Abstract
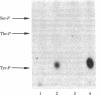
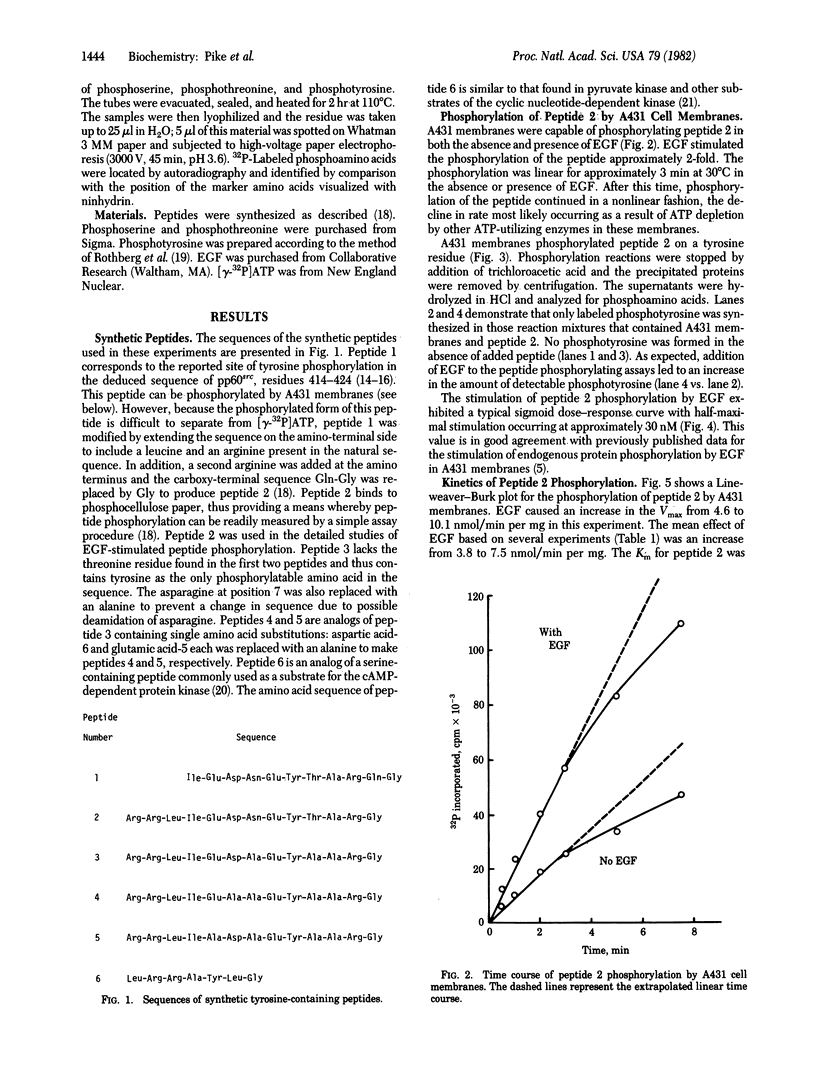
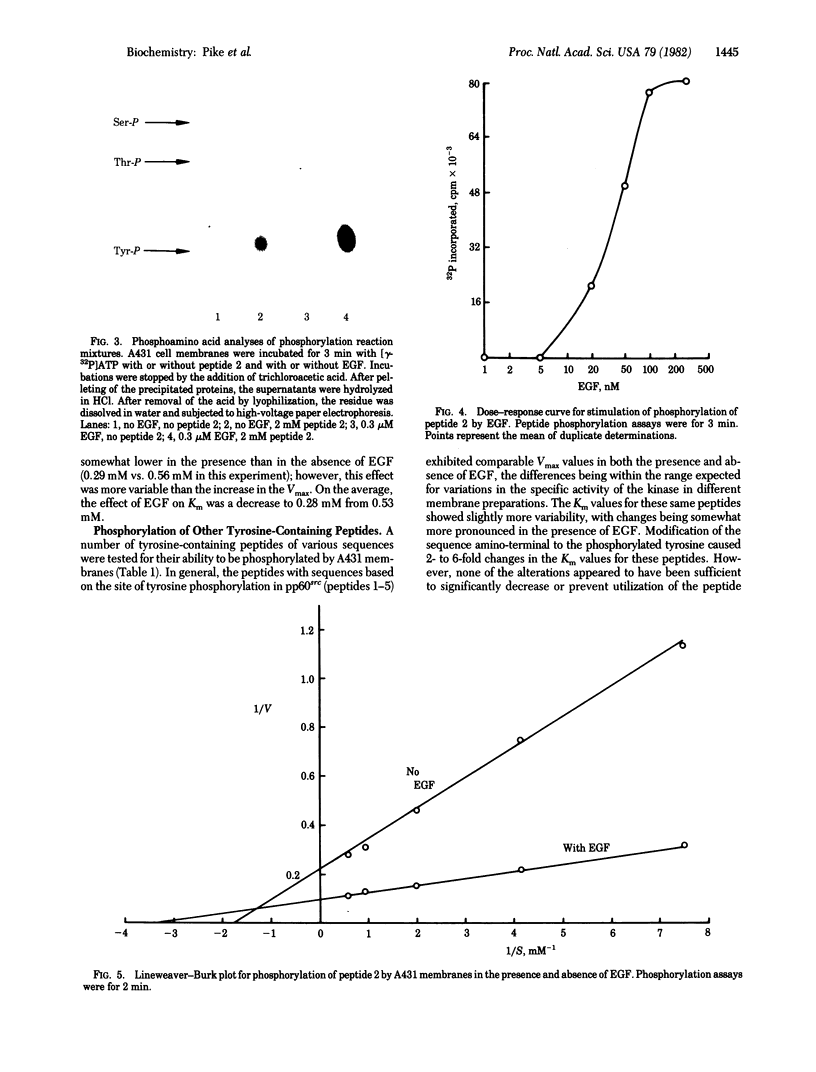
A431 cell membranes phosphorylate a synthetic peptide (Arg-Arg-Leu-Ile-Glu-Asp-Asn-Glu-Tyr-Thr-Ala-Arg-Gly) in which residues 2--12 correspond to the sequence of the reported site of tyrosine phosphorylation in pp60src. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the phosphorylation of this peptide 2-fold over basal levels in a dose-dependent fashion. Phosphorylation is linear for approximately 3 min at 30 degrees C and occurs on the tyrosine residue. Kinetic analysis of the phosphorylation reaction indicates that epidermal growth factor increases the average Vmax from 3.8 to 7.5 nmol/min per mg and slightly decreases the average Km from 0.53 mM to 0.28 mM. A number of other peptides analogous to this tridecapeptide are also phosphorylated by A431 membranes. The data suggest that peptides with sequences similar to the site of tyrosine phosphorylation in pp60src are preferred substrates for the kinase in these membranes. Thus, the epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase has the potential to interact with and phosphorylate pp60src. However, the A431 membranes also phosphorylate a tyrosine-containing peptide of totally unrelated sequence, suggesting that the kinase possesses a broad specificity for peptide phosphorylation that may not reflect its specificity with protein substrates.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beemon K. Transforming proteins of some feline and avian sarcoma viruses are related structurally and functionally. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90510-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Bornstein P., Gallis B. Phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase. Specific inhibition by Zn. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6519–6522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preparations in vitro. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):409–410. doi: 10.1038/276409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Rapid enhancement of protein phosphorylation in A-431 cell membrane preparations by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4884–4891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Harrison M. L., Pike L. J., Hellström K. E., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of synthetic peptides by a tyrosine protein kinase from the particulate fraction of a lymphoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):282–286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Cohen S. Purified EGF receptor-kinase interacts specifically with antibodies to Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):516–519. doi: 10.1038/290516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence of an avian sarcoma virus oncogene (src) and proposed amino acid sequence for gene product. Nature. 1980 Sep 18;287(5779):198–203. doi: 10.1038/287198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhart W., Hutchinson M. A., Hunter T. An activity phosphorylating tyrosine in polyoma T antigen immunoprecipitates. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):925–933. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmquist G., Andersson J., Edlund B., Engstroöm L. Amino acid sequence of a (32P) phosphopeptide from pig liver pyruvate kinase phosphorylated by cyclic 3',5'-AMP-stimulated protein kinase and gamma-(32P)ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 27;61(2):559–563. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90993-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Graves D. J., Benjamini E., Krebs E. G. Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4888–4894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudlow J. E., Buss J. E., Gill G. N. Anti-pp60src antibodies are substrates for EGF-stimulated protein kinase. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):519–521. doi: 10.1038/290519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The purified product of the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11973–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Ghysdael J., Vogt P. K., Smart J. E. Homologous tyrosine phosphorylation sites in transformation-specific gene products of distinct avian sarcoma viruses. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):675–677. doi: 10.1038/291675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg P. G., Harris T. J., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. O4-(5'-uridylyl)tyrosine is the bond between the genome-linked protein and the RNA of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4868–4872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Oppermann H., Czernilofsky A. P., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L., Bishop J. M. Characterization of sites for tyrosine phosphorylation in the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus (pp60v-src) and its normal cellular homologue (pp60c-src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessmer G. W., Skuster J. R., Tabatabai L. B., Graves D. J. Studies on the specificity of phosphorylase kinase using peptide substrates. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5666–5671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Dasgupta A., Baltimore D. Abelson murine leukaemia virus protein is phosphorylated in vitro to form phosphotyrosine. Nature. 1980 Feb 28;283(5750):826–831. doi: 10.1038/283826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrann M. M., Fox C. F. Identification of epidermal growth factor receptors in a hyperproducing human epidermoid carcinoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8083–8086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]