Abstract
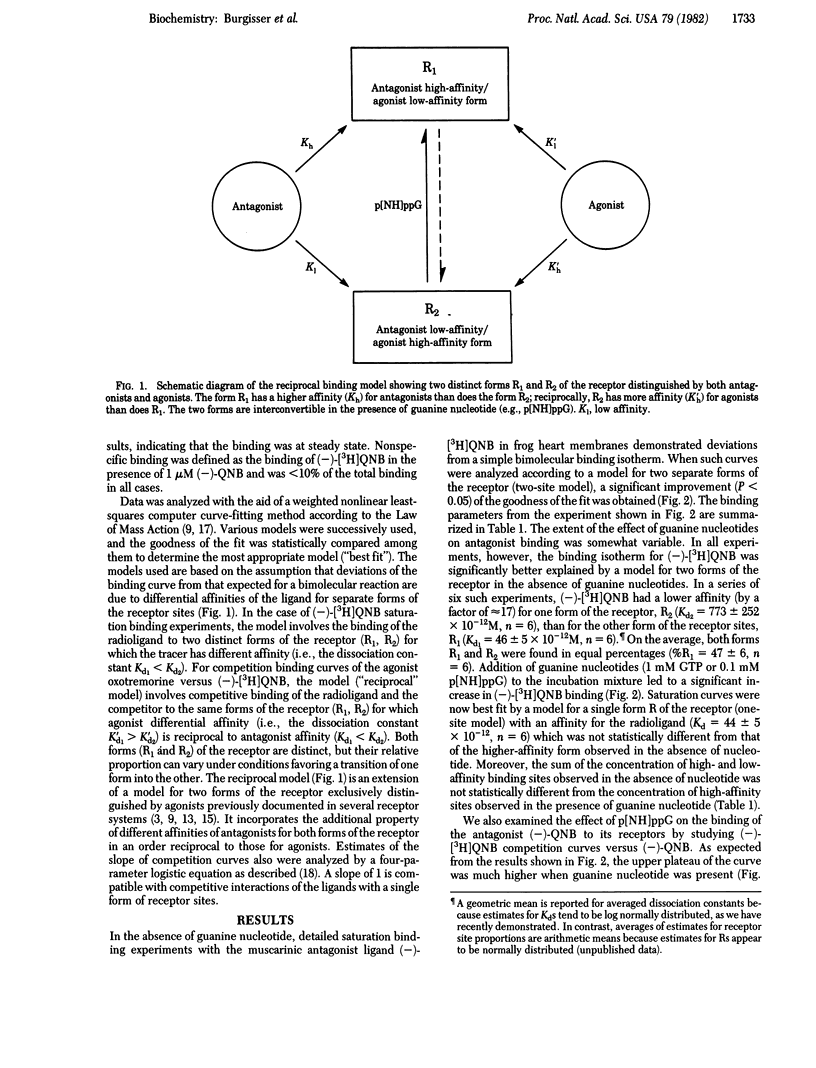
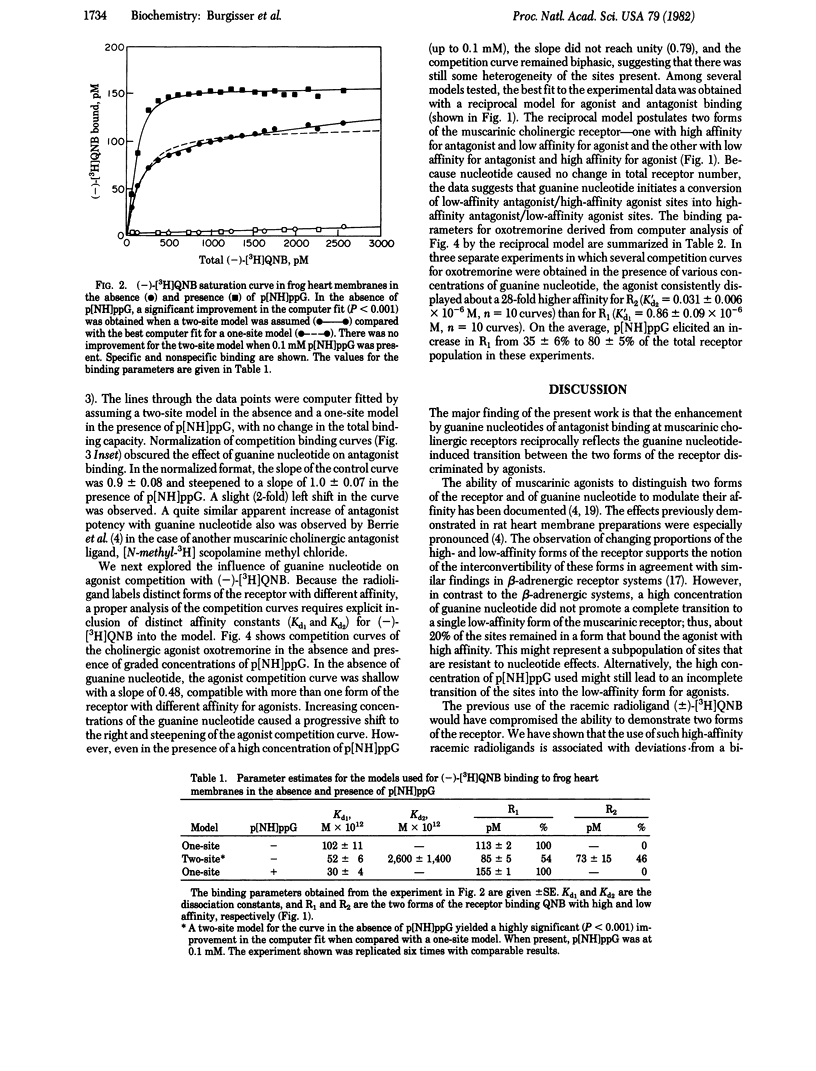
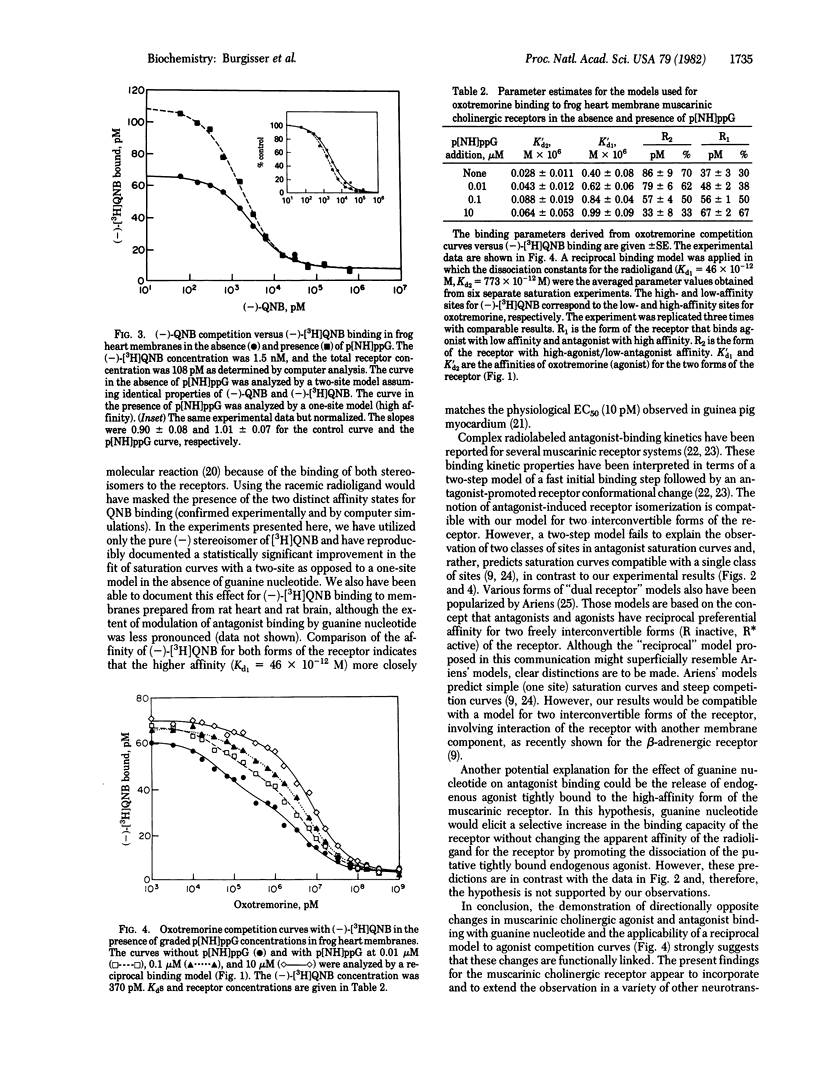
The ability of guanine nucleotide to decrease the binding affinity of agonists but not antagonists has been documented in a number of hormone and neurotransmitter receptor systems. By contrast, recent reports indicate that both agonist and antagonist binding to the muscarinic cholinergic receptors appear to be regulated in a reciprocal fashion by guanine nucleotide. We document two forms of the muscarinic cholinergic receptor in frog heart, which are present in approximately equal proportions and which display high-agonist/low antagonist and low-agonist/high-antagonist affinities, respectively. Guanine nucleotide appears to convert the former type of site into the latter type. These observations can be interpreted in terms of a model for two interconvertible forms of the muscarinic cholinergic receptor reciprocally favored by agonists and antagonists. This model has implications both for the understanding of neurotransmitter-receptor interactions generally and for the nature of the biological effects of receptor antagonists.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berrie C. P., Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. Guanine nucleotides modulate muscarinic receptor binding in the heart. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 27;87(4):1000–1005. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(79)80006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. The binding of agonists to brain muscarinic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1978 Sep;14(5):723–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürgisser E., Hancock A. A., Lefkowitz R. J., De Lean A. Anomalous equilibrium binding properties of high-affinity racemic radioligands. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 Mar;19(2):205–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. R., Snyder S. H. Differential regulation by guanine nucleotides or opiate agonist and antagonist receptor interactions. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):583–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Stadel J. M., Lefkowitz R. J. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7108–7117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlert F. J., Roeske W. R., Yamamura H. I. Muscarinic receptor: regulation by guanine nucleotides, ions, and N-ethylmaleimide. Fed Proc. 1981 Feb;40(2):153–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlert F. J., Roeske W. R., Yamamura H. I. Regulation of muscarinic receptor binding by guanine nucleotides and N-ethylmaleimide. J Supramol Struct. 1980;14(2):149–162. doi: 10.1002/jss.400140204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlert F. J., Roeske W. R., Yamamura H. I. Striatal muscarinic receptors: regulation by dopaminergic agonists. Life Sci. 1981 May 21;28(21):2441–2448. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90512-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F. Pharmacological characterization of receptors: its relation to radioligand-binding studies. Fed Proc. 1978 Feb;37(2):115–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galper J. B., Klein W., Catterall W. A. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in developing chick heart. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8692–8699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent R. S., De Lean A., Lefkowitz R. J. A quantitative analysis of beta-adrenergic receptor interactions: resolution of high and low affinity states of the receptor by computer modeling of ligand binding data. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;17(1):14–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein W. L. Multiple binding states of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in membranes from neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1058–1066. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90596-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., De Lean A., Hoffman B. B., Stadel J. M., Kent R., Michel T., Limbird L. Molecular pharmacology of adenylate cyclase-coupled alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;14:145–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Mullikin D., Caron M. G. Regulation of beta-adrenergic receptors by guanyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate and other purine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4686–4692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Gill D. M., Stadel J. M., Hickey A. R., Lefkowitz R. J. Loss of beta-adrenergic receptor-guanine nucleotide regulatory protein interactions accompanies decline in catecholamine responsiveness of adenylate cyclase in maturing rat erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1854–1861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Van Arsdale P. M., Gilman A. G. An agonist-specific effect of guanine nucleotides on binding to the beta adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;12(2):335–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirro M. J., Manalan A. S., Bailey J. C., Watanabe A. M. Anticholinergic effects of disopyramide and quinidine on guinea pig myocardium. Mediation by direct muscarinic receptor blockade. Circ Res. 1980 Dec;47(6):855–865. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.6.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee C., Caron M. G., Coverstone M., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification of adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptors in frog erythrocytes with (minus)-[3-H] alprenolol. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):4869–4876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger L. B., Roeske W. R., Yamamura H. I. The regulation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors by guanine nucleotides in cardiac tissue. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Jun;56(1-2):179–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90451-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai B. S., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-specific effects of guanine nucleotides on alpha-adrenergic receptors in human platelets. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):61–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahniser N. R., Molinoff P. B. Effect of guanine nucleotides on striatal dopamine receptors. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):453–455. doi: 10.1038/275453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


