Abstract
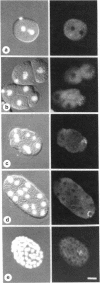
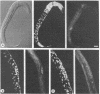
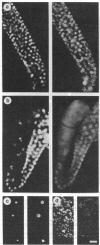
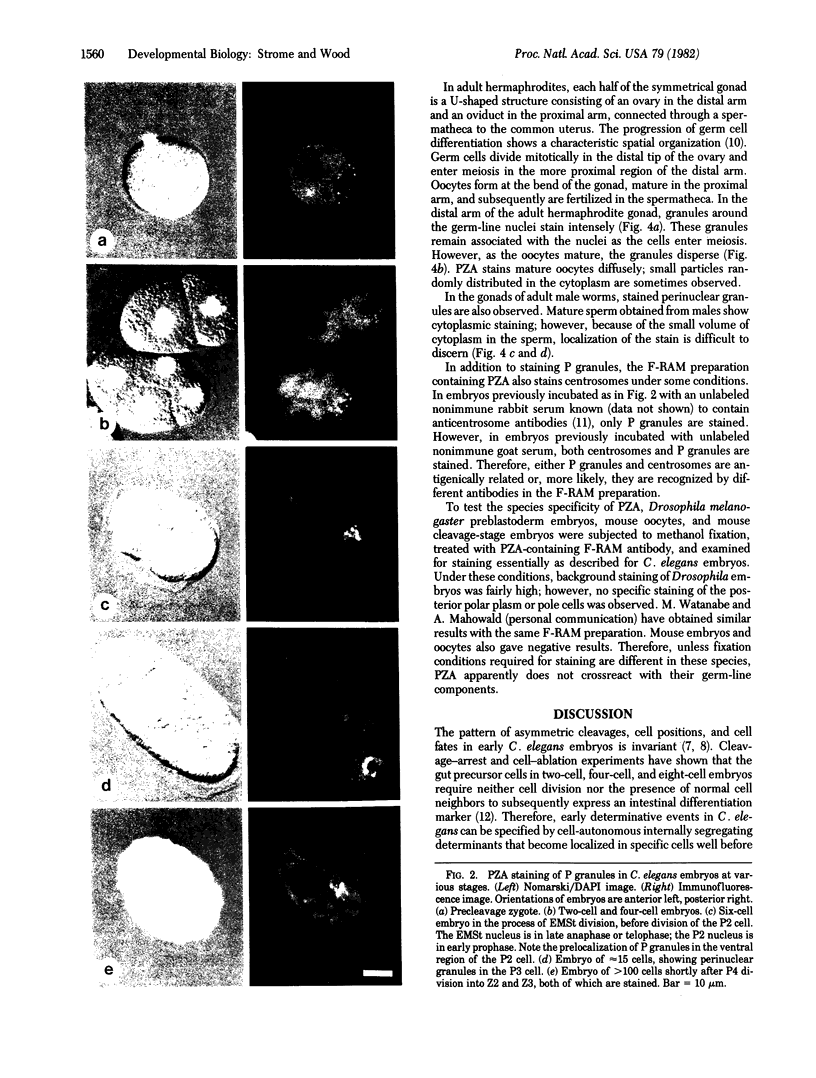
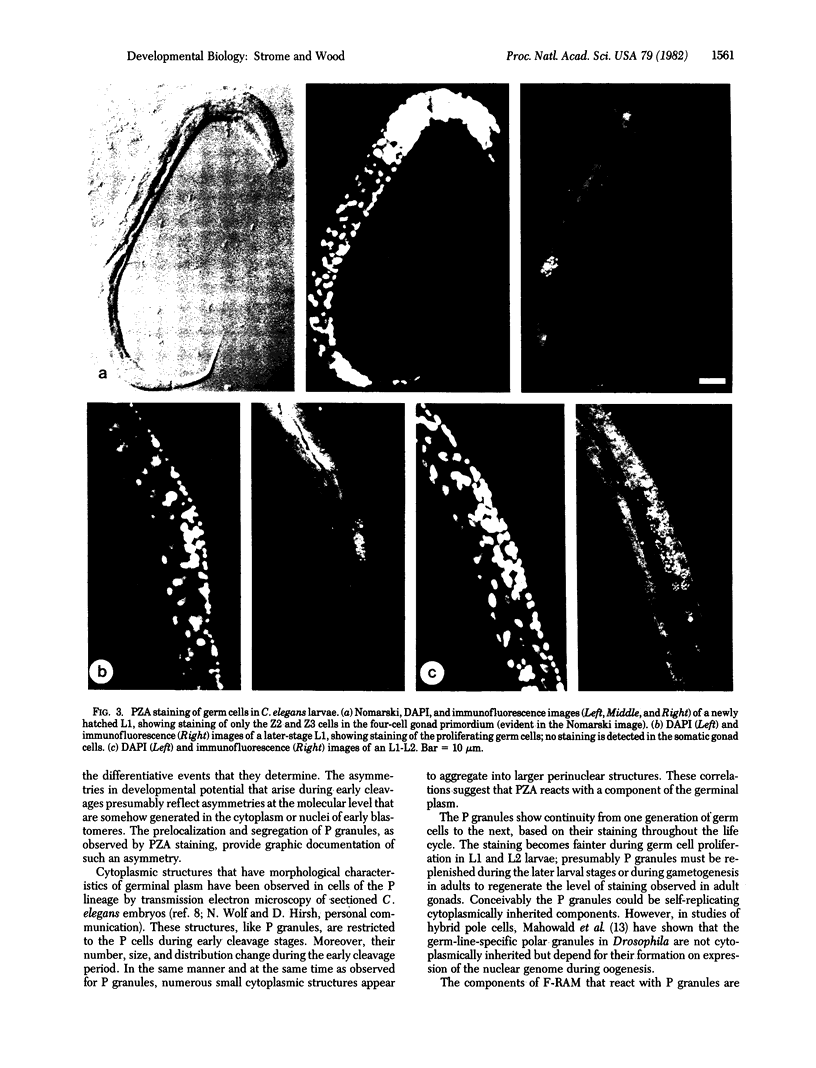
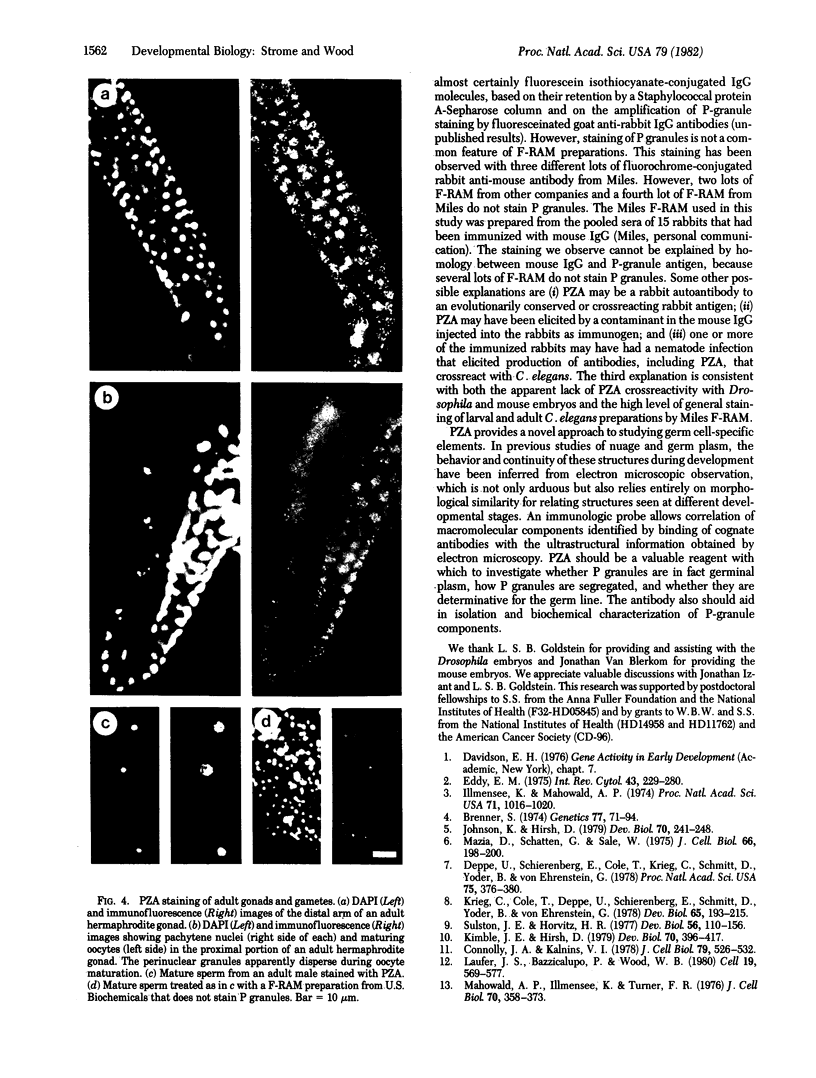
By using fluorescent antibody staining, we have followed cytoplasmic granules unique to germ-line cells throughout the life cycle of Caenorhabditis elegans. These elements, designated P granules, are segregated exclusively to germ-line precursor cells during early embryogenesis. Prior to mitosis at each of the early cleavages that produce a somatic and germ-line daughter cell, the granules become localized in the region of cytoplasm destined for the germ-line daughter. After the 16-cell stage, the granules appear to be associated with the nuclear envelope. P granules persist in the germ cells throughout the larval and adult stages. The P granules are similar in number, size, and distribution to germ-line-specific structures identified as "germinal plasm" by electron microscopy in C. elegans embryos.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974 May;77(1):71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. A., Kalnins V. I. Visualization of centrioles and basal bodies by fluorescent staining with nonimmune rabbit sera. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):526–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppe U., Schierenberg E., Cole T., Krieg C., Schmitt D., Yoder B., von Ehrenstein G. Cell lineages of the embryo of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):376–380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddy E. M. Germ plasm and the differentiation of the germ cell line. Int Rev Cytol. 1975;43:229–280. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illmensee K., Mahowald A. P. Transplantation of posterior polar plasm in Drosophila. Induction of germ cells at the anterior pole of the egg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1016–1020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K., Hirsh D. Patterns of proteins synthesized during development of Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1979 May;70(1):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimble J., Hirsh D. The postembryonic cell lineages of the hermaphrodite and male gonads in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1979 Jun;70(2):396–417. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg C., Cole T., Deppe U., Schierenberg E., Schmitt D., Yoder B., con Ehrenstein G. The cellular anatomy of embryos of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Analysis and reconstruction of serial section electron micrographs. Dev Biol. 1978 Jul;65(1):193–215. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer J. S., Bazzicalupo P., Wood W. B. Segregation of developmental potential in early embryos of Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):569–577. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahowald A. P., Illmensee K., Turner F. R. Interspecific transplantation of polar plasm between Drosophila embryos. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):358–373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazia D., Schatten G., Sale W. Adhesion of cells to surfaces coated with polylysine. Applications to electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):198–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J. E., Horvitz H. R. Post-embryonic cell lineages of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1977 Mar;56(1):110–156. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]