Abstract
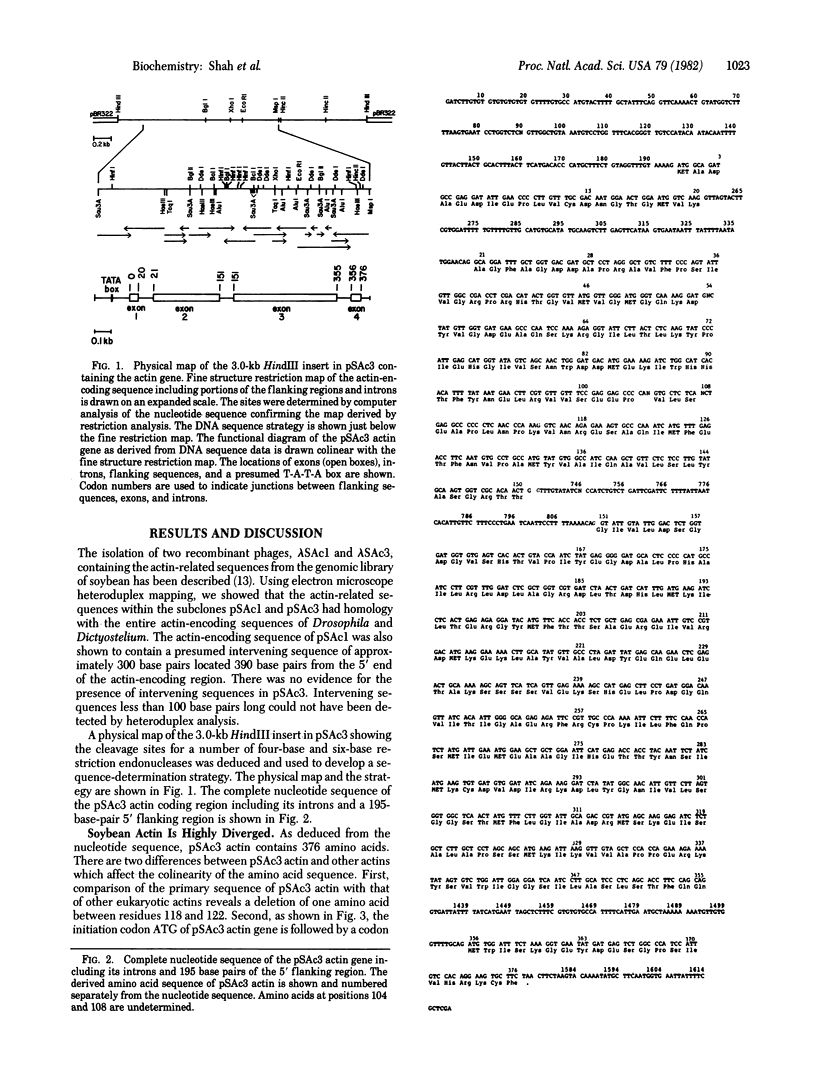
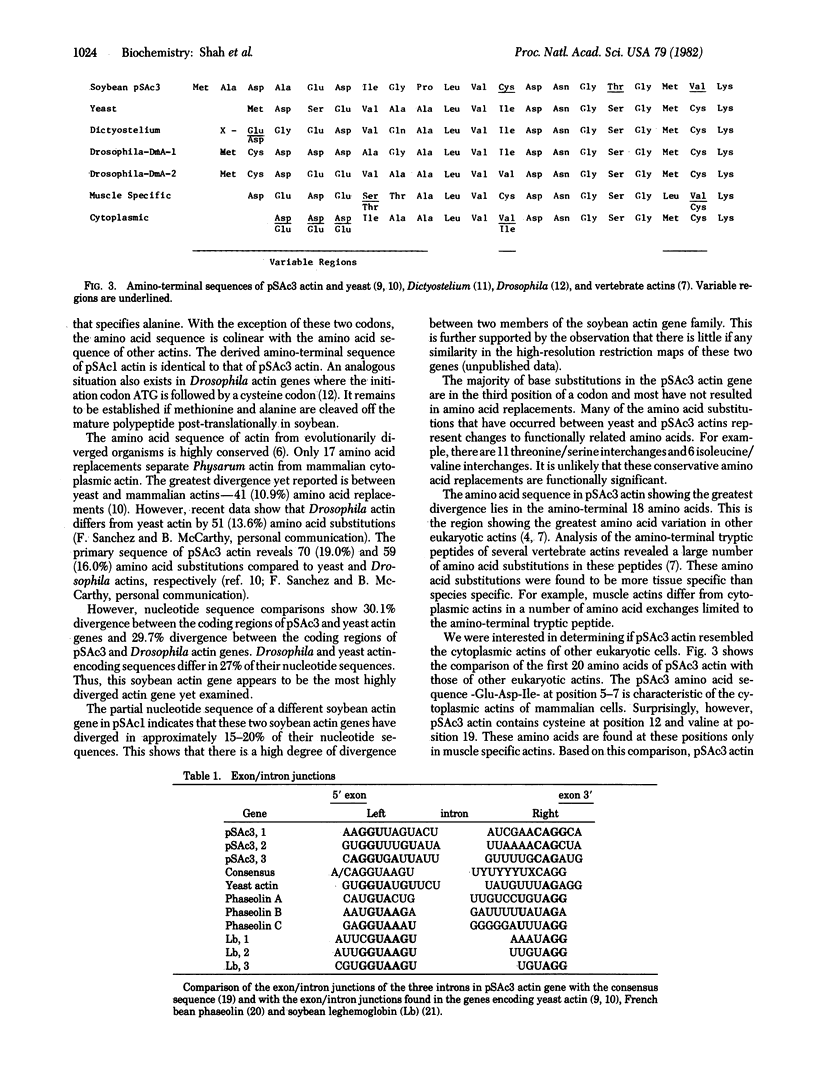
Soybean contains a small multigene family of actin-related sequences. We have determined the complete nucleotide sequence of a soybean actin gene carried on the recombinant plasmid pSAc3. As deduced from the nucleotide sequence, this soybean actin is composed of 376 amino acids. Compared to other eukaryotic actins, pSAc3 actin has a deletion of one amino acid between residues 118 and 122. The initiator methionine is followed by alanine, which is not found at this position in other eukaryotic actins. pSAc3 actin differs, in primary sequence, more from fungal and animal actins than any of the known nonplant actins differ from each other. pSAc3 actin appears to be related to both cytoplasmic and muscle specific actins in the location of specific NH2-terminal amino acids. The coding sequence is interrupted by three small introns, each less than 90 base pairs long. The splice junctions are similar to those found in other eukaryotic genes, suggesting the presence of a similar splicing apparatus in higher plants. Introns 1 and 3 interrupt the reading frame after codons 20 and 355, respectively. Intron 2 splits a glycine codon at position 151. None of these intron positions is conserved relative to the positions of introns in other actin genes examined.
Keywords: introns, gene structure, multigene family, evolution
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baralle F. E., Shoulders C. C., Proudfoot N. J. The primary structure of the human epsilon-globin gene. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):621–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carreira L. H., Carlton B. C., Bobbio S. M., Nagao R. T., Meagher R. B. Construction and application of a modified "gene machine": a circular concentrating preparative gel electrophoresis device employing discontinuous elution. Anal Biochem. 1980 Aug;106(2):455–468. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90548-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durica D. S., Schloss J. A., Crain W. R., Jr Organization of actin gene sequences in the sea urchin: molecular cloning of an intron-containing DNA sequence coding for a cytoplasmic actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5683–5687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A. Multigene families encoding actin and tubulin. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):6–7. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90494-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Bond B. J., Hershey N. D., Mixter K. S., Davidson N. The actin genes of Drosophila: protein coding regions are highly conserved but intron positions are not. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Perrin F., Seidel R. The actin gene in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: 5' and 3' end mapping, flanking and putative regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6339–6350. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Seidel R. Molecular cloning of the actin gene from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):1043–1059. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go M. Correlation of DNA exonic regions with protein structural units in haemoglobin. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):90–92. doi: 10.1038/291090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Irminger J. C., Bucher P., Birnstiel M. L. Sea urchin histone mRNA termini are located in gene regions downstream from putative regulatory sequences. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):147–151. doi: 10.1038/285147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersey Y. M., Hepler P. K., Palevitz B. A., Wessells N. K. Polarity of actin filaments in Characean algae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):165–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersey Y. M., Wessells N. K. Localization of actin filaments in internodal cells of characean algae. A scanning and transmission electron microscope study. J Cell Biol. 1976 Feb;68(2):264–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.2.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meagher R. B., Shepherd R. J., Boyer H. W. The structure of cauliflower mosaic virus. I. A restriction endonuclease map of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Virology. 1977 Jul 15;80(2):362–375. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(77)80012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao R. T., Shah D. M., Eckenrode V. K., Meagher R. B. Multigene family of actin-related sequences isolated from a soybean genomic library. DNA. 1981;1(1):1–9. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Rogers J. H., Hüppi K., Brack C., Traunecker A., Maki R., Wall R., Tonegawa S. Domains and the hinge region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain are encoded in separate DNA segments. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):627–633. doi: 10.1038/277627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Catterall J. F., Kristo P., Means A. R., O'Malley B. W. Ovomucoid intervening sequences specify functional domains and generate protein polymorphism. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S., Maxam A. M., Tizard R., Bernard O., Gilbert W. Sequence of a mouse germ-line gene for a variable region of an immunoglobulin light chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1485–1489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. At least six different actins are expressed in a higher mammal: an analysis based on the amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal tryptic peptide. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):783–802. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of Physarum actin. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):720–721. doi: 10.1038/276720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Vegetative Dictyostelium cells containing 17 actin genes express a single major actin. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):475–477. doi: 10.1038/284475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Lis J., Wu R. Elution of DNA from agarose gels after electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:176–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


