Abstract
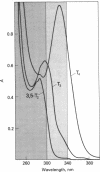
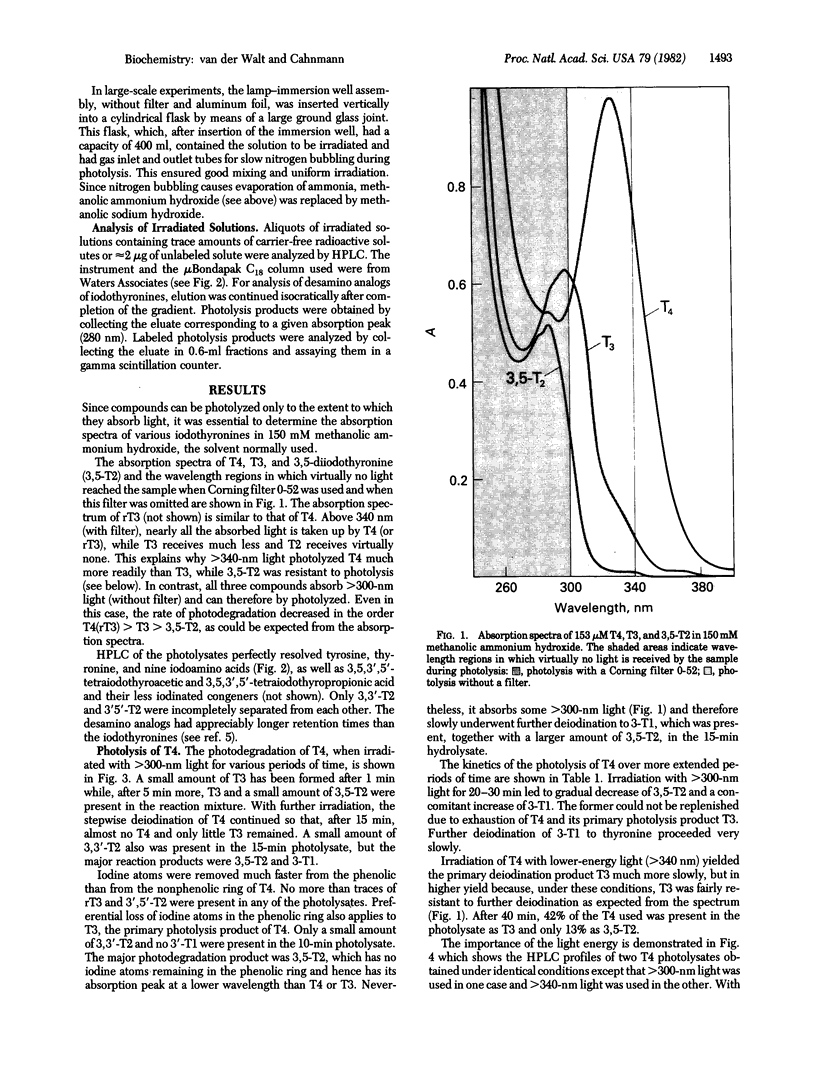
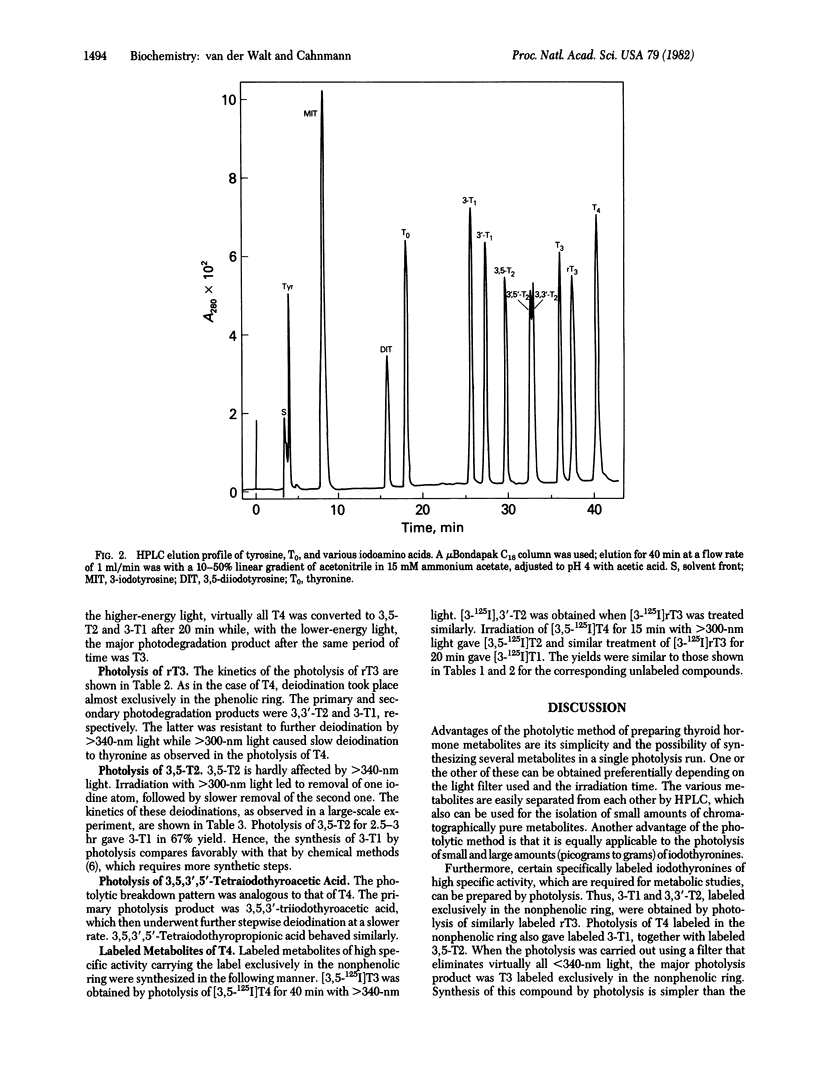
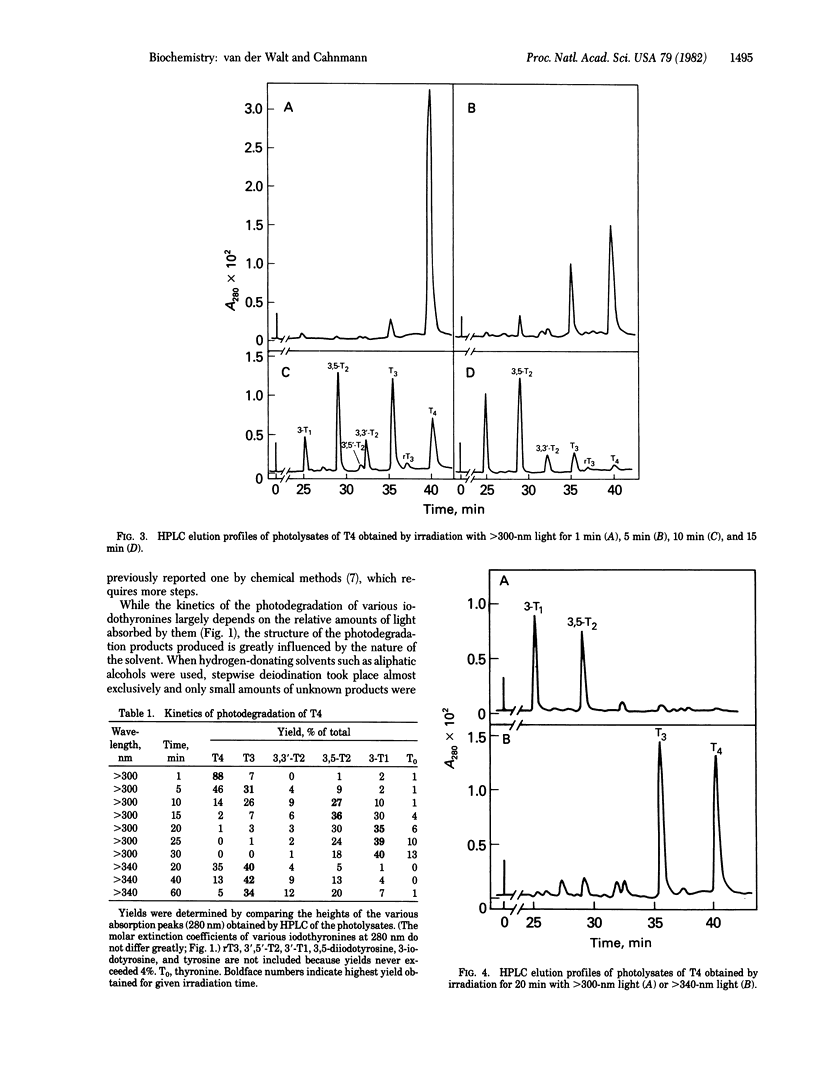
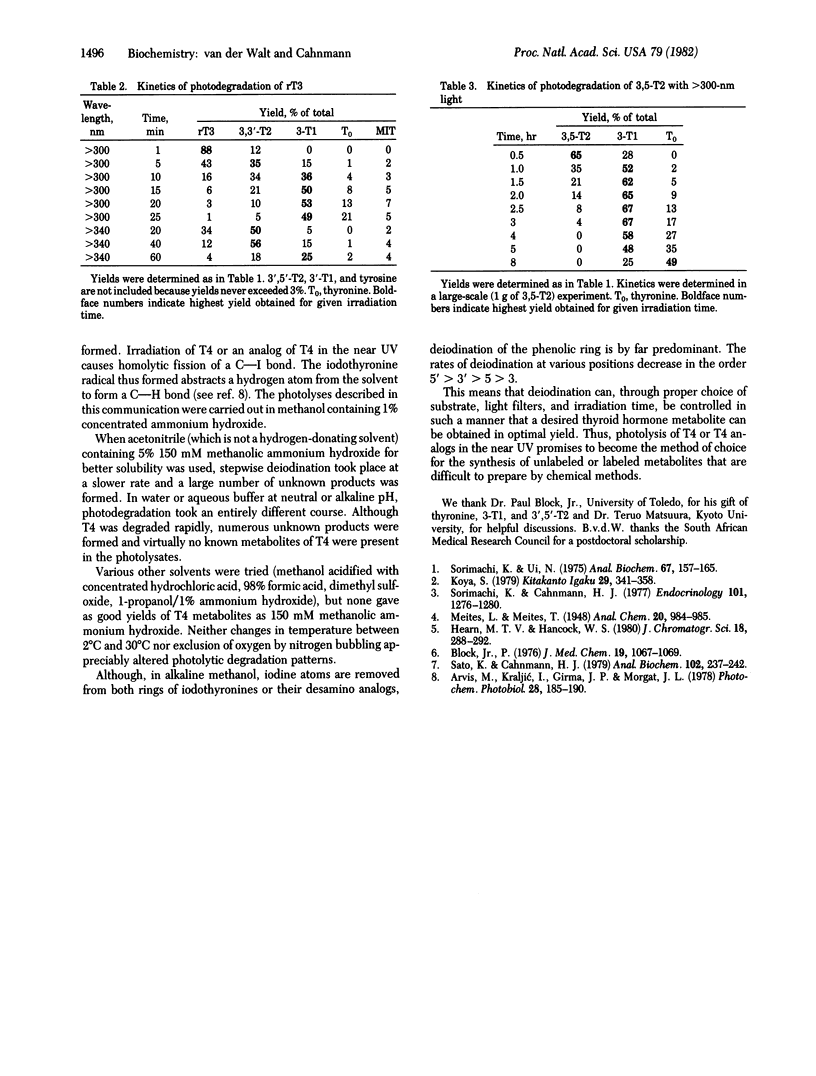
Photolysis of thyroxine and its analogs in the near UV permitted synthesis in good yield of picogram to gram quantities of thyroid hormone metabolites. Preparation of the same metabolites by classical chemical synthesis requires multistep procedures. Specifically labeled metabolites of high specific activity (e.g., those carrying the label in the nonphenolic ring) were obtained by photolysis of appropriately labeled thyroxine or 3',3',5'-triiodothyronine (reverse triiodothyronine). Some of these labeled metabolites, which are required for metabolic studies (3-iodothyronine and 3,3'-diiodothyronine, labeled in the nonphenolic ring), had not previously been obtained by other methods. Irradiation of thyroxine and reverse triiodothyronine in 150 mM methanolic ammonium hydroxide with greater than 340-nm light caused removal of one iodine atom from the phenolic ring with formation of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine and 3,3'-diiodothyronine, respectively. Irradiation with higher-energy light (greater than 300 nm) led to stepwise removal of additional iodine atoms. Those in the phenolic ring were removed preferentially, so that 3,5-diiodothyronine and 3-iodothyronine, respectively, were formed. The iodine atoms in the nonphenolic ring were lost more slowly. Tetraiodothyroacetic acid followed a similar photodeiodination pattern. Photolysis with light in the near UV is a simple method for the synthesis of thyroid hormone metabolites.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Block P., Jr Synthesis of 3-iodo-L-thyronine and its iodinated derivatives. J Med Chem. 1976 Aug;19(8):1067–1069. doi: 10.1021/jm00230a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Cahnmann H. J. Synthesis of [3,5-125I]triiodo-L-thyronine of high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90345-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorimachi K., Cahnmann H. J. A simple synthesis of [3,5-125I]Diiodo-L-thyroxine of high specific activity. Endocrinology. 1977 Oct;101(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-4-1276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorimachi K., Ui N. Ion-exchange chromatographic analysis of iodothyronines. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90283-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]