaging of the sections suggests that the transduced cells were neuronal with non–pyramidal morphology (Fig. 3b).
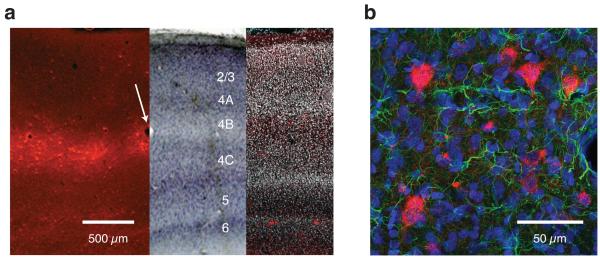
Figure 3.
Histological analysis of ChR2 expression in V1. (a) Montage of three coronal sections of V1 near the injection site. The left section was unstained and was imaged for red fluorescence (ChR2–mCherry), the middle section was stained with cresyl violet and imaged under bright field, and the right section was stained with DAPI and imaged for red and blue fluorescence (DAPI has been rendered white). The unstained and cresyl violet–stained sections, which were 50 μm apart, were aligned digitally on the basis of blood vessels (e.g. white arrow). The DAPI–stained section, which was approximately 1 mm from the injection site, had fewer transduced cells (scattered red spots). (b) Fluorescence image of a coronal section of V1 near the site of injection showing ChR2–expressing cells (red) along with DAPI (blue) and GFAP staining (green). Because GFAP is expressed in glial cells, the absence of GFAP staining in ChR2–expressing cells suggests that the transduced cells were not glial.
Surprisingly, ChR2 expression was layer–specific. Using cresyl violet and DAPI staining (Fig. 3a, right and middle respectively), we estimated that cell bodies with strong ChR2 expression were in layer 4B. We also found scattered ChR2–expressing neurons in layers 5 and 6, and rare expression in other layers. This expression pattern is not straightforwardly explained by the injection protocol since the viral vector was injected uniformly throughout the cortical depth. The observed laminar specificity might be due to a characteristic tropism of the AAV1 vector we used in macaque V1.
What factors contributed to the successful manipulation of primate behavior using a technique that has been unsuccessful previously? One key factor may be that we activated a sensory cortical area, whereas previous attempts to manipulate behavior targeted motor structures. It may seem paradoxical that manipulations of sensory signals could be more effective in driving behavior than those targeted directly at motor structures, but there are three reasons why optically–induced neural signals could be more effective in sensory areas. First, signals initiated in sensory cortex undergo a complex series of processing stages, providing ample opportunity for amplifying weak signals so that they can become manifest in behavior 10. In contrast, weak signals initiated in motor areas might not have the opportunity to be sufficiently amplified. Indeed, the effectiveness of near–threshold signals in both sensory and motor areas in driving behavior is thought to depend on further cortical processing 11, 12. Second, we found that optical stimulation activated some V1 neurons while suppressing others. Because ChR2 conducts a depolarizing current, this bidirectional effect probably reflects the combined influence of both excitatory and inhibitory ChR2–expressing neurons on local V1 networks (consistent with pan–neuronal expression from the human synapsin I promoter 6). In V1, such an unfamiliar pattern of activation may nonetheless induce a phosphene percept, draw attention, and engage visuomotor circuits that lead to an orienting behavior. In motor structures, on the other hand, only suitably structured patterns of activity might be able to drive the muscles 13. More generally, this observation highlights the need for more sophisticated stimulation techniques that better emulate native patterns of activity during normal function. Third, we observed the highest ChR2 expression in layers 4B, 5, and 6 – layers that target dorsal stream and subcortical structures that are known to play a role in orienting behaviors. We have histological confirmation of dense ChR2+ axonal projections to the superficial layers of the superior colliculus (data not shown), but these direct projections are unlikely to mediate the saccades we studied; saccade latencies in our task were too long 9. A more parsimonious explanation of the monkeys’ behavior is that optogenetic activation of V1 causes a localized visual sensation, or phosphene, that engages the oculomotor system.
Methods
Two female rhesus monkeys (7.2 and 8.3 Kg) (Macaca mulatta) participated in these experiments. Behavioral protocols, animal care and surgical procedures were all in accordance with the US National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the University of Washington Animal Care Committee.
Monkeys were surgically implanted with a titanium head–holding device and recording chamber. We characterized a target V1 site using standard electrophysiological techniques, and pressured injected 10–12 μL of the viral vector containing the ChR2 gene (rAAV1–hSyn–ChR2(H134R)–mCherry) over the course of 4–5 hours into that site using a cannula with a ~150 μm inner diameter. The viral vector was made via the helper–free triple–transfection procedure, dialyzed in PBS, and titered at 5.5×1011 particles/ml.
During experiments, monkeys were seated in primate chairs with their heads fixed, and they viewed stimuli on a computer monitor (background luminance = 90 cd/m2) binocularly from a distance of 100 cm. The behavioral task consisted of two randomly interleaved trial types. On Fix trials, the monkey fixated a black square (side = 0.2°, luminance > 2 cd/m2) for 500–1000 ms and received a juice reward when the fixation point (FP) was extinguished. On Tar trials, a peripheral square target (side = 0.2–0.4° side, luminance = 49 cd/m2) was displayed 100 ms after the FP was extinguished, and the monkey was rewarded for making a saccade to the target within 300 ms after target onset. Trials were aborted without reward if the eye position deviated > 1° from the FP prior to FP disappearance. In the Tar condition, reward was delivered only if the saccade landed within 1.8° of the target.
We recorded neural activity using tungsten electrodes and measured eye position with scleral search coils. Digitized gaze position signals, extracellular neural activity and other behavioral timing events were stored using a Plexon MAP system for offline analysis. Saccades were identified based on velocity criteria. The recording electrode and the optical fiber were placed inside a common guide tube above the dura mater and were advanced independently using a custom microdrive. First, the electrode was advanced until neural activity was detected. Afterwards, the optical fiber was advanced until light pulses (473 nm, ≤ 50 mW) clearly modulated neural activity. Neural responses were not modulated if the tip of the optical fiber was far from the where electrical activity was detected (> ~1 mm) or if both were located far (> ~2 mm) from the injection site. Data in Figure 1 are from trials in which the optical fiber was advanced to its terminal point (i.e., closest to the depth at which electrical activity was recorded).
In the main experiment, the saccade target was presented inside the RF of the neurons at the injection site, as measured from the multi–unit activity. In the control experiment, the saccade target was presented in the opposite hemifield. Optical stimulation was applied to the site of injection on a random half of trials of each category. In Opt+Fix trials, the optical stimulation was applied 130 ms after the FP was extinguished. On Tar+Op trials the stimulation was applied 30 ms after target onset. This timing, which was based on a previous study 9, ensured that the ChR2 activation was roughly synchronous with the visually driven response in V1. The visual target was presented 100 ms after the disappearance of the FP, and it takes an additional ~30 ms for the effect of the visual target to go from retina to V1.
We verified the effectiveness of light pulses of various durations (100–250 ms) and various frequencies (0–200 Hz) in eliciting saccades in the Opt+Fix condition. To determine whether neural responses in the Tar+Op condition were predicted by responses to the target and optical stimulation alone, we used linear regression model to relate the firing rates in the Tar+Op condition to the firing rates in the Fix+Op and Tar trials. We measured average firing rates within the 30 to 130 ms after FP disappearance and minimized the least squares error of the linear prediction and the data to fit the regression coefficients. We shifted the beginning and the end of the window from which firing rates were estimated independently by up to 30 ms (in 5 ms steps) and found that our estimates of the regression coefficients were robust with respect to these changes.
We performed histological analysis of the brain of one monkey to characterize the spread and efficacy of our viral expression system. The animal was euthanized with an overdose of pentobarbital, and perfused transcardially with 4% paraformaldehyde. The brain was removed, cryoprotected in 30% sucrose, and 50–μm thick sections were cut on a sliding microtome. Standard procedures were performed for cresyl violet staining. We also immunostained for GFAP using primary antibody rabbit anti–GFAP 1:400 (DAKO) with secondary antibody 1:500 conjugated to DyLight 488 dye. Afterwards, sections were cover–slipped using FluoroGel mounting medium with DAPI.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Karl Deisseroth and Michael Shadlen for sharing resources, Farrel Robinson, Jonathan Garlid, Elise Grover, Jing Huang, Dan Possin and Leah Tait for technical assistance, Chris Fetch and Charlie Hass for help with the experiments, and an anonymous reviewer for assistance with the figures. This work was supported by The McKnight Foundation and research grants EY001730 and RR000166 from the NIH.
Footnotes
Author Contributions MJ, ZLB, and GH conducted the experiments and analyzed the data. MJ and GH wrote the manuscript.
References
- 1.Aravanis AM, et al. An optical neural interface: in vivo control of rodent motor cortex with integrated fiberoptic and optogenetic technology. Journal of neural engineering. 2007;4:S143–156. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/4/3/S02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bernstein JG, Boyden ES. Optogenetic tools for analyzing the neural circuits of behavior. Trends in cognitive sciences. 2011;15:592–600. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.10.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gradinaru V, et al. Targeting and readout strategies for fast optical neural control in vitro and in vivo. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 2007;27:14231–14238. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3578-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Fenno L, Yizhar O, Deisseroth K. The development and application of optogenetics. Annual review of neuroscience. 2011;34:389–412. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Han X, et al. Millisecond-timescale optical control of neural dynamics in the nonhuman primate brain. Neuron. 2009;62:191–198. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Diester I, et al. An optogenetic toolbox designed for primates. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14:387–397. doi: 10.1038/nn.2749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Han X, et al. A high-light sensitivity optical neural silencer: development and application to optogenetic control of non-human primate cortex. Frontiers in systems neuroscience. 2011;5:18. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2011.00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gerits A, et al. Optogenetically Induced Behavioral and Functional Network Changes in Primates. Current biology : CB. 2012 doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2012.07.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tehovnik EJ, Slocum WM, Schiller PH. Saccadic eye movements evoked by microstimulation of striate cortex. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17:870–878. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Britten KH, Newsome WT, Shadlen MN, Celebrini S, Movshon JA. A relationship between behavioral choice and the visual responses of neurons in macaque MT. Vis Neurosci. 1996;13:87–100. doi: 10.1017/s095252380000715x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shadlen MN, Newsome WT. Motion perception: seeing and deciding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:628–633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schafer RJ, Moore T. Selective attention from voluntary control of neurons in prefrontal cortex. Science. 2011;332:1568–1571. doi: 10.1126/science.1199892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Churchland MM, Shenoy KV. Temporal complexity and heterogeneity of single-neuron activity in premotor and motor cortex. Journal of neurophysiology. 2007;97:4235–4257. doi: 10.1152/jn.00095.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.