Abstract
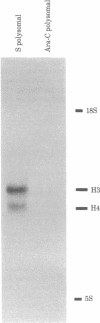
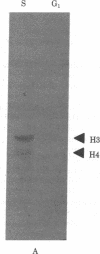
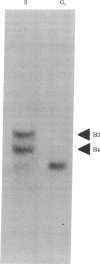
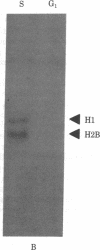
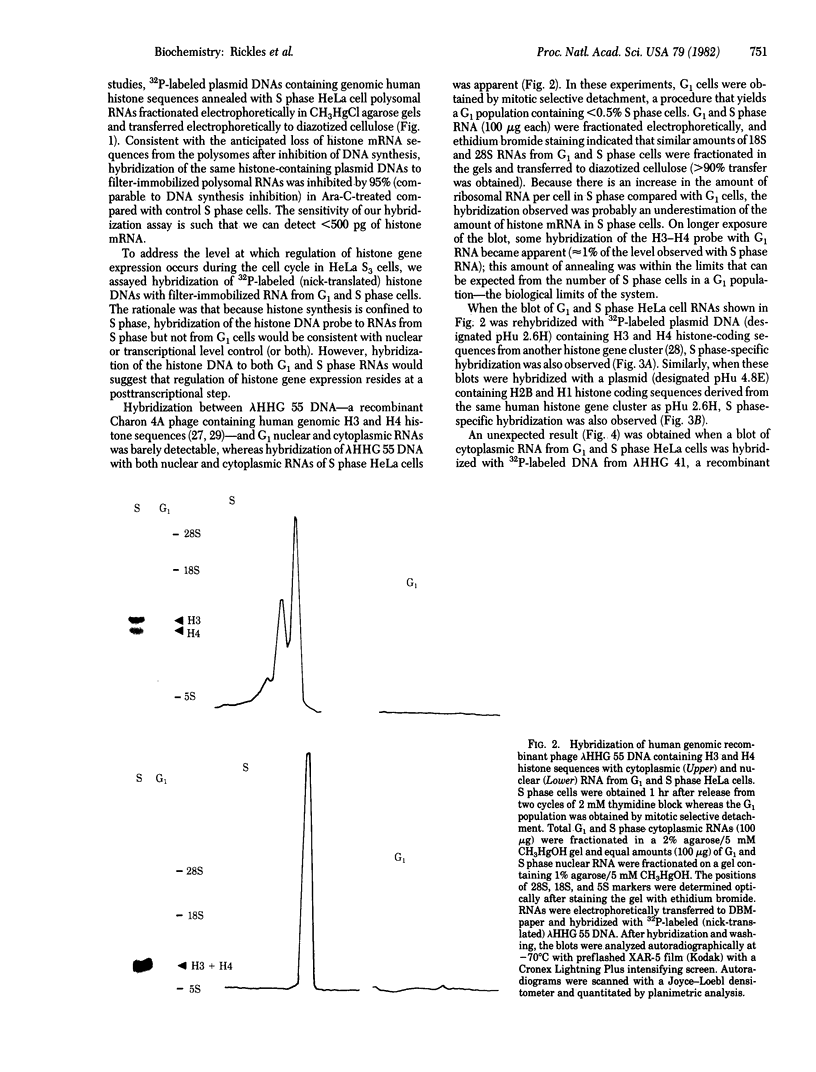
Although it is generally agreed that histone protein synthesis is restricted to the S phase of the cell cycle--and therefore parallels DNA replication--both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels of control have been invoked. Using blot hybridization with several cloned genomic human histone sequences representing different histone gene clusters as probes, we have assessed the steady-state level of histone RNAs in the nucleus and cytoplasm of G1 and S phase HeLa S3 cells. The representation of histone mRNA sequences of G1 compared with S phase cells was less than 1% in the cytoplasm and approximately 1% in the nucleus. These data are consistent with transcriptional control, but we cannot completely dismiss the possibility that regulation of histone gene expression is, to some extent, mediated posttranscriptionally. If histone gene transcription does occur in G1, the RNAs must either be rapidly degraded or be transcribed to a limited extent compared with S phase. An unexpected result was obtained when a blot of cytoplasmic RNA from G1 and S phase cells was hybridized with lambda HHG 41 DNA (containing H3 and H4 human genomic histone sequences). Although hybridization with histone mRNAs was observed for RNAs from S phase but not from G1 cells, hybridization with a nonhistone RNA of approximately 330 nucleotides present predominantly in G1 was also observed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Birkenmeier C. S. Inhibition of intractable nucleases with ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes: isolation of messenger ribonucleic acid from resting lymphocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5143–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Gabrielli F., Ajiro K., Zweidler A., Baglioni C. Further evidence of transcriptional and translational control of histone messenger RNA during the HeLa S3 cycle. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Scharff M. D., Robbins E. Rapidly labeled, polyribosome-associated RNA having the properties of histone messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1977–1983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Krieg P. A., Wells J. R. Isolation of a clone containing human histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1583–1590. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Properties of a supercoiled deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex and strand specificity of the relaxation event. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4428–4440. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detke S., Lichtler A., Phillips I., Stein J., Stein G. Reassessment of histone gene expression during cell cycle in human cells by using homologous H4 histone cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4995–4999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detke S., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Synthesis of histone messenger RNAs by RNA polymerase II in nuclei from S phase HeLa S3 cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1515–1528. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Breindl M. Synthesis of histones in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free system directed by a polyribosomal RNA fraction from synchronized HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jun 9;47(5):1106–1111. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90948-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Mueller G. C. Histone synthesis in vitro on HeLa cell microsomes. The nature of the coupling to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5947–5952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groppi V. E., Jr, Coffino P. G1 and S phase mammalian cells synthesize histones at equivalent rates. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Lorena M., Baglioni C., Borun T. W. Translation of messenger RNA for histones from HeLa cells by a cell-free extract from mouse ascites tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2095–2099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Samulski R. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Rapid purification of covalently closed circular DNAs of bacterial plasmids and animal tumor viruses. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melli M., Spinelli G., Arnold E. Synthesis of histone messenger RNA of HeLa cells during the cell cycle. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Fitschen W. Histone mRNA metabolism during the mouse fibroblast cell cycle. Cell Differ. 1980 Feb;9(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(80)90004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S. RNA metabolism in the HeLa cell nucleus. J Mol Biol. 1966 May;17(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins E., Borun T. W. The cytoplasmic synthesis of histones in hela cells and its temporal relationship to DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):409–416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding J., Kajiwara K., Mueller G. C. The metabolism of basic proteins in HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1535–1542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. S., Borun T. W. The synthesis of acidic chromosomal proteins during the cell cycle of HeLa S-3 cells. I. The accelerated accumulation of acidic residual nuclear protein before the initiation of DNA replication. J Cell Biol. 1972 Feb;52(2):292–307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. S., Stein J. L., Marashi F., Parker M. I., Sierra L. F. Regulation of specific genes during the cell cycle. Utilization of homologous cDNAs and cloned sequences for studying histone gene expression in human cells. Cell Biophys. 1980 Dec;2(4):291–314. doi: 10.1007/BF02785095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. S., Stein J. L., Park W. D., Detke S., Lichtler A. C., Shephard E. A., Jansing R. L., Phillips I. R. Regulation of histone gene expression in HeLa S3 cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1107–1120. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G., Park W., Thrall C., Mans R., Stein J. Regulation of cell cycle stage-specific transcription of histone genes from chromatin by non-histone chromosomal proteins. Nature. 1975 Oct 30;257(5529):764–767. doi: 10.1038/257764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. L., Thrall C. L., Park W. D., Mans R. J., Stein G. S. Hybridization analysis of histone messenger RNA: association with polyribosomes during the cell cycle. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):557–558. doi: 10.1126/science.1145212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwag E. J., Dahlberg A. E. Electrophoretic transfer of DNA, RNA and protein onto diazobenzyloxymethyl (DBM) - paper. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):299–317. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]