Abstract
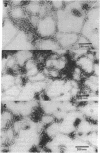
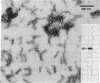
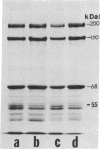
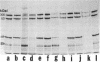
Intermediate filaments (IF) were reconstituted in vitro from bovine neurofilament triplet polypeptides. Neural IF, solubilized in either low salt or 8 M urea solution, assembled into IF when returned to near-physiological solution conditions. The 68,000-dalton component of the triplet, purified to homogeneity by preparative NaDodSO4 electrophoresis, was renatured and reassembled into short (approximatley 0.05-micrometer) approximatley 10 nm-diameter filaments. These results demonstrate that the triplet polypeptides are components of neural IF and that the 68,000-dalton polypeptide is an IF structural protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Korey B., Norton W. T. Intermediate filaments from bovine, rat, and human CNS: mapping analysis of the major proteins. J Neurochem. 1980 May;34(5):1149–1159. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacourte A., Filliatreau G., Boutteau F., Biserte G., Schrevel J. Study of the 10-nm-filament fraction isolated during the standard microtubule preparation. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 1;191(2):543–546. doi: 10.1042/bj1910543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. S., Newby B. J. Neurofilament disguise, destruction and discipline. Nature. 1975 Aug 14;256(5518):586–589. doi: 10.1038/256586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Konigsberg W. A micromethod for complete removal of dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Anal Biochem. 1979 Feb;93(1):153–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huiatt T. W., Robson R. M., Arakawa N., Stromer M. H. Desmin from avian smooth muscle. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6981–6989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huneeus F. C., Davison P. F. Fibrillar proteins from squid axons. I. Neurofilament protein. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):415–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem R. K., Yen S. H., Salomon G. D., Shelanski M. L. Intermediate filaments in nervous tissues. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):637–645. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueger D. C., Huston J. S., Dahl D., Bignami A. Formation of 100 A filaments from purified glial fibrillary acidic protein in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 25;135(1):53–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer W. W., Freeman L. A. Neurofilament proteins of rat peripheral nerve and spinal cord. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):653–662. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer W. W., Micko S. Calcium-dependent alterations of neurofilament proteins of rat peripheral nerve. J Neurochem. 1979 Jan;32(1):211–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Liem R. K. Neurofilaments. J Neurochem. 1979 Jul;33(1):5–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Gullino M. I. Bovine epidermal keratin filament assembly in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 3;70(1):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments of baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells and bovine epidermal keratinocytes have similar ultrastructures and subunit domain structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4534–4538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Zimmerman S. B. Self-assembly of bovine epidermal keratin filaments in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 15;108(3):547–567. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard M., Simon C. Antibody decoration of neurofilaments. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):198–205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackroff R. V., Goldman R. D. In vitro assembly of intermediate filaments from baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6226–6230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackroff R. V., Goldman R. D. In vitro reassembly of squid brain intermediate filaments (neurofilaments): purification by assembly-disassembly. Science. 1980 Jun 6;208(4448):1152–1155. doi: 10.1126/science.7189605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]