Abstract
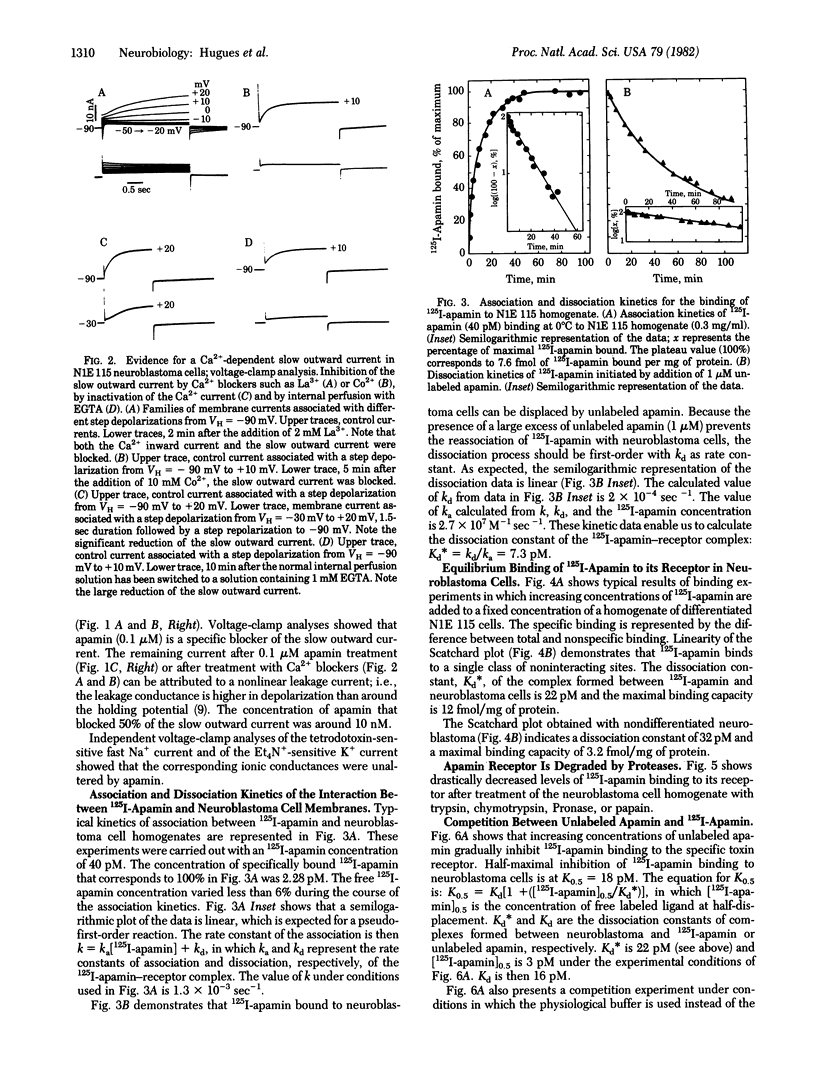
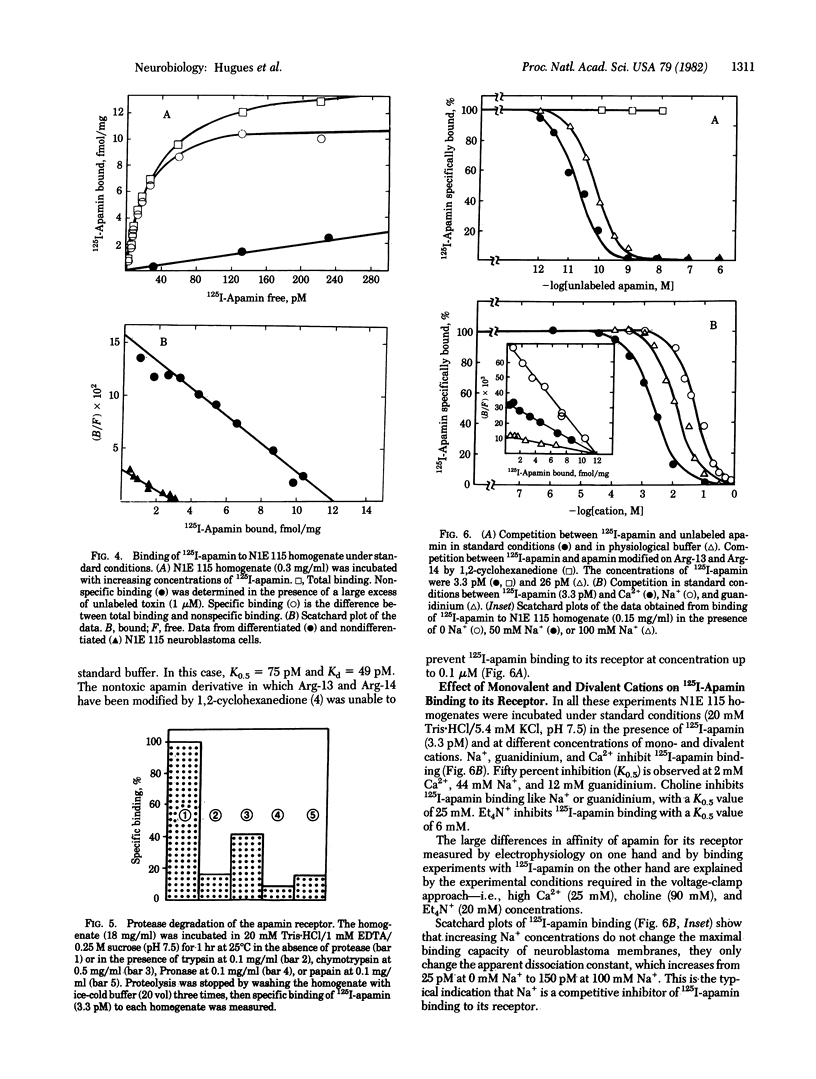
This paper describes the interaction of apamin, a bee venom neurotoxin, with the mouse neuroblastoma cell membrane. Voltage-clamp analyses have shown that apamin at low concentrations specifically blocks the Ca2+-dependent K+ channel in differentiated neuroblastoma cells. Binding experiments with highly radiolabeled toxin indicate that the dissociation constant of the apamin-receptor complex in differentiated neuroblastoma cells is 15-22 pM and the maximal binding capacity is 12 fmol/mg of protein. The receptor is destroyed by proteases, suggesting that it is a protein. The binding capacity of neuroblastoma cells for radiolabeled apamin dramatically increases during the transition from the nondifferentiated to the differentiated state. The number of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels appears to be at most 1/5th the number of fast Na+ channels in differentiated neuroblastoma. The binding of radiolabeled apamin to its receptor is antagonized by monovalent and divalent cations. Na+ inhibition of the binding of 125I-labeled apamin is of the competitive type (Kd(Na+) = 44 mM). Guanidinium and guanidinated compounds such as amiloride or neurotensin prevent binding of 125I-labeled apamin, the best antagonist being neurotensin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks B. E., Brown C., Burgess G. M., Burnstock G., Claret M., Cocks T. M., Jenkinson D. H. Apamin blocks certain neurotransmitter-induced increases in potassium permeability. Nature. 1979 Nov 22;282(5737):415–417. doi: 10.1038/282415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Barrett E. F., Dribin L. B. Calcium-dependent slow potassium conductance in rat skeletal myotubes. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90450-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavey D., Vincent J. P., Lazdunski M. A search for the apamin receptor in the central nervous system. Toxicon. 1979;17(2):176–179. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C., Vigne P., Lazdunski M. The specificity of the sodium channel for monovalent cations. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(2):437–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Hanson J. M., Rumjanek F. D., Shipolini R. A., Vernon C. A. The peptide components of bee venom. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):369–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E. Bee and wasp venoms. Science. 1972 Jul 28;177(4046):314–322. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4046.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habermann E., Fischer K. Bee venom neurotoxin (apamin): iodine labeling and characterization of binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar;94(2):355–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. D., Gundersen C. B., Jr Effects and mechanisms of polypeptide neurotoxins that act presynaptically. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1980;20:307–336. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.20.040180.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacques Y., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Molecular properties of the action potential Na+ ionophore in neuroblastoma cells. Interactions with neurotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7383–7392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Poustis C., Granier C., Van Rietschoten J., Rivier J., Morgat J. L., Freychet P. Neurotensin binding to extraneural and neural receptors: comparison with biological activity and structure--activity relationships. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;18(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Shakhovalov Y. A. Separation of sodium and calcium currents in the somatic membrane of mollusc neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Sep;270(3):545–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Akaike N., Brown A. M. Properties of internally perfused, voltage-clamped, isolated nerve cell bodies. J Gen Physiol. 1978 May;71(5):489–507. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.5.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann B. The beginning of fluctuation analysis of epithelial ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1980;54(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF01875371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Calcium-dependent potassium activation in nervous tissues. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:1–18. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. Ionic currents in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:265–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. The calcium action potential and a prolonged calcium dependent after-hyperpolarization in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:297–306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Spector I. The calcium current and the activation of a slow potassium conductance in voltage-clamped mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:307–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T. Chemicals as tools in the study of excitable membranes. Physiol Rev. 1974 Oct;54(4):813–889. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1974.54.4.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H., Stevens C. F. Ion conductance and ion selectivity of potassium channels in snail neurones. J Membr Biol. 1980 Dec 15;57(2):103–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01868997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Schweitz H., Lazdunski M. Structure-function relationships and site of action of apamin, a neurotoxic polypeptide of bee venom with an action on the central nervous system. Biochemistry. 1975 Jun 3;14(11):2521–2525. doi: 10.1021/bi00682a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



