Abstract
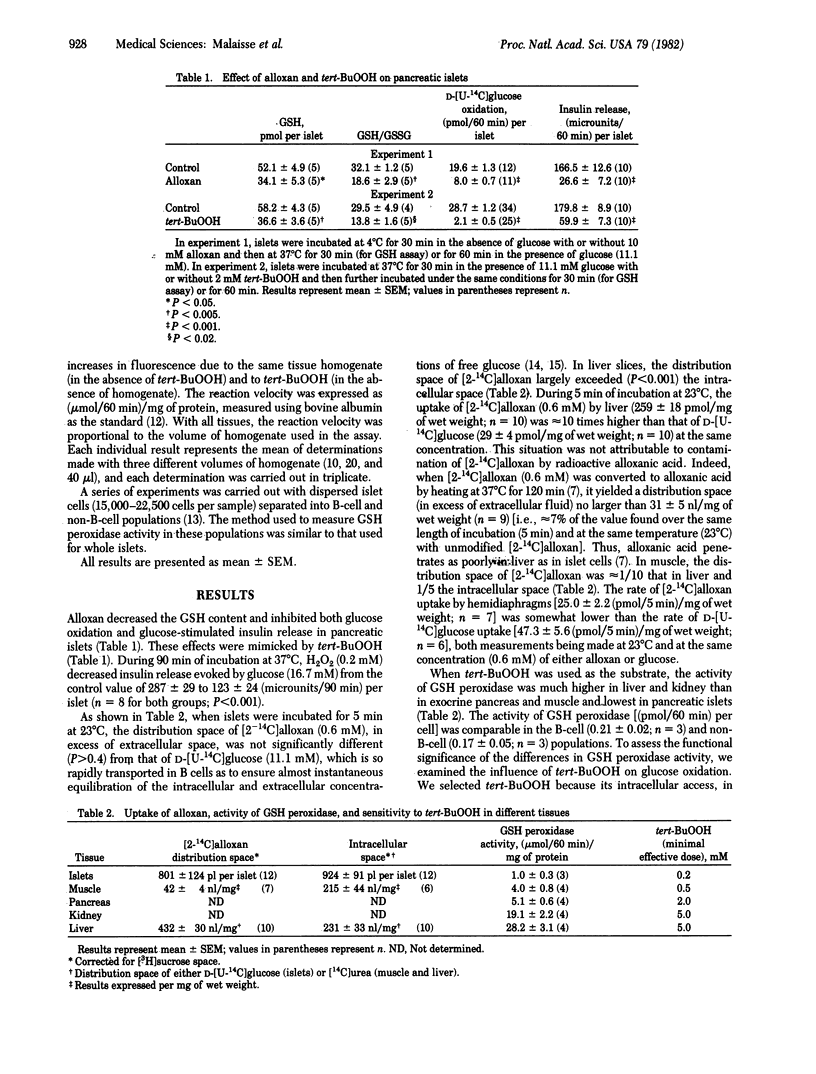
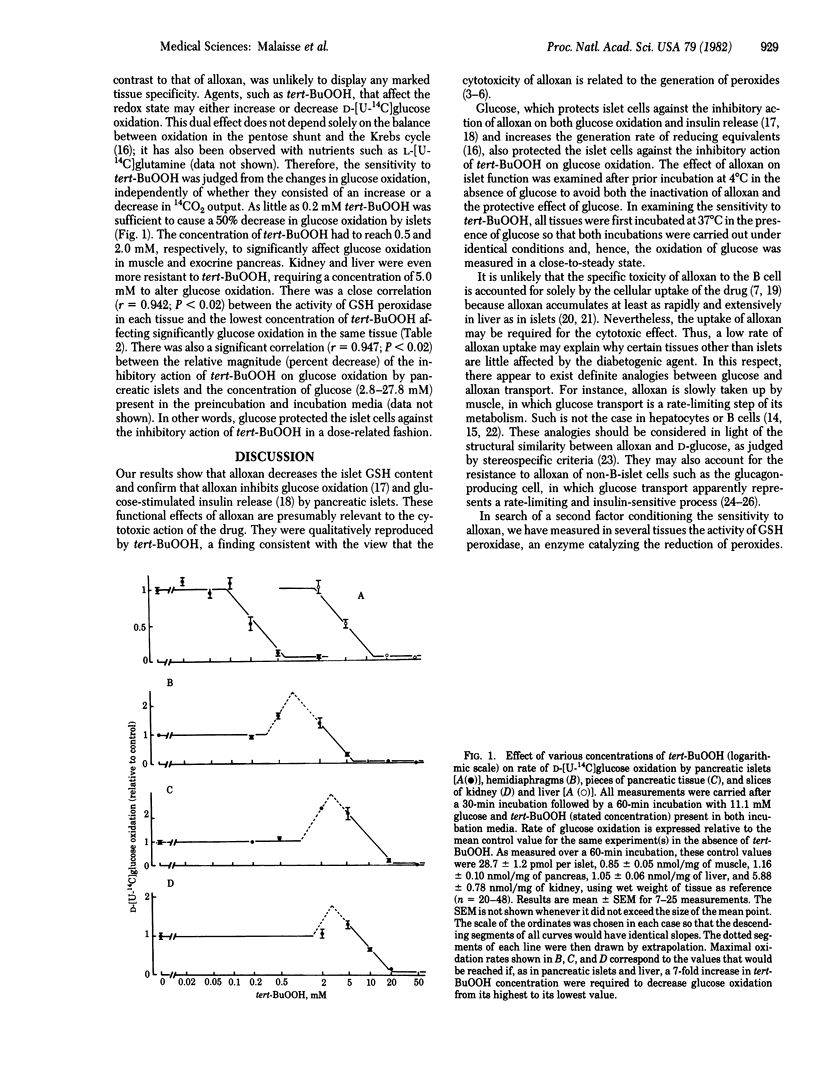
The diabetogenic agent alloxan exerts a preferential cytotoxic effect on the pancreatic B cell. The determinants of such a tissue specificity were investigated. Alloxan accumulated rapidly in liver and pancreatic islets but much more slowly in muscle. The activity of glutathione peroxidase and the resistance to exogenous peroxide were approximately 20 times higher in liver and kidney than in islets, intermediate values being found in exocrine pancreas and muscle. These findings suggest that the selective cytotoxicity of alloxan to the pancreatic B cell is attributable to the conjunction of two features: a rapid cellular uptake of the drug and an exquisite sensitivity of the B cell to peroxide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borg L. A., Eide S. J., Andersson A., Hellerström C. Effects in vitro of alloxan on the glucose metabolism of mouse pancreatic B-cells. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 15;182(3):797–802. doi: 10.1042/bj1820797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boschero A. C., Kawazu S., Duncan G., Malaisse W. J. Effect of glucose on K+ handling by pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1977 Nov 1;83(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80662-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAHILL G. F., Jr, ASHMORE J., RENOLD A. E., HASTINGS A. B. Blood glucose and the liver. Am J Med. 1959 Feb;26(2):264–282. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(59)90316-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpinelli A. R., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. Stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Effect of intracellular acidification upon calcium efflux from islet cells. Metabolism. 1980 Jun;29(6):540–545. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer L. J., Hamburger S. A. Inhibition of alloxan action in isolated pancreatic islets by superoxide dismutase, catalase, and a metal chelator. Diabetes. 1980 Mar;29(3):213–216. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.3.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grankvist K., Marklund S., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Superoxide dismutase, catalase and scavengers of hydroxyl radical protect against the toxic action of alloxan on pancreatic islet cells in vitro. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 15;182(1):17–25. doi: 10.1042/bj1820017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström L., Hellman B., Ullberg S. On the accumulation of alloxan in the pancreatic beta-cells. Diabetologia. 1967 Jun;3(3):340–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00429866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R. E., Cabbat F. S. The prevention of alloxan-induced diabetes by amygdalin. Life Sci. 1980 Aug 25;27(8):659–662. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heikkila R. E., Winston B., Cohen G. Alloxan-induced diabetes-evidence for hydroxyl radical as a cytotoxic intermediate. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 May 1;25(9):1085–1092. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90502-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. Evidence for mediated transport of glucose in mammalian pancreatic -cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 6;241(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASKE H., WEINGES K. Untersuchungen über das Verhalten der Meerschweinchen gegenüber verschiedenen diabetogenen Noxen; Alloxan und Dithizon. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1957;230(4):406–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Biochemical basis of a species difference in sensitivity to alloxan. FEBS Lett. 1981 Oct 12;133(1):181–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80500-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Brisson G., Malaisse-Lagae F. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. I. Interaction of epinephrine and alkaline earth cations. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Dec;76(6):895–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Hutton J. C., Kawazu S., Sener A. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Metabolic effects of menadione in isolated islets. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 1;87(1):121–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matschinsky F. M., Pagliara A. S., Hover B. A., Pace C. S., Ferrendelli J. A., Williams A. Hormone secretion and glucose metabolism in islets of Langerhans of the isolated perfused pancreas from normal and streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 10;251(19):6053–6061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A. A method for the purification of single A, B and D cells and for the isolation of coupled cells from isolated rat islets. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):654–663. doi: 10.1007/BF00257436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Lacy P. E., Natschinsky F. M., McDaniel M. L. Effect of alloxan on insulin secretion in isolated rat islets perifused in vitro. Diabetes. 1974 Jun;23(6):517–524. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.6.517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. C., McDaniel M. L., Lacy P. E. Alloxan uptake by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Endocrinology. 1978 Jun;102(6):1847–1855. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-6-1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. C., McDaniel M. L., Naber S. P., Barry C. D., Lacy P. E. Alloxan stimulation and inhibition of insulin release from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1978 Dec;27(12):1205–1214. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.12.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



