Abstract
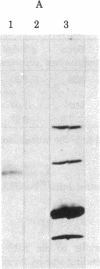
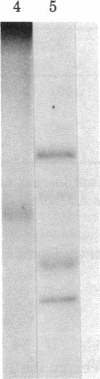
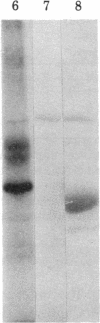
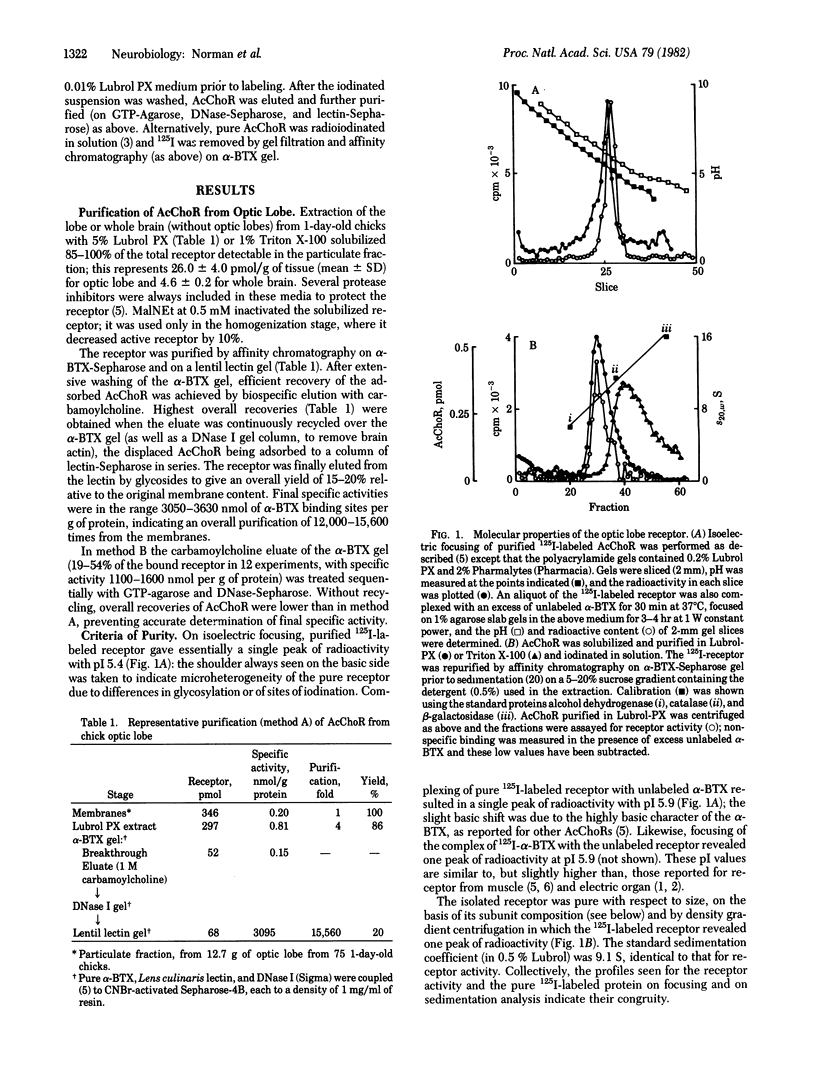
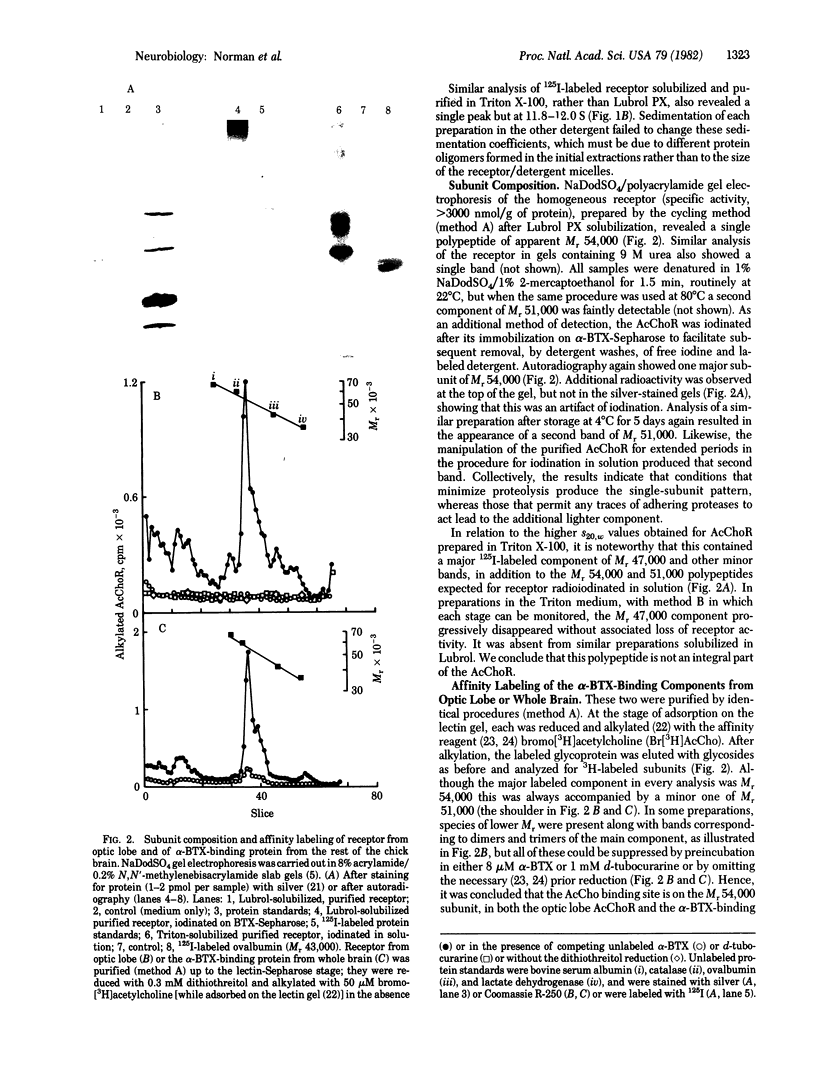
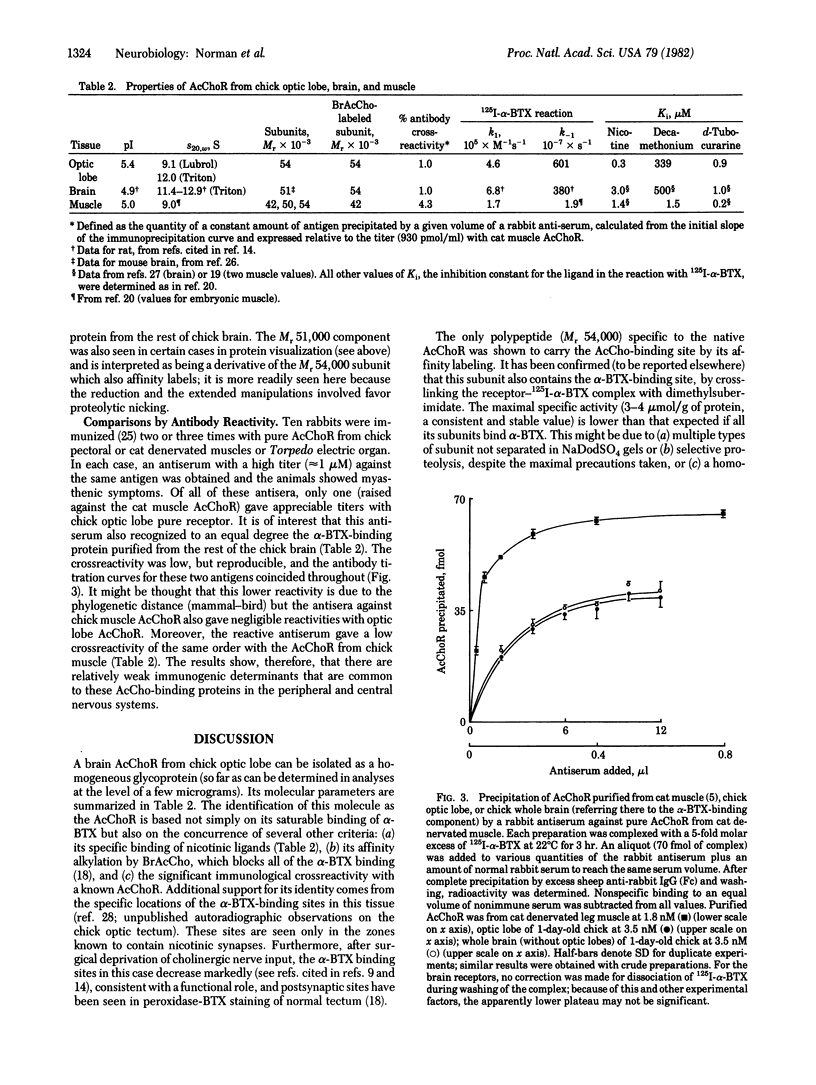
An alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic cholinergic receptor from chick optic lobe has been completely purified. Its standard sedimentation coefficient is 9.1 S. The value near 12 S reported for the related component from other brain regions can be reproduced when the initial extraction is by Triton X-100 (rather than Lubrol PX), but other protein is then complexed with it. A single subunit of apparent molecular weight 54,000 is detected, and this subunit is specifically labeled by bromo-[3H]acetylcholine, but only after disulfide reduction. The same size subunit likewise is labeled in the protein (purified similarly) from the rest of the chick brain which can also bind alpha-bungarotoxin and nicotinic ligands. Immunological crossreactivity is demonstrated between both of these proteins with an antiserum to pure acetylcholine receptor from skeletal muscle. The acetylcholine receptor from chick optic lobe and the alpha-bungarotoxin-binding protein from the rest of the brain appear similar or identical by a series of criteria and are related to (but with differences from) peripheral acetylcholine receptors.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnard E. A., Dolly J. O., Lang B., Lo M., Shorr R. G. Application of specifically acting toxins to the detection of functional components common to peripheral and central synapses. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1979;3:409–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Hall Z. W. Acetylcholine receptors in normal and denervated rat diaphragm muscle. II. Comparison of junctional and extrajunctional receptors. Biochemistry. 1975 May 20;14(10):2100–2106. doi: 10.1021/bi00681a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A. Neurotoxins and the ganglionic (C6) type of nicotinic receptor. Adv Cytopharmacol. 1979;3:225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonetto S. T., Fambrough D. M., Muller K. J. Nonequivalence of alpha-bungarotoxin receptors and acetylcholine receptors in chick sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):1016–1020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolly J. O., Barnard E. A. Purification and characterization of an acetylcholine receptor from mammalian skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5053–5060. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman J. A., Schmidt J. T., Oswald R. E. Effect of alpha-bungarotoxin on retinotectal synaptic transmission in the goldfish and the toad. Neuroscience. 1980;5(5):929–942. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Reiness C. G., Hall Z. W. Subunit structure of the acetylcholine receptor from denervated rat skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8589–8596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouvelas E. D., Dichter M. A., Greene L. A. Chick sympathetic neurons develop receptors for alpha-bungarotoxin in vitro, but the toxin does not block nicotinic receptors. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 6;154(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)91053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouvelas E. D., Greene L. A. The binding properties and regional ontogeny of receptors for alpha-bungarotoxin in chick brain. Brain Res. 1976 Aug 20;113(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo M. M., Dolly J. O., Barnard E. A. Molecular forms of the acetylcholine receptor from vertebrate muscles and Torpedo electric organ. Interactions with specific ligands. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):155–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas R. J., Bennett E. L. Interaction of nicotinic receptor affinity reagents with central nervous system alpha-bungarotoxin-binding entities. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;17(2):149–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyddiatt A., Sumikawa K., Wolosin J. M., Dolly J. O., Barnard E. A. Affinity labelling by bromoacetylcholine of a characteristic subunit in the acetylcholine receptor from muscle and Torpedo electric organ. FEBS Lett. 1979 Dec 1;108(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQuarrie C., Salvaterra P. M., Mahlers H. R. Studies on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in mammalian brain. Interaction of solubilized protein with cholinergic ligands. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2743–2747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore H. P., Raftery M. A. Studies of reversible and irreversible interactions of an alkylating agonist with Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor in membrane-bound and purified states. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1862–1867. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley B. J., Kemp G. E. Characterization of a putative nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in mammalian brain. Brain Res. 1981 Aug;228(1):81–104. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(81)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald R. E., Freeman J. A. Alpha-bungarotoxin binding and central nervous system nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuroscience. 1981;6(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90239-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald R. E., Freeman J. A. Characterization of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor isolated from goldfish brain. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3419–3426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Stallcup W. B. Immunological distinction between acetylcholine receptor and the alpha-bungarotoxin-binding component on sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4689–4692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polz-Tejera G., Schmidt J., Karten H. J. Autoradiographic localisation of alpha-bungarotoxin-binding sites in the central nervous system. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):349–351. doi: 10.1038/258349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raftery M. A., Hunkapiller M. W., Strader C. D., Hood L. E. Acetylcholine receptor: complex of homologous subunits. Science. 1980 Jun 27;208(4451):1454–1456. doi: 10.1126/science.7384786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto A., Arimatsu Y., Amano T. Subunit structure of alpha-bungarotoxin binding component in mouse brain. J Neurochem. 1981 Jul;37(1):210–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb05310.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shorr R. G., Lyddiatt A., Lo M. M., Dolly J. O., Barnard E. A. Acetylcholine receptor from mammalian skeletal muscle. Oligomeric forms and their subunit structures. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):143–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. K., Molinaro S., Schmidt J. Ligand responses of alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites from skeletal muscle and optic lobe of the chick. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8507–8512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]