Abstract
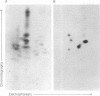
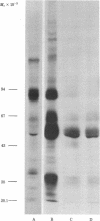
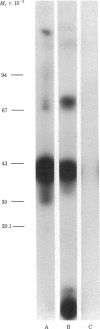
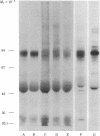
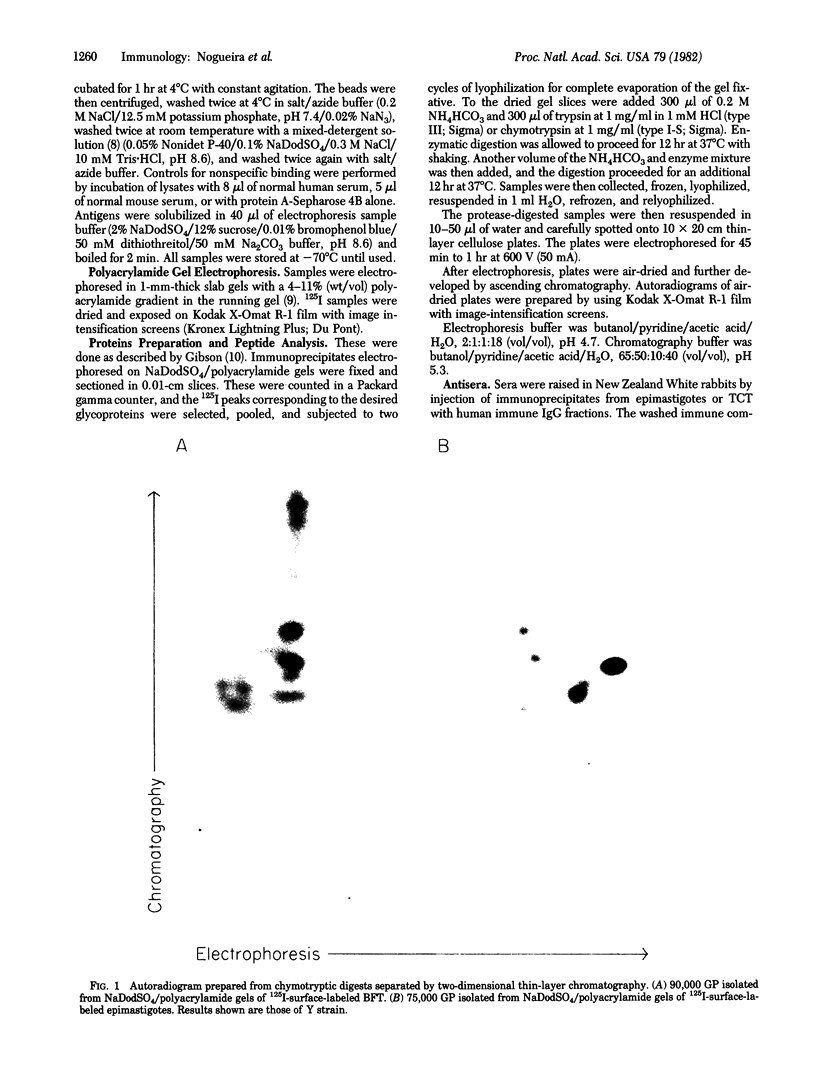
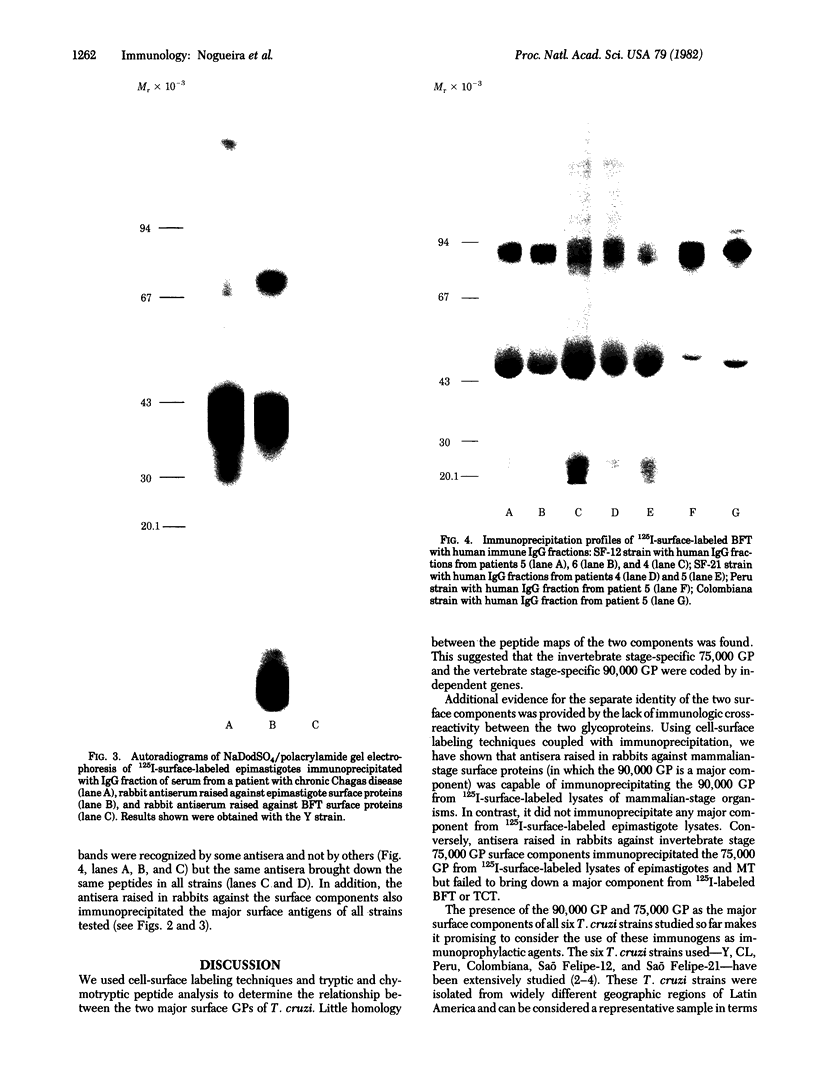
Two major surface antigens on Trypanosoma cruzi, the causative agent of Chagas disease, have been described [Nogueira, N., Chaplan, S., Tydings, J., Unkeless, J. & Cohn, Z. (1981) J. Exp. Med. 153, 629-639]. One, a Mr 75,000 glycoprotein (GP), is specific for the culture forms (insect-host stages) of the organisms--epimastigotes and metacyclic trypomastigotes. The other, a Mr 90,000 GP, was found in vertebrate-host stages of the organisms--bloodstream-form trypomastigotes. We now report that these two major surface antigens of T. cruzi seem to be unrelated proteins, as judged by tryptic and chymotryptic peptide analysis. Antibodies were raised in rabbits against epimastigote or trypomastigote proteins which had been immunoprecipitated with human antisera. These trypomastigote and epimastigote protein antisera reacted only with the homologous immunogen, as determined by immunoprecipitation of surface-labeled organisms and by immunofluorescence. The Mr 75,000 GP is detected only in cultured (insect stage) epimastigotes and metacyclic trypomastigotes. The Mr 90,000 GP is only present in bloodstream-form trypomastigotes, amastigotes, and trypomastigotes obtained from infected muscle cells in vitro. Therefore, the insect and vertebrate stages of this species display distinctive surface GPs that can be identified by surface labeling and immunoprecipitation techniques in six strains of T. cruzi (Y, CL, Peru, Colombiana, SF-12, and SF-21) isolated from widely different areas of South America.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gibson W. Polyoma virus proteins: a description of the structural proteins of the virion based on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and peptide analysis. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff R. Killing in vitro of Trypanosoma cruzi by macrophages from mice immunized with T. cruzi or BCG, and absence of cross-immunity on challege in vivo. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):299–311. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. Externally disposed plasma membrane proteins. I. Enzymatic iodination of mouse L cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):438–460. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A. The serum proteins in multiple myelomatosis. Biochem J. 1940 Sep;34(8-9):1248–1257. doi: 10.1042/bj0341248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr, Glossmann H. Molecular weight determination of membrane protein and glycoprotein subunits by discontinuous gel electrophoresis in dodecyl sulfate. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:92–102. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Bianco C., Cohn Z. Studies on the selective lysis and purification of Trypanosoma cruzi. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):224–229. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Chaplan S., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi. Factors modifying ingestion and fate of blood form trypomastigotes. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):447–451. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Chaplan S., Tydings J. D., Unkeless J., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi. Surface antigens of blood and culture forms. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):629–639. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Cohn Z. A. Trypanosoma cruzi: in vitro induction of macrophage microbicidal activity. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):288–300. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Ellis J., Chaplan S., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: in vivo and in vitro correlation between T-cell activation and susceptibility in inbred strains of mice. Exp Parasitol. 1981 Jun;51(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(81)90120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira N., Gordon S., Cohn Z. Trypanosoma cruzi: modification of macrophage function during infection. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):157–171. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]