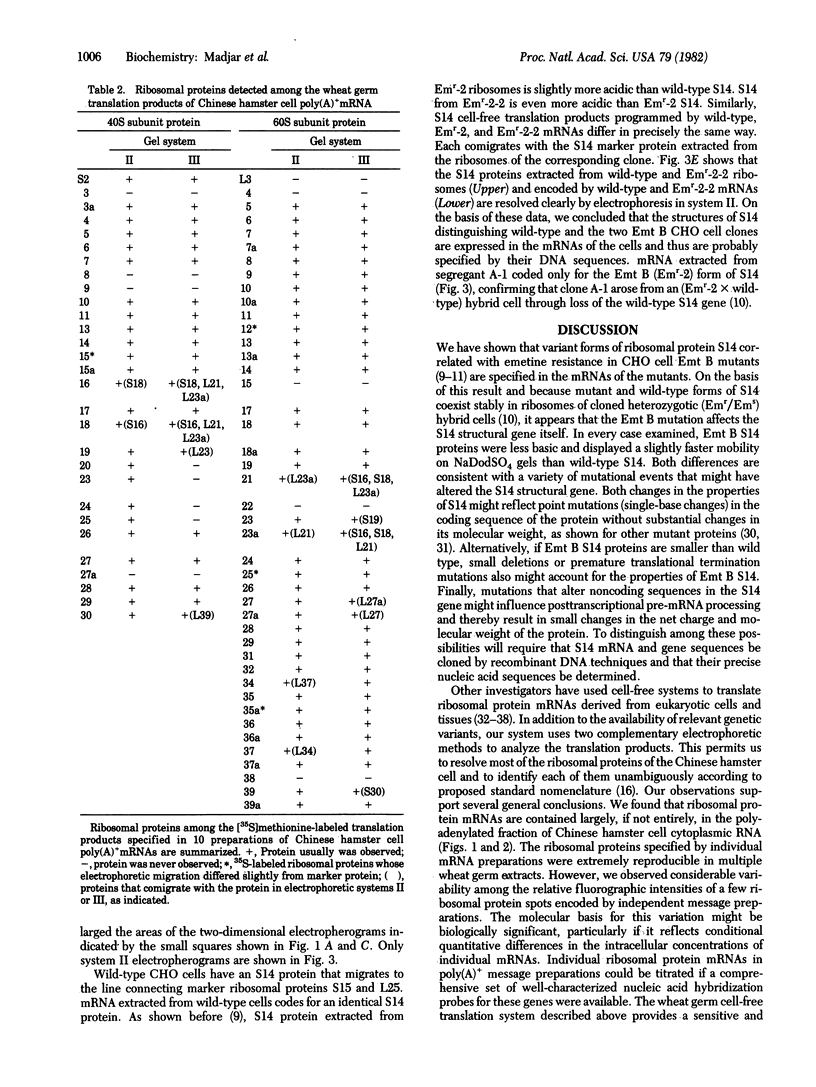
Abstract
Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants resistant to the translational inhibitor emetine (Emt B mutants) express a single genetically altered 40S ribosomal subunit protein, S14. that appears to account for their drug resistance. To determine whether Emt B mutation affect the structural gene for the S14 protein, we isolated mRNAs from several wild-type and Emt B mutant clones. We translated the mRNAs in a cell-free system derived from wheat germ, and we discerned the biosynthesis of 59 ribosomal proteins, including S14. In every case, poly(A)+ mRNA programmed the cell-free system to synthesize an S14 protein electrophoretically identical to the S14 extracted from the ribosomes of the corresponding cell line. Messages from two Emt B mutants (Emr-2 and Emr-2-2) specified S14s that were electrophoretically distinct from the wild-type protein. Thus, Emt B mutations were expressed in mutant cell mRNAs, apparently reflecting mutagen-induced changes in S14 structural genes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boersma D., McGill S. M., Mollenkamp J. W., Roufa D. J. Emetine resistance in Chinese hamster cells is linked genetically with an altered 40S ribosomal subunit protein, S20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):415–419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boersma D., McGill S., Mollenkamp J., Roufa D. J. Emetine resistance in Chinese hamster cells. Analysis of ribosomal proteins prepared from mutant cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):559–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Roufa D. J., Beaudet A. L., Caskey C. T. 8-Azaguanine resistance in mammalian cells. I. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Genetics. 1972 Oct;72(2):239–252. doi: 10.1093/genetics/72.2.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Chan D. Y., Siminovitch L. Evidence for functional hemizygosity at the Emtr locus in CHO cells through segregation analysis. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):1007–1013. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. An in vitro analysis of the dominance of emetine sensitivity in Chinese hamster ovary cell hybrids. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3978–3982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. Genetic and biochemical characterization of mutants of CHO cells resistant to the protein synthesis inhibitor trichodermin. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 May;4(3):355–374. doi: 10.1007/BF01542848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. Mutants of CHO cells resistant to the protein synthesis inhibitors, cryptopleurine and tylocrebrine: genetic and biochemical evidence for common site of action of emetine, cryptopleurine, tylocrebine, and tubulosine. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3209–3214. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. The isolation and preliminary characterization of somatic cell mutants resistant to the protein synthesis inhibitor-emetine. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Siminovitch L. The molecular basis of emetine resistance in Chinese hamster ovary cells: alteration in the 40S ribosomal subunit. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett P. B., Egberts E., Traub P. Characterization of Ehrlich ascites tumor cell messenger RNA specifying ribosomal proteins by translation in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1978 Feb 25;119(2):253–267. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90437-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haralson M. A., Roufa D. J. A temperature-sensitive mutation affecting the mammalian 60 S ribosome. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8618–8623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madjar J. J., Arpin M., Buisson M., Reboud J. P. Spot position of rat liver ribosomal proteins by four different two-dimensional electrophoreses in polyacrylamide gel. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 20;171(2):121–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00269998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madjar J. J., Michel S., Cozzone A. J., Reboud J. P. A method to identify individual proteins in four different two-dimensional gel electrophoresis systems: application to Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):174–182. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90641-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madjar J. J., Traut R. R. Differences in electrophoretic behaviour of eight ribosomal proteins from rat and rabbit tissues and evidence for proteolytic action on liver proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):89–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00268450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey E. H., Bielka H., Gordon J., Lastick S. M., Lin A., Ogata K., Reboud J. P., Traugh J. A., Traut R. R., Warner J. R. Proposed uniform nomenclature for mammalian ribosomal proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 16;169(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00267538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Construction and identification of cDNA clones for mouse ribosomal proteins: application for the study of r-protein gene expression. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):113–129. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Imai K., Ogata K. Biosynthesis of ribosomal proteins by poly(A)-containing mRNAs from rat liver in a wheat germ cell-free system and sizes of mRNAs coding ribosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 29;564(1):105–121. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel D., Nikaido K., Ames G. F. A single amino acid substitution in a histidine-transport protein drastically alters its mobility in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4159–4165. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Beccari E. Messenger RNA for ribosomal proteins in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 May;106(2):603–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöche H., Varshaver N. B., Theille M., Geissler E. Cycloheximide resistance in Chinese hamster cells. II. Induction of Chm resistance in Chinese hamster cells by N-nitrosomethylurea. Mutat Res. 1975 Oct;30(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90256-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichenbecher V. E., Jr, Caskey C. T. Emetine-resistant Chinese hamster cells. The identification of an electrophoretically altered protein of the 40 S ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6207–6210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufa D. J., Moses R. E., Reed S. J. The DNA polymerases of Chinese hamster cells. Subcellular distribution and properties of two DNA polymerases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Apr;167(2):547–559. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90498-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufa D. J., Reed S. J. Temperature-sensitive mutants of a Chinese hamster cell line. I. Selection of clones with defective macromolecular biosynthesis. Genetics. 1975 Jul;(3):549–566. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.3.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufa D. J., Sadow B. N., Caskey C. T. Derivation of TK- clones from revertant TK+ mammalian cells. Genetics. 1973 Nov;75(3):515–530. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.3.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez L., Vásquez D., Jiménez A. Genetics and biochemistry of cryptopleurine resistance in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Nov 18;156(3):319–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00267188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaslet C. A., O'Connell P., Izquierdo M., Rosbash M. Isolation and mapping of a cloned ribosomal protein gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):674–676. doi: 10.1038/285674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLER J. P., HARRIS J. I. Studies on the composition of the protein from Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Jan 15;47:18–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Gorenstein C. The synthesis of eucaryotic ribosomal proteins in vitro. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hill J. M., Vock L. S. Biochemical and genetic evidence for a new class of emetine-resistant Chinese hamster cells with alterations in the protein biosynthetic machinery. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Jul;6(4):495–516. doi: 10.1007/BF01539152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasmuth J. J., Hill J. M., Vock L. S. Identification and characterization of a third complementation group of emetine-resistant Chinese hamster cell mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;1(1):58–65. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford J. L., Jr, Hereford L. M., Rosbash M. Isolation of cloned DNA sequences containing ribosomal protein genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1247–1259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. W., Zweers A., Cohen L. H. Influence of single amino acid substitutions on electrophoretic mobility of sodium dodecyl sulfate-protein complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90907-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






