Abstract
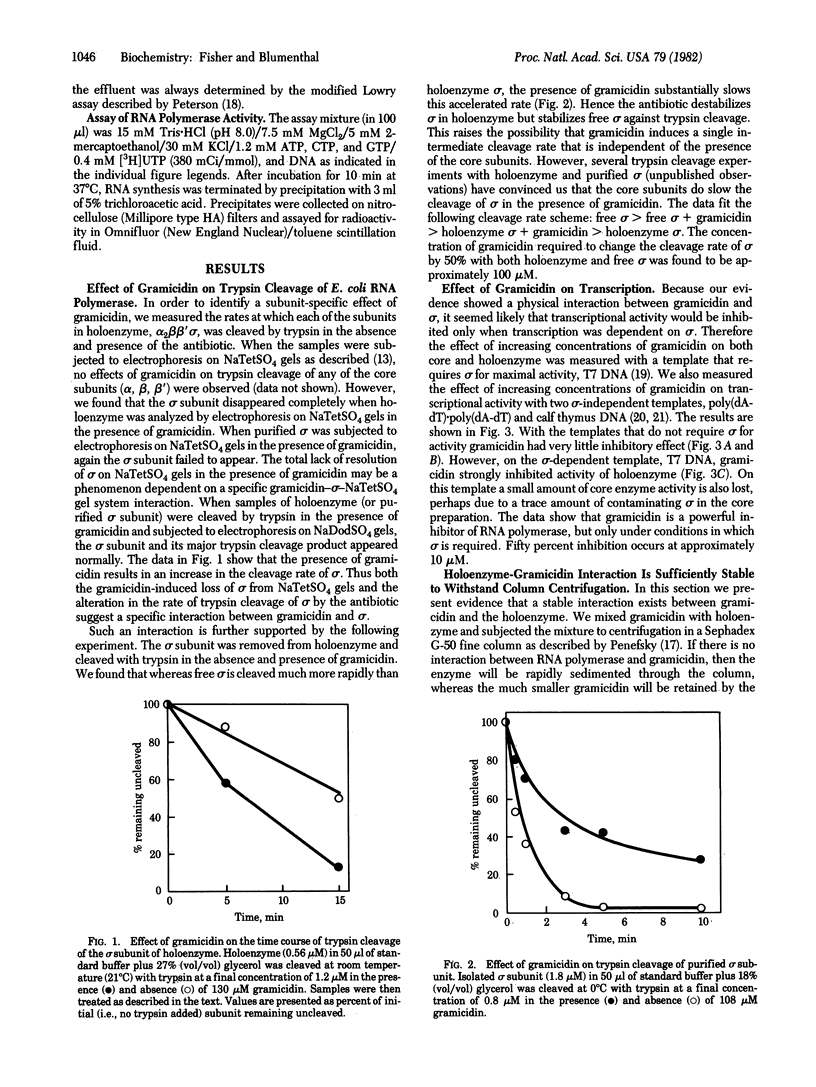
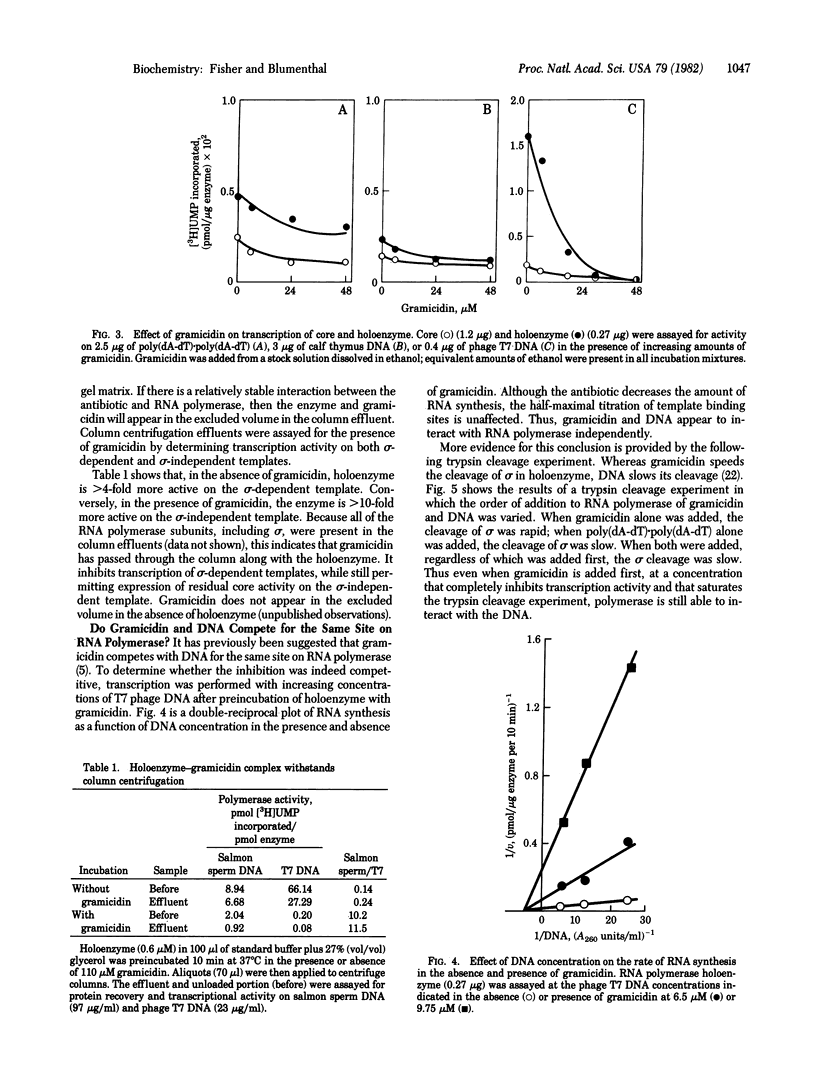
Gramicidin, a peptide antibiotic produced by Bacillus brevis, inhibits initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase (nucleosidetriphosphate:RNA nucleotidyltransferase, EC 2.7.7.6). We show here that the presence of gramicidin causes an increase in the rate of cleavage of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase by trypsin, although it does not alter the cleavage rate of any of the core subunits. Furthermore, whereas isolated sigma is cleaved much faster than is sigma in holoenzyme, gramicidin substantially decreases the trypsin cleavage rate of isolated sigma. Inhibition of RNA polymerase activity by gramicidin in consistent with a sigma-specific effect: the antibiotic is a strong inhibitor of transcription of T7 phage DNA, which requires sigma for activity, but it has little effect on transcription of sigma-independent templates, such as poly(dA-dT).poly)dA-dT) and calf thymus DNA. These results are discussed in light of the hypothesized role for gramicidin in the initiation of sporulation of B. brevis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bautz E. K., Bautz F. A., Dunn J. J. E. coli sigma factor: a positive control element in phage T4 development. Nature. 1969 Sep 6;223(5210):1022–1024. doi: 10.1038/2231022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Blumenthal T. Analysis of RNA polymerase by trypsin cleavage. Evidence for a specific association between subunits sigma and beta involved in the closed to open complex transition. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):11056–11062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. A modified RNA polymerase transcribes a cloned gene under sporulation control in Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):256–260. doi: 10.1038/282256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. Novel RNA polymerase sigma factor from Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7000–7004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Baarda J. R. Gramicidin, valinomycin, and cation permeability of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):53–60. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.53-60.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and properties of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangel W. F., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of ribonucleic acid chain initiation by Escherichia coli ribonucleic acid polymerase bound to T7 deoxyribonucleic acid. I. An assay for the rate and extent of ribonucleic acid chain initiation. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):2995–3001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee P. K., Paulus H. Biological function of gramicidin: studies on gramicidin-negative mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):780–784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristow H., Schazschneider B., Bauer K., Kleikauf H. Tyrocidine and the linear gramicidin. Do these peptide antibiotics play an antagonistic regulative role in sporulation? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 1;390(2):246–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristow H., Schazschneider B., Vater J., Kleinkauf H. Some characteristics of the DNA-tyrocidine complex and a possible mechanism of the gramicidin action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 18;414(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N., Langley D., Paulus H. Biological function of gramicidin: selective inhibition of RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1478–1482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N., Langley D., Paulus H. Studies on the mechanism and specificity of inhibition of ribonucleic acid polymerase by linear gramicidin. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 16;18(21):4536–4541. doi: 10.1021/bi00588a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N., Paulus H. Function of peptide antibiotics in sporulation. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 25;239(95):228–230. doi: 10.1038/newbio239228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schazschneider B., Ristow H., Kleinkauf H. Interaction between the antibiotic tyrocidine and DNA in vitro. Nature. 1974 Jun 21;249(459):757–759. doi: 10.1038/249757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorenstein R. G., Losick R. Comparative size and properties of the sigma subunits of ribonucleic acid polymerase from Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6170–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Stinchcomb D., Losick R. Antibody directed against Bacillus subtilis rho factor purified by sodium dodecyl sulfate slab gel electrophoresis. Effect on transcription by RNA polymerase in crude extracts of vegetative and sporulating cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8824–8828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Burgessrr Cyclic re-use of the RNA polymerase sigma factor. Nature. 1969 May 10;222(5193):537–540. doi: 10.1038/222537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggs J. L., Gilman M. Z., Chamberlin M. J. Heterogeneity of RNA polymerase in Bacillus subtilis: evidence for an additional sigma factor in vegetative cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]