Abstract
Accumulation of neurofibrillary tangles (NFT), intracellular inclusions of fibrillar forms of tau, is a hallmark of Alzheimer Disease. NFT have been considered causative of neuronal death, however, recent evidence challenges this idea. Other species of tau, such as soluble misfolded, hyperphosphorylated, and mislocalized forms, are now being implicated as toxic. Here we review the data supporting soluble tau as toxic to neurons and synapses in the brain and the implications of these data for development of therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies.
Keywords: Alzheimer, tauopathy, neurofibrillary tangle, hyperphosphorylated tau
Introduction
More than 35 million individuals currently suffer from Alzheimer Disease (AD), a progressive neurodenegerative disorder with no known cure [1, 2]. The recent failure of several phase III clinical trials [3] and the knowledge that the number of AD patients is expected to double in the coming decades [4], instigates the need for a closer look at the progress made in understanding AD and the gaps that still remain.
Since its original description in 1907, Alzheimer Disease (AD) brain has been defined by the presence of extracellular β-amyloid (Aβ) containing plaques and cytoplasmic neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) consisting of abnormal microtubule associated protein tau [5, 6]. These proteinaceous aggregates are accompanied by synapse loss and neuronal cell death, which are thought to subserve the clinical syndrome of progressive cognitive impairment in AD [7–9]. The exact relationships and mechanisms between these four pathological hallmarks of AD have yet to be clearly defined, though it is largely believed that the initiating pathogen is the Aβ peptide [3, 10–14]. The strong support for the amyloid hypothesis has led the majority of the clinical trials to date to be rather Aβ-centric [15, 16]. For some time following the discovery of the Aβ-linked genetics of AD, no tau mutations were identified that contributed to the disease, leading to the supposition that NFT are a downstream side-effect of Aβ toxicity and indicative of cell death [15]. Though it is still true that no mutations of tau have been linked to AD, a number of dementias known as tauopathies are known to result from alterations to the tau gene [17, 18] suggesting that changes in the tau protein are, in fact, sufficient to induce neurodegenerative processes. Furthermore, tau pathology correlates more closely than amyloid burden to neuronal loss, synaptic deficits and severity of disease and cognitive decline in AD [19–21]. These findings reinvigorated the investigation of tau as a pathologic entity in AD, ultimately leading to several clinical trials for tau-targeted therapies [2, 15]. In more recent years it has been shown that tau is a necessary mediator of Aβ toxicity [22–26] spurring the suggestion that AD may have several phases, first Aβ-dependent and then Aβ-independent but rather potentially tau dependent [27]. If this is the case, it is of course important to continue discovering Aβ mediated mechanisms of neurotoxicity and developing appropriately targeted therapeutics, but even more important is furthering our understanding of the mechanisms by which tau contributes to AD in order to develop complementary tau-targeted therapies.
Biology of Tau
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein encoded by the MAPT gene on chromosome 17. Alternative splicing of 16 exons yields six isoforms of human tau that differ in number of amino acids (352–441), in number of N-terminal inserts (0–2N) and in number of microtubule binding domains (3R or 4R). In normal adult brain, the ratio of 3R:4R tau is ~1 and in AD this ratio is shifted toward excess 4R tau [1, 18]. Many of the tau mutations leading to dementia alter the splicing of the tau protein also increasing the presence of 4R tau [18, 28]. The number of microtubule binding domains in tau determines the affinity for microtubules (3R < 4R), thereby mediating the primary function of tau in stabilizing axonal microtubules and enabling their polymerization and assembly [4, 28]. As microtubules serve as the highways for trafficking of molecules within the axon, this places tau as a central player in neuronal transport and therefore function [29]. Also contributing to the microtubule stabilizing capacity of tau are post-translational modifications, particularly phosphorylation, which when elevated decreases affinity of tau for microtubules and causes it to detach [4, 18]. Tau has over 80 phosphorylation sites, some of which are considered physiological while others are ‘de-novo’ phosphorylated in disease states [30]. Two families of protein kinases contribute to tau phosphorylation, those that are proline directed and tend to phosphorylate serine and threonine motifs outside the microtubule binding domain and those that are KXGS-motif and non-proline directed and tend to phosphorylate within the repeat domain [14, 31]. Proline directed kinases that phosphorylate tau include GSK3β, MAPK (mitogen activated protein kinase), JNK (c-Jun N terminal kinase) and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) and have been the target of some of the preliminary tau-targeted therapies [14–16, 18]. Kinases targeting KXGS and other non-proline motives include microtubule affinity regulating kinase (MARK), P70S6K, BRSK, PKA and CaMKII [14, 28], with MARK recently being implicated as a critical mediator of both Aβ and tau toxicity [26]. In physiological conditions the activities of the kinases are dynamically counterbalanced by the primary tau directed protein phosphatases PP2A and PP1 [18, 28].
Pathological forms of tau
In disease states such as AD, it is thought that the balance of kinase and phosphatase activity is shifted, creating a hyperphosphorylated species of tau [1, 28]. This increases the fraction of tau that is no longer attached to microtubules, allowing for monomeric hyperphosphorylated tau to bind one another to produce oligomers [32–34]. These oligomers are missorted from the axonal to somatodendritic compartment [35–37], where they undergo further hyperphosphorylation and conformational change and take on a beta-sheet structure that is considered insoluble. Fusion of these oligomeric species contributes to the formation of paired helical filaments (PHF), the primary constituent of NFT [28, 38–40].
As is the case with other proteins involved in neurodegenerative diseases, the question of which variety of tau is most toxic and whether that toxicity represents a gain or loss of function continues to be debated [11, 37, 41]. As tau progresses from normal to NFT it passes through a loosely defined ‘soluble’ state in which the protein may be hyperphosphorylated, mislocalized, conformationally changed and/or oligomeric but not yet fibrillar. It is these forms of soluble tau protein that vie against NFT in the debate of pathogenic entity in neurodegenerative disease. The toxicity of tau can be argued in several ways 1) aggregated fibrillar tau (NFT) is toxic and causative of cell death and cognitive decline in AD, 2) soluble species of hyperphosphorylated, misfolded tau that accumulate in abnormal cellular compartments are toxic and NFT act as a sink for these toxic species, implicating NFT as protective, or 3) both soluble forms of pathological tau and NFT are toxic to cells in different ways and on different time scales. We favor the third model of toxicity as will be discussed.
Historically, NFT were considered indicators of cell death, particularly given that their progression and number correlate well with severity of cognitive decline in AD, while Aβ plaque deposition does not [19–21, 42, 43]. NFT bearing neurons of human AD brain have been shown to have abnormal quantity or distribution of molecules necessary for proper function such as synaptic proteins [7, 37], and calcium binding proteins [44–47] and NFT have been suggested to interfere with basic cell function as they serve as a physical disruption or space occupying lesion [28, 29]. In a mouse model of tauopathy, expression of an aggregation prone tau molecule causes morphological and functional deficits while expression of a similar but anti-aggregation tau molecule has no such negative consequences [39, 48, 49]. NFT toxicity is also supported by cell culture models in which tau aggregation leads to activation of caspase cascades and cell death [18].
Significant data, however, have also accumulated for the contrarian view that NFT may be silent bystanders, thereby implicating soluble tau species or other pathological processes, but in an indirect manner. Many cognitively normal individuals accumulate NFT, with pathological changes in tau occurring as early as the age of 6 in brainstem nuclei [43]. AD is often not diagnosed until NFT have spread throughout much of the brain [42, 50]. Frontotemporal dementias known to be caused by mutations in tau in humans, and a number of animal models demonstrate severe neuronal cell loss and dysfunction in the absence of overt or coinciding NFT pathology [18, 21, 28, 38, 51–53]. Several studies in a mouse model that reversibly expresses a human mutant form of tau (rTg4510) show dissociation between neuronal loss and NFT accumulation, particularly after suppressing the tau transgene at which point neuronal loss stops though NFT persist and continue to accumulate [54, 55]. Additional studies in these animals have shown that the presence of a tangle does not alter spine density, electrophysiological function [2, 56] or ability to respond to physiologically relevant stimuli [57] in comparison to non-tangle bearing neighboring neurons. In fact, NFT appearance in these animals is preceded by caspase activation and these neurons endure longer than anticipated following activation of these traditional cell death signaling cascades [58, 59]. Emerging from these findings is a theory that NFT, rather than representing silent markers of cell death, may serve as a protective mechanism of sequestering toxic soluble tau species [18, 37].
Evidence for the toxicity of soluble tau species has been growing in recent years despite the fact that it remains an ill-defined species. It is now thought that phosphorylation, localization and conformational changes to tau are sufficient for occurrence of toxic effects and represent a pre-tangle stage. These early alterations have been proposed as the beginning of the pathological process of AD [35, 42, 43, 50, 60]. A large number of in-vitro studies have shown that over-expression of tau or alterations in its phosphorylation state, localization or conformation induce changes in calcium homeostasis, loss of dendritic spines, impaired trafficking of organelles, particularly mitochondria, and cell death [14, 18, 28, 36, 37, 40, 60–67]. Studies in mouse models support these findings, demonstrating correlations between soluble tau species and neuronal or synaptic dysfunction [37, 49, 52, 68–70]. A recent study by Lasagna-Reeves et al (2011) demonstrated that injection of tau oligomers, but not monomers or fibrils, into the brain of wild-type mice was sufficient to induce synaptic deficits, mitochondrial dysfunction and memory impairments. Furthermore, recent studies suggest that these soluble species of tau may be transmitted between neurons and may contribute to or be responsible for the pathological spread of disease through the brain [43, 71–74].
Mechanisms of tau toxicity
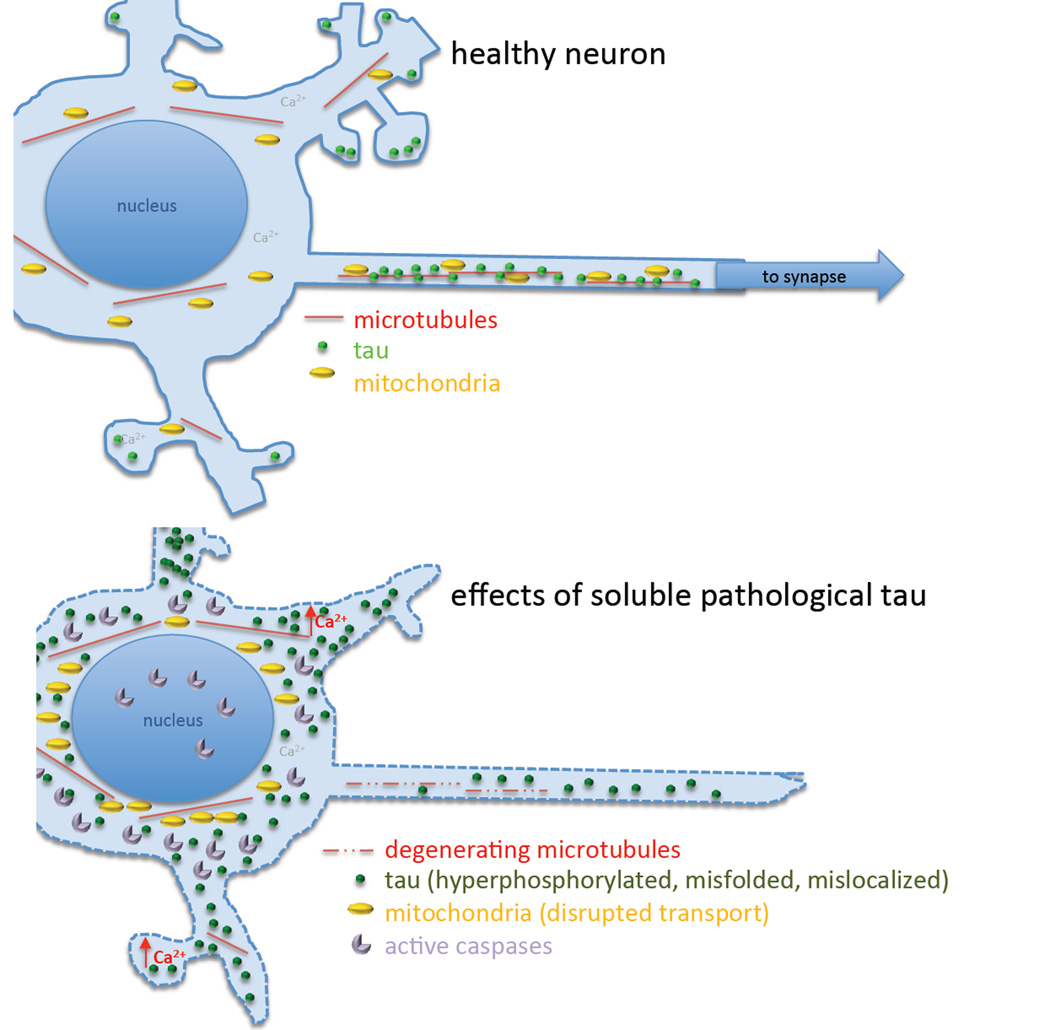
Several molecular mechanisms may underlie the toxicity of either soluble or aggregated tau. These include the well-established tau-induced disruptions in microtubule-based transport (which importantly effect mitochondrial transport) and the less well understood phenomena of tau-related calcium dyshomeostasis, synaptic dysfunction and loss, and caspase activation (summarized in Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of tau toxicity. Strong evidence supports a role of soluble pathological forms of tau in several mechanistic pathways leading to synapse and neuronal death. Tau is normally largely bound to axonal microtubules and plas a role in dendritic spine plasticity. During Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies, tau becomes hyperphosphorylated and misfolded. It detaches from microtubules and accumulates in the somatodendritic compartment. Accumulation of soluble tau in the soma is associated with caspase activation and disruptions of membrane integrity, which resolve after the soluble tau coalesces into a neurofibrillary tangle. Removal of tau from microtubules causes them to degenerate, and pathological tau may also directly interfere with microtubule based transport mechanisms. Disturbances in microtubule transport affect mitochondrial trafficking to distal parts of the neuron resulting in perinuclear clumping. Synapses become dysfunctional and dendritic spines are lost, and calcium levels increase in dendrites with accumulations of soluble tau. Synapse loss and the inability to energetically maintain axons are thought to contribute to the dying back of processes and cell death.
Tau toxicity has largely been attributed to disruption of neuronal transport, particularly as the main function of tau is stipulated to be maintaining microtubule stability and assembly in CNS axons. Neurons, due to their morphological structure with extended processes and high-energy demands, rely heavily upon regulated transport of organelles and vital materials for cell function [75, 76]. Impairment of these transport processes has been proposed as an early pathological phenomenon and underlying cause of neurodegenerative diseases, including AD [13, 76–82]. Both loss and gain of function mechanisms for tau interference with transport have been proposed, but interestingly, recent studies in tau knock out models have shown that the loss of tau, even in its entirety, is not lethal and actually demonstrates very mild phenotypes [41, 83, 84]. Tau over-expression in cell culture without the formation of NFT has been shown to inhibit fast axonal transport, with mitochondria emerging as the cargo most susceptible to deficits in localization, implicating soluble tau in these deficits [62–68, 85, 86]. Patches of “soluble” tau bound to microtubules have been proposed to serve as a roadblock, preferentially causing anterograde-moving kinesins to detach from the microtubule [62]. A second theory suggests that soluble tau can interfere with transport by directly competing with cargo or hampering signaling cascades [78, 87, 88]. Ittner et al (2009) demonstrated that pathologically hyperphosphorylated tau directly interacts with JIP1, a protein involved in linking cargoes to the kinesin motor, thereby preventing proper association of cargo and motor. Other studies have suggested that tau may bind influential molecules such as GSK3β, or mitochondria themselves to alter transport and localization of organelles in a more indirect manner [78, 89–92]. Yet other studies have suggested that tau itself is a kinesin cargo and when cytosolic concentration of tau is pathologically increased, it may out compete other cargoes [63]. Aggregates of misfolded tau (NFT and neuropil threads) have been argued to interfere with transport by serving as a space-occupying lesion, thereby inhibiting kinesin binding and movement [85, 86].
Consequences of impaired neuronal transport due to any of the mechanisms discussed above include altered distribution and function of organelles, particularly mitochondria, resultant perturbations in cell function, synapse loss and dying back of the neuron ultimately leading to cell death [78, 93]. Mitochondria have been increasingly recognized for their potential contribution to disease pathogenesis [13, 76, 94, 95], with evidence mounting that disruptions to mitochondrial localization and function may serve as the intersection for Aβ and tau-mediated toxicity [1, 2, 96, 97]. Tau over-expression in cultured cells leads to perinuclear clumping of mitochondria [63–66, 98], while application of oligomeric Aβ leads to depletion of mitochondria, especially in distal dendrites, and this deficit is thought to be mediated by missorting or hyperphosphorylation of tau [14, 81, 91]. Recent evidence from our group suggests that mitochondrial transport deficits are due in large part to soluble forms of tau. Mitochondrial distribution in the brains of rTg4510 mice was significantly altered in cells containing aggregates of tau at an early age and in neurites regardless of whether aggregates of tau are present. These deficits are exacerbated with age and completely recovered when soluble tau is reduced by transgene suppresion, even in the continued presence of aggregated tau, pointing to the importance of soluble tau in this process [99]. We also observed deficits in mitochondrial distribution in human AD tissue in both tangle and non-tangle bearing neurons in superior temporal gyrus [99]. Other groups have observed similar alterations to mitochondrial localization in human AD brain, with depletion of mitochondria from the dendritic tree and concomitant accumulation within the soma [80, 81].
Loss of proper transport processes leaves synapses depleted of mitochondria, which are essential for the high-energy demand and frequent calcium fluxes of normal synaptic function and could therefore contribute to synapse loss evident in AD [100]. With distribution deficits often comes mitochondrial dysfunction, with altered electron transport chain function and loss of ATP, damaged processing of reactive oxygen species, calcium buffering impairments and release of molecules leading to cell death signaling cascades [13, 77, 96, 101]. A study in cultured neurons demonstrated that over-expression of tau induces mitochondrial distribution deficits and concomitant dysfunction, but functional deficits only emerged when challenged with thapsigargin, which results in global increase in cytosolic calcium levels [102]. These data raise an interesting relationship between mitochondria and calcium homeostasis. In 2009, Wang and Schwarz proved that local elevations in calcium can arrest mitochondria along their transport route, serving as a mechanism of securing mitochondria where they are needed. In this reciprocal relationship, calcium influences mitochondrial localization and mitochondria play an influential role in regulating intracellular calcium homeostasis [44, 46, 93, 103, 104].
Calcium dysregulation is another potential mechanism downstream of pathological tau changes. Calcium signaling is thought to be critically important for learning and memory processes, and is known to be altered in human AD brain, with the calcium hypothesis first appearing in the late 1980s [13, 46, 103–106]. In concert with the prominence of the amyloid cascade hypothesis, much of the understanding of calcium changes in AD has been in relation to presence of Aβ. In-vitro studies have revealed that administration of Aβ can induce intracellular calcium increases that are associated with subsequent spine loss [14, 107]. It is thought that Aβ peptides can create holes within the plasma membrane, creating a non-specific cation channel, permitting calcium to pass through easily. Ion channel function can also be altered by Aβ presence, including those at synaptic sites such as NMDA and AMPA receptors, and within membranes of internal calcium stores such as at the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria [44, 103, 104, 108]. Studies in APP/PS1 mice that have altered Aβ production and develop plaque pathology show distinct calcium overload in neurites surrounding plaques in-vivo [109]. Much less is understood about calcium dynamics and homeostasis and tau, though recently calcium dysregulation has been proposed as another potential cellular mechanism upon which Aβ and tau toxicity may converge [2]. Electrophysiological studies in mice over-expressing a human mutant form of tau support a role for elevated calcium levels in pathology [56, 110]. Mutations of tau that lead to frontotemporal dementia have been shown to alter function of voltage gated calcium channels [45] and recent studies have placed physiological tau at the dendritic spine, as a crucial mediator of normal NMDA receptor stability and function [22, 30, 69]. Tackenberg & Brandt (2009) reported that blockade of NMDA receptor activity was sufficient to prevent tau toxicity. When tau is pathologically missorted in this scenario, the NMDA receptor is susceptible to damage or altered function. This may serve as a potential patho-mechanism in which tau contributes to Aβ toxicity [22–24, 26, 111]. Interestingly, one of the few FDA approved treatments currently prescribed for AD targets the NMDA receptor [1, 2, 32]. Other receptors have also been implicated, as extracellular application of tau to cells in culture has shown to elevate intracellular calcium levels, but purportedly through muscarinic receptors rather than NMDARs [74].
Evidence from in vivo multiphoton imaging studies suggests that in rTg4510 tau overexpressing mice, membrane integrity is disrupted in a small subset of neurons [112], which could cause disruptions in cellular calcium levels. This disruption is coincident with caspase activation, which precedes tangle formation, and both caspase activation and membrane disruption resolve after tangles form [112, 113], implicating soluble tau as toxic to membranes and potentially causative in disrupting calcium homeostasis. Normal cell function requires tight regulation of calcium dynamics, so disruption of these processes can have significant deleterious effects, including disrupted transport, altered signaling cascades, mitochondrial dysfunction, synaptic deficits and even cell death [104].
Dendritic spines and synapses are especially vulnerable to changes in either calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial distribution or function [44, 46, 75, 80, 82, 114, 115]. Synapse loss is the leading correlate to cognitive decline in AD [7, 8, 116], correlating more closely even than NFT [19–21], and yet the mechanism of synaptic degeneration in AD and other tauopathies is not clearly understood and rather controversial. Reports of synapse loss in tau models vary dramatically with some studies suggesting negligible or no spine loss [38, 60, 69, 88], others demonstrating significant synaptic deterioration [10, 14, 39, 49, 56, 67] and others still indicating increases in synapse density, potentially serving as a compensatory mechanism [89, 110, 111, 117]. Dysregulation of synaptic protein levels in homogenates from a number of tau mouse models have been demonstrated with or without associated synapse loss in the same model [39, 69, 92, 96]. Synapse loss and dysfunction are argued to precede neuronal loss and NFT accumulation with decreased expression of some, but not all, synaptic markers [69, 70]. These and other data argue that synaptic deficits occur in an NFT-independent manner, again making the case that soluble tau serves as the toxic entity [51, 52, 56, 70, 92, 118]. Kimura et al (2010) suggest that tau aggregates induce neuronal, but not synapse loss while hyperphosphorylated species of tau are associated with decreased expression of synaptic proteins. Work from the Mandelkow group, however, suggests that it is the amyloidogenicity of tau that induces spine loss, arguing that it is the aggregates that are detrimental to synapse density and function [35, 39, 48, 49].
Implications for therapeutic strategies
Given the considerable evidence for each argument in the debate of NFT versus soluble tau toxicity, it remains unclear which species of tau is truly the culprit. As a result, tau targeted therapeutics vary significantly in their targets and approaches. Inhibiting or reversing tau aggregation has been one of the most avidly pursued and more promising avenues of tau targeted therapies to date [1, 16]. Methylene blue, a member of the phenothiazine family used historically for treatment of other human diseases, has been shown to prevent tau aggregation in vitro [119] and progressed to phase II clinical trial in human AD patients with promising results [1, 2, 84, 120]. Several studies in mouse models of tauopathy have indicated that immunization with a late stage tau phospho-epitope can dramatically reduce tau aggregation and improve cognitive impairments [121–123], suggesting this may serve as a viable opportunity for clinical trial. Continued screens for other compounds that can reverse or inhibit tau aggregation have yielded several promising candidates including anthraquinones, n-phenylamines and rhodanines that have yet to be thoroughly evaluated [1, 16, 124]. However, it should be noted that if NFT are not the detrimental tau species, therapies targeted at decreasing their aggregation could in fact be contributing to disease pathogenesis if soluble tau levels are not also decreased by these treatments.
The predominant means by which it is thought that pathological changes in tau may disrupt axonal transport, is via destabilization of microtubules, leading to their disassembly [11, 29]. Based on this reasoning, microtubule stabilizing drugs have been suggested as therapeutic agents for AD, with one reaching clinical trial [1–3, 14, 84, 107]. Zempel et al (2010) demonstrated that application of taxol to cells in culture can allow for recovery of microtubule density, mitochondrial localization, missorting of tau and loss of spines, though calcium changes and hyperphosphorylation of tau persisted. Treatment of tau transgenic mice with microtubule stabilizer paclitaxel generated improved axonal transport and motor phenotype [16, 125, 126]. A peptide (NAPVSIPQ) with better blood brain barrier permeability but similar microtubule stabilizing capabilities yielded comparable results in mouse models [16, 127–129] and recently completed Phase II clinical trial with evidence of improved performance on several of the memory tasks [3, 130]. Though promising, unfortunately, microtubule stabilizers often have significant side effects and suffer from having poor blood brain barrier permeability, so other methods of influencing microtubule stability continue to be explored [15, 16].
Since aberrant tau phosphorylation is thought to be a crucial mediator of affinity of tau for microtubules and a critical step toward tau-induced toxicity, significant effort has been directed toward developing kinase inhibitors or phosphatase activators that can modulate this process. Lithium (LiCl), which is a GSK3β inhibitor used for treatment of human psychiatric conditions, has been linked to behavioral improvements in tau mice that are associated with decreased levels of insoluble and hyperphosphorylated tau. Similar findings resulted from treatment of tau mice with sodium selenate, but via a PP2A dependent mechanism leading to dephosphorylation of tau [1, 16]. Developing kinase inhibitors or phosphatase activators that are both selective and without significant side effects, however, is not trivial as they have many targets and are involved in many signaling cascades [16]. Other post-translational modifications of tau and tau degradation pathways have also been tested as preliminary targets for tau therapeutics [2, 16, 84], but stand much further from clinical trial. In addition, since tau reduction or elimination has been shown to ameliorate Aβ-induced toxicity [23–25] it is, therefore, now being pursued as a therapeutic mechanism [84]. To date, three tau-targeted therapeutics have reached clinical trial - kinase inhibitor LiCl, tau aggregation inhibitor methylene blue and microtubule stabilizer NAP [16, 84], yet the mechanism of tau toxicity continues to be clearly defined. With better understanding of the species of tau that is detrimental to neuronal function and morphology, and the manner in which it exerts its toxicity, comes a wealth of new potential therapeutic targets.
Based on the evidence that mitochondrial transport deficits caused by tau-induced transport failure may interfere with mitochondrial function, therapeutics targeting mitochondrial processes may prove advantageous. Antioxidants have long been mentioned as beneficial for potential prevention and treatment of AD [1, 2, 97]. Though unlikely to serve as a stand-alone cure, alleviating mitochondrial stress in conjunction with Aβ and tau therapies may prove useful. Similarly, calcium buffering or stabilizing compounds have also been suggested [47, 131]. It is via this mechanism that exercise is argued to benefit neuronal health, by increasing neurotrophic and neurogenic factors in the brain, which are efficient at stabilizing calcium changes [44, 47]. Further understanding of the newly proposed dendritic function of tau, both physiologically and pathologically, along with other lesser-known functions of tau may generate new, more effective, therapeutic targets [4, 18, 28, 29].
Conclusions and Future directions
The studies discussed here show that there is evidence for both soluble (hyperphosphorylated, misfolded, and mislocalized) and fibrillar tau contributing to neuronal and synaptic dysfunction and loss. On balance, there is very little direct evidence that tau fibrils themselves are toxic, thus we favor the hypothesis that soluble forms of tau are more toxic to neuronal function (mitochondrial trafficking, calcium regulation, etc) and synaptic function (electrophysiological deficits and dendritic spine loss) and ultimately contribute to synaptic and neuronal degeneration. In this model, we hypothesize that soluble forms of pathological tau induce neuronal transport deficits, synaptic dysfunction, caspase activation, and membrane disruptions, which may contribute to dying back of denervated processes and neuronal death. Formation of tangles may protect neurons acutely from the effects of toxic soluble tau, as seen in vivo by the caspase activation that precedes tangle formation that resolves after NFT form [112]. The strong evidence implicating soluble tau as toxic does not preclude a toxic role for NFT also. Long-term, further inhibition of cellular transport by NFT and neuropil threads acting as space-occupying lesions may lead to slower cell death, or NFT may reach “capacity” unable to further absorb soluble tau which continues to accumulate and causes cell death as outlined above. These NFT-bearing neurons may then then die more slowly leaving the ghost tangles observed in Alzheimer patient brains.
Future studies are needed to confirm these hypotheses about the toxicity of soluble vs fibrillar tau and the molecular mechanisms of toxicity. In vivo multiphoton imaging provides a powerful tool for addressing these issues of causality and temporal progression of disease. We have observed cell death over the course of days in YFPxrTg4510 mice occurring at a rate of approximately 2% per week (Figure 2) using cranial window implantation and multiphoton imaging of YFP as described previously [132]. This is similar to the 4.6% loss of yfp cells per month reported in living 3XTg mice that express mutant amyloid precursor protein, mutant tau, and mutant presenilin [10], but technical limitations have thus far prevented concurrently imaging whether NFT or hyperphosphorylated, misfolded tau are present in soma that are dying. Future studies may overcome this limitation by introduction of strong NFT labeling fluorophores by adsorption onto nanoparticles which can carry molecules across the blood-brain-barrier [133].
Figure 2.
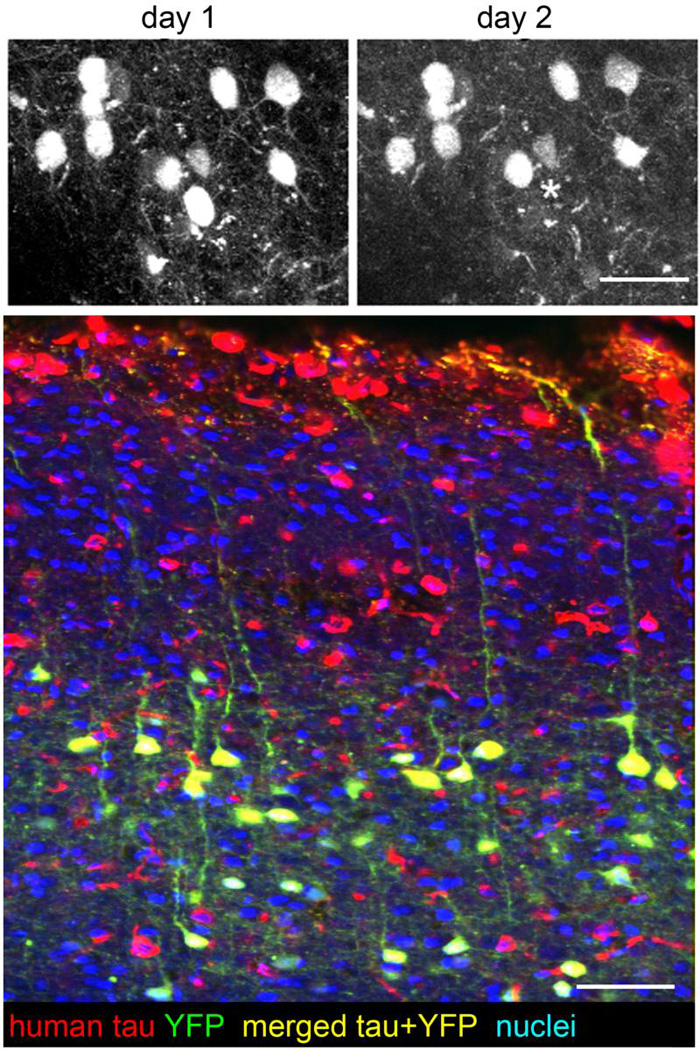
Cell death in tauopathy model mice. In vivo multiphoton imaging of neurons in mice expressing yellow fluorescent protein and P301L mutant tau (YFPxrTg4510 line) in pyramidal neurons undergo cell death (asterisk indicates a cell that died between one day and the next). Postmortem staining (bottom) confirms that YFP expressing neurons also express human tau in this model. Neuronal death is halted by transgene suppression in rTg4510 mice without removing existing tangles [54], and caspase activation, which occurs in neurons before NFT form, is turned off after tangle formation [113], both implicating soluble tau in cell death. However, the forms of tau present in dying neurons have not yet been elucidated. Scale bars 50 µm. Thanks to Rose Pitstick and George Carlson for mouse breeding and genotyping.
Taken together, these studies implicate soluble species of tau, rather than aggregates, as more detrimental to neuronal morphology and function. The idea that NFT may serve as a silent or potentially protective mechanism of sequestering soluble tau is supported by these studies. The presence of a tangle may indicate that the neuron has reached a threshold for soluble tau, initiating a compensatory mechanism that ultimately is unable to save the cell. These data also suggest that therapeutics aimed at preventing or reversing tau aggregation may, in fact, prove deleterious by increasing the concentration of toxic soluble tau species. Tau reduction mechanisms may prove a more promising avenue to pursue.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by National Institute of Health Grants AG08487, T32AG000277, AG026249, K99AG33670, P50AG05134 and the Alzheimer's Association Zenith Award. We thank Rose Pitstick and George Carlson at the McLaughlin Research Institute for animal breeding and genotyping.
References
- 1.Gotz J, Ittner A, Ittner LM. Tau-targeted treatment strategies in Alzheimer's disease. Br J Pharmacol. 2012;165:1246–1259. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Huang Y, Mucke L. Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell. 2012;148:1204–1222. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Selkoe DJ. Resolving controversies on the path to Alzheimer's therapeutics. Nat Med. 2011;17:1060–1065. doi: 10.1038/nm.2460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ittner LM, Gotz J. Amyloid-beta and tau--a toxic pas de deux in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12:65–72. doi: 10.1038/nrn2967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alzheimer A, Stelzmann RA, Schnitzlein HN, Murtagh FR. An English translation of Alzheimer's 1907 paper, "Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde". Clin Anat. 1995;8:429–431. doi: 10.1002/ca.980080612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Maurer K, Volk S, Gerbaldo H. Auguste D and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1997;349:1546–1549. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)10203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Coleman PD, Yao PJ. Synaptic slaughter in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24:1023–1027. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2003.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.DeKosky ST, Scheff SW, Styren SD. Structural correlates of cognition in dementia: quantification and assessment of synapse change. Neurodegeneration. 1996;5:417–421. doi: 10.1006/neur.1996.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, Butters N, DeTeresa R, Hill R, et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer's disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 1991;30:572–580. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bittner T, Fuhrmann M, Burgold S, Ochs SM, Hoffmann N, Mitteregger G, et al. Multiple events lead to dendritic spine loss in triple transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice. PLoS One. 2010;5:e15477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bretteville A, Planel E. Tau aggregates: toxic, inert, or protective species? J Alzheimers Dis. 2008;14:431–436. doi: 10.3233/jad-2008-14411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:741–766. doi: 10.1152/physrev.2001.81.2.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Swerdlow RH, Burns JM, Khan SM. The Alzheimer's disease mitochondrial cascade hypothesis. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20(Suppl 2):S265–S279. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-100339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zempel H, Thies E, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow EM. Abeta oligomers cause localized Ca(2+) elevation, missorting of endogenous Tau into dendrites, Tau phosphorylation, and destruction of microtubules and spines. J Neurosci. 2010;30:11938–11950. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2357-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Brunden KR, Ballatore C, Crowe A, Smith AB, 3rd, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-directed drug discovery for Alzheimer's disease and related tauopathies: a focus on tau assembly inhibitors. Exp Neurol. 2010;223:304–310. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.08.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brunden KR, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. Advances in tau-focused drug discovery for Alzheimer's disease and related tauopathies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:783–793. doi: 10.1038/nrd2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, Baker M, Froelich S, Houlden H, et al. Association of missense and 5'-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature. 1998;393:702–705. doi: 10.1038/31508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Spires-Jones TL, Stoothoff WH, de Calignon A, Jones PB, Hyman BT. Tau pathophysiology in neurodegeneration: a tangled issue. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32:150–159. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Arriagada PV, Growdon JH, Hedley-Whyte ET, Hyman BT. Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992;42:631–639. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.3.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Giannakopoulos P, Herrmann FR, Bussiere T, Bouras C, Kovari E, Perl DP, et al. Tangle and neuron numbers, but not amyloid load, predict cognitive status in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 2003;60:1495–1500. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000063311.58879.01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gomez-Isla T, Hollister R, West H, Mui S, Growdon JH, Petersen RC, et al. Neuronal loss correlates with but exceeds neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol. 1997;41:17–24. doi: 10.1002/ana.410410106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ittner LM, Ke YD, Delerue F, Bi M, Gladbach A, van Eersel J, et al. Dendritic function of tau mediates amyloid-beta toxicity in Alzheimer's disease mouse models. Cell. 2010;142:387–397. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Roberson ED, Halabisky B, Yoo JW, Yao J, Chin J, Yan F, et al. Amyloid-{beta}/Fyn-Induced Synaptic, Network, and Cognitive Impairments Depend on Tau Levels in Multiple Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease. J Neurosci. 2011;31:700–711. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4152-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Roberson ED, Scearce-Levie K, Palop JJ, Yan F, Cheng IH, Wu T, et al. Reducing endogenous tau ameliorates amyloid beta-induced deficits in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Science. 2007;316:750–754. doi: 10.1126/science.1141736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vossel KA, Zhang K, Brodbeck J, Daub AC, Sharma P, Finkbeiner S, et al. Tau reduction prevents Abeta-induced defects in axonal transport. Science. 2010;330:198. doi: 10.1126/science.1194653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yu W, Polepalli J, Wagh D, Rajadas J, Malenka R, Lu B. A critical role for the PAR-1/MARK-tau axis in mediating the toxic effects of Abeta on synapses and dendritic spines. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:1384–1390. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hyman BT. Amyloid-dependent and amyloid-independent stages of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2011;68:1062–1064. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gendron TF, Petrucelli L. The role of tau in neurodegeneration. Mol Neurodegener. 2009;4:13. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-4-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:663–672. doi: 10.1038/nrn2194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ittner A, Ke YD, van Eersel J, Gladbach A, Gotz J, Ittner LM. Brief update on different roles of tau in neurodegeneration. IUBMB life. 2011;63:495–502. doi: 10.1002/iub.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Avila J, Perez M, Lim F, Gomez-Ramos A, Hernandez F, Lucas JJ. Tau in neurodegenerative diseases: tau phosphorylation and assembly. Neurotoxicity research. 2004;6:477–482. doi: 10.1007/BF03033284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Alonso AC, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Alzheimer's disease hyperphosphorylated tau sequesters normal tau into tangles of filaments and disassembles microtubules. Nat Med. 1996;2:783–787. doi: 10.1038/nm0796-783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Alonso AC, Zaidi T, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Role of abnormally phosphorylated tau in the breakdown of microtubules in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:5562–5566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Iqbal K, Alonso Adel C, Grundke-Iqbal I. Cytosolic abnormally hyperphosphorylated tau but not paired helical filaments sequester normal MAPs and inhibit microtubule assembly. J Alzheimers Dis. 2008;14:365–370. doi: 10.3233/jad-2008-14402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Eckermann K, Mocanu MM, Khlistunova I, Biernat J, Nissen A, Hofmann A, et al. The beta-propensity of Tau determines aggregation and synaptic loss in inducible mouse models of tauopathy. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:31755–31765. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705282200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li X, Kumar Y, Zempel H, Mandelkow EM, Biernat J, Mandelkow E. Novel diffusion barrier for axonal retention of Tau in neurons and its failure in neurodegeneration. EMBO J. 2011;30:4825–4837. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Spires-Jones TL, Kopeikina KJ, Koffie RM, de Calignon A, Hyman BT. Are tangles as toxic as they look? J Mol Neurosci. 2011;45:438–444. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9566-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kimura T, Fukuda T, Sahara N, Yamashita S, Murayama M, Mizoroki T, et al. Aggregation of detergent-insoluble tau is involved in neuronal loss but not in synaptic loss. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:38692–38699. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.136630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mocanu MM, Nissen A, Eckermann K, Khlistunova I, Biernat J, Drexler D, et al. The potential for beta-structure in the repeat domain of tau protein determines aggregation, synaptic decay, neuronal loss, and coassembly with endogenous Tau in inducible mouse models of tauopathy. J Neurosci. 2008;28:737–748. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2824-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Takashima A. Hyperphosphorylated tau is a cause of neuronal dysfunction in tauopathy. J Alzheimers Dis. 2008;14:371–375. doi: 10.3233/jad-2008-14403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Brunden KR, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. Evidence that non-fibrillar tau causes pathology linked to neurodegeneration and behavioral impairments. J Alzheimers Dis. 2008;14:393–399. doi: 10.3233/jad-2008-14406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Braak H, Braak E. Staging of Alzheimer's disease-related neurofibrillary changes. Neurobiol Aging. 1995;16:271–278. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(95)00021-6. discussion 278–284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Braak H, Del Tredici K. Alzheimer's disease: pathogenesis and prevention. Alzheimers Dement. 2012;8:227–233. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bezprozvanny I, Mattson MP. Neuronal calcium mishandling and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci. 2008;31:454–463. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.06.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Furukawa K, Wang Y, Yao PJ, Fu W, Mattson MP, Itoyama Y, et al. Alteration in calcium channel properties is responsible for the neurotoxic action of a familial frontotemporal dementia tau mutation. J Neurochem. 2003;87:427–436. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mattson MP. Calcium and neurodegeneration. Aging Cell. 2007;6:337–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mattson MP, Chan SL. Neuronal and glial calcium signaling in Alzheimer's disease. Cell Calcium. 2003;34:385–397. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4160(03)00128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sydow A, Van der Jeugd A, Zheng F, Ahmed T, Balschun D, Petrova O, et al. Reversibility of Tau-related cognitive defects in a regulatable FTD mouse model. J Mol Neurosci. 2011;45:432–437. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9604-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sydow A, Van der Jeugd A, Zheng F, Ahmed T, Balschun D, Petrova O, et al. Tau-induced defects in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory are reversible in transgenic mice after switching off the toxic Tau mutant. J Neurosci. 2011;31:2511–2525. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5245-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Braak H, Braak E. Diagnostic criteria for neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18:S85–S88. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(97)00062-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Andorfer C, Acker CM, Kress Y, Hof PR, Duff K, Davies P. Cell-cycle reentry and cell death in transgenic mice expressing nonmutant human tau isoforms. J Neurosci. 2005;25:5446–5454. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4637-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Polydoro M, Acker CM, Duff K, Castillo PE, Davies P. Age-dependent impairment of cognitive and synaptic function in the htau mouse model of tau pathology. J Neurosci. 2009;29:10741–10749. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1065-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wittmann CW, Wszolek MF, Shulman JM, Salvaterra PM, Lewis J, Hutton M, et al. Tauopathy in Drosophila: neurodegeneration without neurofibrillary tangles. Science. 2001;293:711–714. doi: 10.1126/science.1062382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Santacruz K, Lewis J, Spires T, Paulson J, Kotilinek L, Ingelsson M, et al. Tau suppression in a neurodegenerative mouse model improves memory function. Science. 2005;309:476–481. doi: 10.1126/science.1113694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Spires TL, Orne JD, SantaCruz K, Pitstick R, Carlson GA, Ashe KH, et al. Region-specific dissociation of neuronal loss and neurofibrillary pathology in a mouse model of tauopathy. Am J Pathol. 2006;168:1598–1607. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.050840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rocher AB, Crimins JL, Amatrudo JM, Kinson MS, Todd-Brown MA, Lewis J, et al. Structural and functional changes in tau mutant mice neurons are not linked to the presence of NFTs. Exp Neurol. 2010;223:385–393. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.07.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fox LM, William CM, Adamowicz DH, Pitstick R, Carlson GA, Spires-Jones TL, et al. Soluble tau species, not neurofibrillary aggregates, disrupt neural system integration in a tau transgenic model. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2011;70:588–595. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e318220a658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.de Calignon AF LM, Pitstick R, Carlson GA, Bacskai BJ, Spires-Jones TL, Hyman BT. Caspase activation precedes and leads to tangles. Nature. 2010 doi: 10.1038/nature08890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Spires-Jones TL, de Calignon A, Matsui T, Zehr C, Pitstick R, Wu HY, et al. In vivo imaging reveals dissociation between caspase activation and acute neuronal death in tangle-bearing neurons. J Neurosci. 2008;28:862–867. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3072-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Shahani N, Subramaniam S, Wolf T, Tackenberg C, Brandt R. Tau aggregation and progressive neuronal degeneration in the absence of changes in spine density and morphology after targeted expression of Alzheimer's disease-relevant tau constructs in organotypic hippocampal slices. J Neurosci. 2006;26:6103–6114. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4245-05.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Baas PW, Qiang L. Neuronal microtubules: when the MAP is the roadblock. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:183–187. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2005.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Dixit R, Ross JL, Goldman YE, Holzbaur EL. Differential regulation of dynein and kinesin motor proteins by tau. Science. 2008;319:1086–1089. doi: 10.1126/science.1152993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Dubey M, Chaudhury P, Kabiru H, Shea TB. Tau inhibits anterograde axonal transport and perturbs stability in growing axonal neurites in part by displacing kinesin cargo: neurofilaments attenuate tau-mediated neurite instability. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2008;65:89–99. doi: 10.1002/cm.20243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ebneth A, Godemann R, Stamer K, Illenberger S, Trinczek B, Mandelkow E. Overexpression of tau protein inhibits kinesin-dependent trafficking of vesicles, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum: implications for Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Biol. 1998;143:777–794. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Stamer K, Vogel R, Thies E, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow EM. Tau blocks traffic of organelles, neurofilaments, and APP vesicles in neurons and enhances oxidative stress. J Cell Biol. 2002;156:1051–1063. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200108057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Stoothoff W, Jones PB, Spires-Jones TL, Joyner D, Chhabra E, Bercury K, et al. Differential effect of three-repeat and four-repeat tau on mitochondrial axonal transport. J Neurochem. 2009;111:417–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Thies E, Mandelkow EM. Missorting of tau in neurons causes degeneration of synapses that can be rescued by the kinase MARK2/Par-1. J Neurosci. 2007;27:2896–2907. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4674-06.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Berger Z, Roder H, Hanna A, Carlson A, Rangachari V, Yue M, et al. Accumulation of pathological tau species and memory loss in a conditional model of tauopathy. J Neurosci. 2007;27:3650–3662. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0587-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Hoover BR, Reed MN, Su J, Penrod RD, Kotilinek LA, Grant MK, et al. Tau mislocalization to dendritic spines mediates synaptic dysfunction independently of neurodegeneration. Neuron. 2010;68:1067–1081. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Yoshiyama Y, Higuchi M, Zhang B, Huang SM, Iwata N, Saido TC, et al. Synapse loss and microglial activation precede tangles in a P301S tauopathy mouse model. Neuron. 2007;53:337–351. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Clavaguera F, Bolmont T, Crowther RA, Abramowski D, Frank S, Probst A, et al. Transmission and spreading of tauopathy in transgenic mouse brain. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:909–913. doi: 10.1038/ncb1901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.de Calignon A, Polydoro M, Suarez-Calvet M, William C, Adamowicz DH, Kopeikina KJ, et al. Propagation of tau pathology in a model of early Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 2012;73:685–697. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Frost B, Jacks RL, Diamond MI. Propagation of tau misfolding from the outside to the inside of a cell. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:12845–12852. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808759200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Gomez-Ramos A, Diaz-Hernandez M, Rubio A, Miras-Portugal MT, Avila J. Extracellular tau promotes intracellular calcium increase through M1 and M3 muscarinic receptors in neuronal cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;37:673–681. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2007.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hollenbeck PJ, Saxton WM. The axonal transport of mitochondria. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:5411–5419. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Wang X, Schwarz TL. The mechanism of Ca2+ -dependent regulation of kinesin-mediated mitochondrial motility. Cell. 2009;136:163–174. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lin MT, Beal MF. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature. 2006;443:787–795. doi: 10.1038/nature05292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Morfini GA, Burns M, Binder LI, Kanaan NM, LaPointe N, Bosco DA, et al. Axonal transport defects in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurosci. 2009;29:12776–12786. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3463-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:329–344. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0909142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Wang X, Su B, Lee HG, Li X, Perry G, Smith MA, et al. Impaired balance of mitochondrial fission and fusion in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 2009;29:9090–9103. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1357-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Wang X, Su B, Zheng L, Perry G, Smith MA, Zhu X. The role of abnormal mitochondrial dynamics in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 2009;109(Suppl 1):153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Westermann B. Mitochondrial fusion and fission in cell life and death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:872–884. doi: 10.1038/nrm3013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Yuan A, Kumar A, Peterhoff C, Duff K, Nixon RA. Axonal transport rates in vivo are unaffected by tau deletion or overexpression in mice. J Neurosci. 2008;28:1682–1687. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5242-07.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Morris M, Maeda S, Vossel K, Mucke L. The many faces of tau. Neuron. 2011;70:410–426. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.LaPointe NE, Morfini G, Pigino G, Gaisina IN, Kozikowski AP, Binder LI, et al. The amino terminus of tau inhibits kinesin-dependent axonal transport: implications for filament toxicity. J Neurosci Res. 2009;87:440–451. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Muresan V, Muresan Z. Is abnormal axonal transport a cause, a contributing factor or a consequence of the neuronal pathology in Alzheimer's disease? Future Neurol. 2009;4:761–773. doi: 10.2217/fnl.09.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Ittner LM, Ke YD, Gotz J. Phosphorylated Tau interacts with c-Jun N-terminal kinase-interacting protein 1 (JIP1) in Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:20909–20916. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Tackenberg C, Brandt R. Divergent pathways mediate spine alterations and cell death induced by amyloid-beta, wild-type tau, and R406W tau. J Neurosci. 2009;29:14439–14450. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3590-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Amadoro G, Corsetti V, Stringaro A, Colone M, D'Aguanno S, Meli G, et al. A NH2 tau fragment targets neuronal mitochondria at AD synapses: possible implications for neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;21:445–470. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-100120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Bobba A, Petragallo VA, Marra E, Atlante A. Alzheimer's proteins, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction interplay in a neuronal model of Alzheimer's disease. Int J Alzheimers Dis. 2010 doi: 10.4061/2010/621870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Decker H, Lo KY, Unger SM, Ferreira ST, Silverman MA. Amyloid-beta peptide oligomers disrupt axonal transport through an NMDA receptor-dependent mechanism that is mediated by glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in primary cultured hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 2010;30:9166–9171. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1074-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Lasagna-Reeves CA, Castillo-Carranza DL, Sengupta U, Clos AL, Jackson GR, Kayed R. Tau oligomers impair memory and induce synaptic and mitochondrial dysfunction in wild-type mice. Mol Neurodegener. 2011;6:39. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-6-39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Sheng ZH, Cai Q. Mitochondrial transport in neurons: impact on synaptic homeostasis and neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13:77–93. doi: 10.1038/nrn3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Chen H, Chan DC. Mitochondrial dynamics--fusion, fission, movement, and mitophagy--in neurodegenerative diseases. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:R169–R176. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Gibson GE, Starkov A, Blass JP, Ratan RR, Beal MF. Cause and consequence: mitochondrial dysfunction initiates and propagates neuronal dysfunction, neuronal death and behavioral abnormalities in age-associated neurodegenerative diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1802:122–134. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.08.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.David DC, Hauptmann S, Scherping I, Schuessel K, Keil U, Rizzu P, et al. Proteomic and functional analyses reveal a mitochondrial dysfunction in P301L tau transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:23802–23814. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500356200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Eckert A, Schulz KL, Rhein V, Gotz J. Convergence of amyloid-beta and tau pathologies on mitochondria in vivo. Mol Neurobiol. 2010;41:107–114. doi: 10.1007/s12035-010-8109-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Mandelkow EM, Thies E, Trinczek B, Biernat J, Mandelkow E. MARK/PAR1 kinase is a regulator of microtubule-dependent transport in axons. J Cell Biol. 2004;167:99–110. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200401085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Kopeikina KJ, Carlson GA, Pitstick R, Ludvigson AE, Peters A, Luebke JI, et al. Tau Accumulation Causes Mitochondrial Distribution Deficits in Neurons in a Mouse Model of Tauopathy and in Human AD Brain. Am J Pathol. 2011 doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Du H, Guo L, Yan S, Sosunov AA, McKhann GM, Yan SS. Early deficits in synaptic mitochondria in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:18670–18675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006586107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.D'Amelio M, Cavallucci V, Middei S, Marchetti C, Pacioni S, Ferri A, et al. Caspase-3 triggers early synaptic dysfunction in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14:69–76. doi: 10.1038/nn.2709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Quintanilla RA, Matthews-Roberson TA, Dolan PJ, Johnson GV. Caspase-cleaved tau expression induces mitochondrial dysfunction in immortalized cortical neurons: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:18754–18766. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808908200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Berridge MJ. Calcium signalling and Alzheimer's disease. Neurochem Res. 2011;36:1149–1156. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Chakroborty S, Stutzmann GE. Early calcium dysregulation in Alzheimer's disease: setting the stage for synaptic dysfunction. Sci China Life Sci. 2011;54:752–762. doi: 10.1007/s11427-011-4205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Khachaturian ZS. Calcium hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease and brain aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;747:1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb44398.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Sabatini BL, Maravall M, Svoboda K. Ca(2+) signaling in dendritic spines. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2001;11:349–356. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(00)00218-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Zempel H, Mandelkow EM. Linking amyloid-beta and tau: amyloid-beta induced synaptic dysfunction via local wreckage of the neuronal cytoskeleton. Neurodegener Dis. 2011;10:64–72. doi: 10.1159/000332816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Hermes M, Eichhoff G, Garaschuk O. Intracellular calcium signalling in Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14:30–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Kuchibhotla KV, Goldman ST, Lattarulo CR, Wu HY, Hyman BT, Bacskai BJ. Abeta plaques lead to aberrant regulation of calcium homeostasis in vivo resulting in structural and functional disruption of neuronal networks. Neuron. 2008;59:214–225. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.06.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Crimins JL, Rocher AB, Peters A, Shultz P, Lewis J, Luebke JI. Homeostatic responses by surviving cortical pyramidal cells in neurodegenerative tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2011;122:551–564. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0877-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Kremer A, Maurin H, Demedts D, Devijver H, Borghgraef P, Van Leuven F. Early improved and late defective cognition is reflected by dendritic spines in Tau.P301L mice. J Neurosci. 2011;31:18036–18047. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4859-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.de Calignon A, Spires-Jones TL, Pitstick R, Carlson GA, Hyman BT. Tangle-bearing neurons survive despite disruption of membrane integrity in a mouse model of tauopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009;68:757–761. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181a9fc66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.de Calignon A, Fox LM, Pitstick R, Carlson GA, Bacskai BJ, Spires-Jones TL, et al. Caspase activation precedes and leads to tangles. Nature. 2010;464:1201–1204. doi: 10.1038/nature08890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Reddy PH, Reddy TP, Manczak M, Calkins MJ, Shirendeb U, Mao P. Dynamin-related protein 1 and mitochondrial fragmentation in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev. 2010 doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2010.11.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Verstreken P, Ly CV, Venken KJ, Koh TW, Zhou Y, Bellen HJ. Synaptic mitochondria are critical for mobilization of reserve pool vesicles at Drosophila neuromuscular junctions. Neuron. 2005;47:365–378. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease is a synaptic failure. Science. 2002;298:789–791. doi: 10.1126/science.1074069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Dickstein DL, Brautigam H, Stockton SD, Jr, Schmeidler J, Hof PR. Changes in dendritic complexity and spine morphology in transgenic mice expressing human wild-type tau. Brain Struct Funct. 2010;214:161–179. doi: 10.1007/s00429-010-0245-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Lasagna-Reeves CA, Castillo-Carranza DL, Guerrero-Muoz MJ, Jackson GR, Kayed R. Preparation and characterization of neurotoxic tau oligomers. Biochemistry. 2010;49:10039–10041. doi: 10.1021/bi1016233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Medina DX, Caccamo A, Oddo S. Methylene blue reduces abeta levels and rescues early cognitive deficit by increasing proteasome activity. Brain Pathol. 2011;21:140–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2010.00430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Wischik C, Staff R. Challenges in the conduct of disease-modifying trials in AD: practical experience from a phase 2 trial of Tau-aggregation inhibitor therapy. J Nutr Health Aging. 2009;13:367–369. doi: 10.1007/s12603-009-0046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Asuni AA, Boutajangout A, Quartermain D, Sigurdsson EM. Immunotherapy targeting pathological tau conformers in a tangle mouse model reduces brain pathology with associated functional improvements. J Neurosci. 2007;27:9115–9129. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2361-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Bi M, Ittner A, Ke YD, Gotz J, Ittner LM. Tau-targeted immunization impedes progression of neurofibrillary histopathology in aged P301L tau transgenic mice. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26860. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Boutajangout A, Quartermain D, Sigurdsson EM. Immunotherapy targeting pathological tau prevents cognitive decline in a new tangle mouse model. J Neurosci. 2010;30:16559–16566. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4363-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Bulic B, Pickhardt M, Khlistunova I, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E, et al. Rhodanine-based tau aggregation inhibitors in cell models of tauopathy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007;46:9215–9219. doi: 10.1002/anie.200704051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Ishihara T, Hong M, Zhang B, Nakagawa Y, Lee MK, Trojanowski JQ, et al. Age-dependent emergence and progression of a tauopathy in transgenic mice overexpressing the shortest human tau isoform. Neuron. 1999;24:751–762. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)81127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Zhang B, Maiti A, Shively S, Lakhani F, McDonald-Jones G, Bruce J, et al. Microtubule-binding drugs offset tau sequestration by stabilizing microtubules and reversing fast axonal transport deficits in a tauopathy model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:227–231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406361102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Gozes I, Divinski I. The femtomolar-acting NAP interacts with microtubules: Novel aspects of astrocyte protection. J Alzheimers Dis. 2004;6:S37–S41. doi: 10.3233/jad-2004-6s605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Matsuoka Y, Gray AJ, Hirata-Fukae C, Minami SS, Waterhouse EG, Mattson MP, et al. Intranasal NAP administration reduces accumulation of amyloid peptide and tau hyperphosphorylation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease at early pathological stage. J Mol Neurosci. 2007;31:165–170. doi: 10.1385/jmn/31:02:165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Matsuoka Y, Jouroukhin Y, Gray AJ, Ma L, Hirata-Fukae C, Li HF, et al. A neuronal microtubule-interacting agent, NAPVSIPQ, reduces tau pathology and enhances cognitive function in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;325:146–153. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.130526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Gozes I, Stewart A, Morimoto B, Fox A, Sutherland K, Schmeche D. Addressing Alzheimer's disease tangles: from NAP to AL-108. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2009;6:455–460. doi: 10.2174/156720509789207895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Green KN. Calcium in the initiation, progression and as an effector of Alzheimer's disease pathology. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13:2787–2799. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00861.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Meyer-Luehmann M, Spires-Jones TL, Prada C, Garcia-Alloza M, de Calignon A, Rozkalne A, et al. Rapid appearance and local toxicity of amyloid-beta plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 2008;451:720–724. doi: 10.1038/nature06616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Koffie RM, Farrar CT, Saidi LJ, William CM, Hyman BT, Spires-Jones TL. Nanoparticles enhance brain delivery of blood-brain barrier-impermeable probes for in vivo optical and magnetic resonance imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:18837–18842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1111405108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]