Abstract
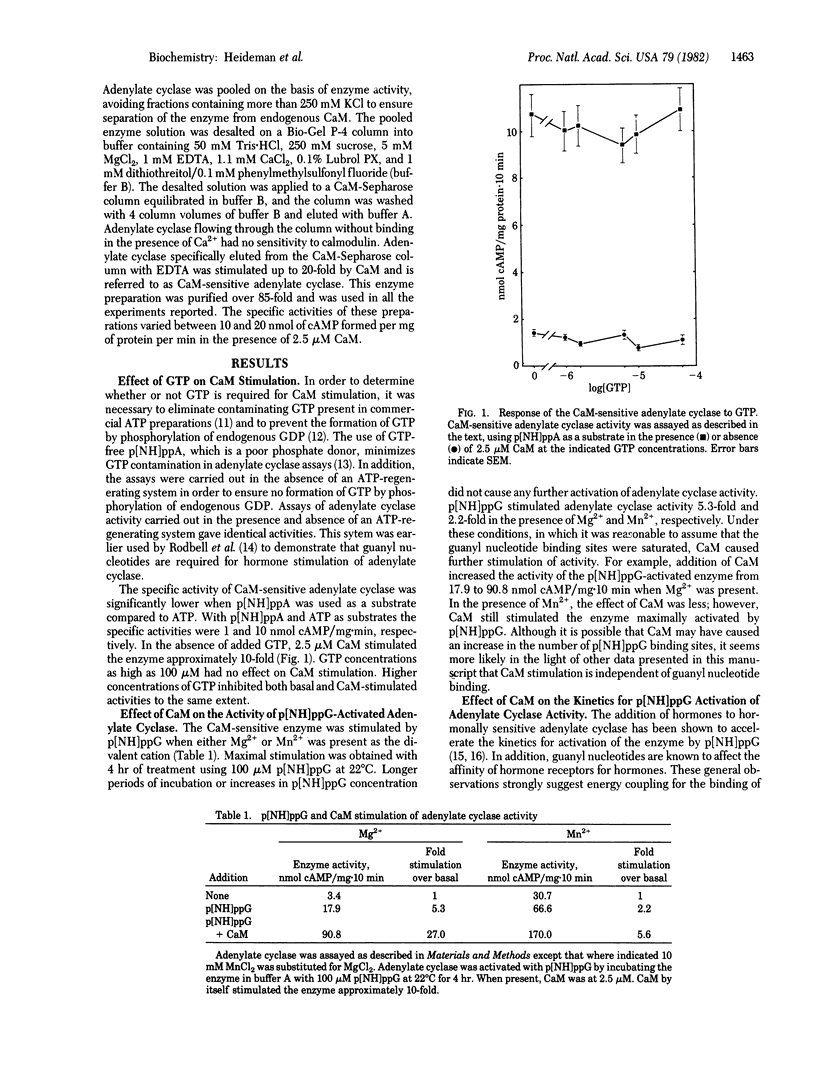
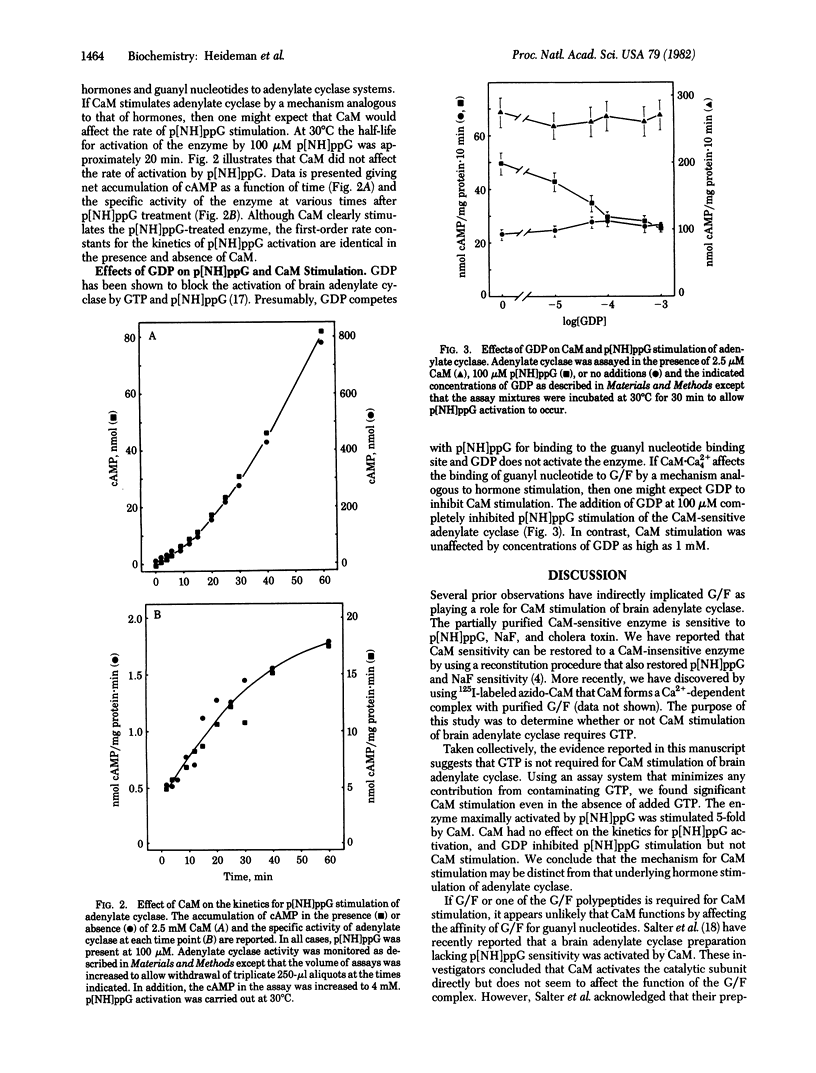
The importance of guanyl nucleotides for calmodulin stimulation of bovine cerebral cortex adenylate cyclase [ATP pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizing), EC 4.6.1.1] was examined by using a partially purified calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase that was resolved from calmodulin-insensitive forms of the enzyme. By using 5'-adenylyl imidodiphosphate as a substrate, in the absence of an ATP-regenerating system, it was determined that GTP is not required for calmodulin stimulation of the enzyme. Maximal activation by 5'-guanylyl imidodiphosphate (p[NH]ppG) was 5.3-fold, whereas the combination of p[NH]ppG and calmodulin stimulated the enzyme 27-fold. Although GDP inhibited p[NH]ppG stimulation of the calmodulin-sensitive adenylate cyclase, it did not affect calmodulin stimulation. In addition, calmodulin did not alter the kinetics for activation of the enzyme by p[NH]ppG. It is concluded that GTP is not required for calmodulin stimulation of brain adenylate cyclase and that calmodulin regulation of this enzyme is probably not due to effects of calmodulin on the affinity of the guanyl nucleotide regulatory complex for guanyl nucleotides.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brostrom C. O., Huang Y. C., Breckenridge B. M., Wolff D. J. Identification of a calcium-binding protein as a calcium-dependent regulator of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation through the beta-adrenergic receptor: catecholamine-induced displacement of bound GDP by GTP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4155–4159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y., Bradham L. S., Lynch T. J., Lin Y. M., Tallant E. A. Protein activator of cyclic 3':5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase of bovine or rat brain also activates its adenylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):1055–1062. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90747-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B. Endogenous GTP and the regulation of epinephrine stimulation of adenylate cyclase. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978 Apr;4(2):71–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedman J. R., Potter J. D., Jackson R. L., Johnson J. D., Means A. R. Physicochemical properties of rat testis Ca2+-dependent regulator protein of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Relationship of Ca2+-binding, conformational changes, and phosphodiesterase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8415–8422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F., Romaniuk P. J., Heideman W., Storm D. R. Stereochemistry of the mammalian adenylate cyclase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9118–9120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura N., Nagata N. The requirement of guanine nucleotides for glucagon stimulation of adenylate cyclase in rat liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3829–3835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Toscano W. A., Jr, Storm D. R. Cross-linking of iodine-125-labeled, calcium-dependent regulatory protein to the Ca2+-sensitive phosphodiesterase purified from bovine heart. Biochemistry. 1979 Jun 26;18(13):2820–2825. doi: 10.1021/bi00580a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Echeverria D., Knox S. Increase in the size of soluble brain adenylate cyclase with activation by guanosine 5'-(beta, gamma-imino)triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9782–9789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Krans H. M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. V. An obligatory role of guanylnucleotides in glucagon action. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1877–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Lin M. C., Londos C., Rendell M., Rodbell M. The hepatic adenylate cyclase system. I. Evidence for transition states and structural requirements for guanine nucloetide activiation. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4239–4245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. S., Krinks M. H., Klee C. B., Neer E. J. Calmodulin activates the isolated catalytic unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9830–9833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Padgett W., Daly J. W. Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sevilla N., Steer M. L., Levitzki A. Synergistic activation of adenylate cyclase by guanylyl imidophosphate and epinephrine. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3493–3499. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toscano W. A., Jr, Westcott K. R., LaPorte D. C., Storm D. R. Evidence for a dissociable protein subunit required for calmodulin stimulation of brain adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5582–5586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Vandermeers A., Anjaneyulu R., Malaisse W. J. Calmodulin activation of adenylate cyclase in pancreatic islets. Science. 1979 Oct 12;206(4415):225–227. doi: 10.1126/science.225798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westcott K. R., La Porte D. C., Storm D. R. Resolution of adenylate cyclase sensitive and insensitive to Ca2+ and calcium-dependent regulatory protein (CDR) by CDR-sepharose affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):204–208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H., Goldhammer A. R., Berkowitz S. A. Calmodulin activates prokaryotic adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3841–3844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



