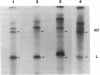
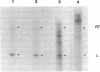
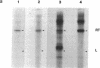
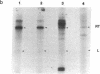
Abstract
We have devised a method to specifically incorporate deoxyribonucleotide base analogs in vitro into either strand of the tryptophan (trp) operon attenuator region, using primed synthesis on bacteriophage M13 derivatives carrying cloned trp attenuator DNA. We have employed these techniques to extend previous studies implicating both RNA-RNA and RNA-DNA interactions in transcription termination in an attempt to determine the nature of the contribution from the template DNA molecule in termination regions. In general, we find that the dramatic effects upon transcription termination seen with base analog incorporation into mRNA do not occur when similar analogs are incorporated into the DNA. Only the analog 2,6-diaminopurine deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate (dDapTP), which strengthens A·T or A·U base pairing, elicits a significant response: in the template DNA strand, the presence of this analog increases read-through at the trp attenuator. The analog 5-bromouracil deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (BrdUTP), which also strengthens pairing with its complementary base, has no detectable effect on termination when it is placed in either strand of the trp attenuator or the mutant attenuator trp a1419. Surprisingly, though the analog 5-iodocytosine deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate (IdCTP) does not affect termination, it has a great effect on initiation of transcription, depressing trp promoter activity as well as stimulating transcription from other regions. These results support the postulated interaction between terminal uridines in mRNA and the template DNA strand in enhancing termination and suggest that there are no significant additional contributions from the DNA. In addition, the novel use of M13 derivatives for incorporating analogs into the DNA on a preparative scale provides a technique for introducing mutations in a general but controlled fashion as a new means for studying other regulatory regions.
Keywords: in vitro transcription, ρ-independent termination, deoxyribonucleotide analogs, primed synthesis, bacteriophage M13
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Sarkar P., Valenzuela D., Maitra U. Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: influence of secondary structure of RNA transcripts on rho-independent and rho-dependent termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1613–1617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Farnham P. J., Platt T. Synthetic sites for transcription termination and a functional comparison with tryptophan operon termination sites in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Platt T. A model for transcription termination suggested by studies on the trp attenuator in vitro using base analogs. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):739–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Platt T. Rho-independent termination: dyad symmetry in DNA causes RNA polymerase to pause during transcription in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):563–577. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Platt T. The attenuator of the tryptophan operon in E.coli: rho-mediated release of RNA polymerase from a transcription termination complex in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4613–4623. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn B., Messing J. Methylation of single-stranded DNA in vitro introduces new restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Nature. 1978 Mar 23;272(5651):375–377. doi: 10.1038/272375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidecker G., Messing J., Gronenborn B. A versatile primer for DNA sequencing in the M13mp2 cloning system. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer B., Köster H. On the influence of thymidine analogues on the activity of phage fd promoters in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):6143–6162. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.6143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Yanofsky C. Transcription termination at the trp operon attenuators of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: RNA secondary structure and regulation of termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4365–4369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. H., Tinoco I., Jr DNA-RNA hybrid duplexes containing oligo(dA:rU) sequences are exceptionally unstable and may facilitate termination of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2295–2299. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Chamberlin M. J. Termination of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in vitro is affected by ribonucleoside triphosphate base analogs. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2455–2460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Cortese R. A fast and simple method for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded bacteriophage M13. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl S. J., Chamberlin M. J. Transcription of T7 DNA containing modified nucleotides by bacteriophage T7 specific RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4951–4959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]