Abstract
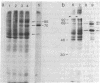
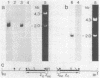
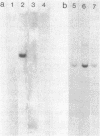
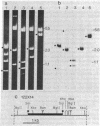
Xenopus cells, like many other eukaryotic cells, respond to heat treatments by increasing the rate of synthesis of a few characteristic proteins, the heat shock proteins. Because of the generality of this response, it seemed possible to examine the expression of isolated heat shock genes in a heterologous system. Phage 122 DNA, containing two identical genes coding for the Drosophila 70,000-dalton heat shock protein (hsp70 genes), was microinjected into Xenopus oocyte nuclei. The Drosophila hsp70 genes are transcribed efficiently in heat-treated oocytes (35-37 degrees C) to give RNA of the correct size and sequence content. Transcription is sensitive to low levels of alpha-amanitin and therefore is carried out by RNA polymerase II. At normal temperatures (20-28 degrees C) essentially no Drosophila-specific RNA is formed. The isolated insert fragment of phage 122 also gives RNA of correct length in heat-treated oocytes which hybridizes to the coding segment of Drosophila hsp70 genes only. At normal temperatures, however, its rate of transcription is variable and only RNA heterogeneous in size is formed.
Full text
PDF


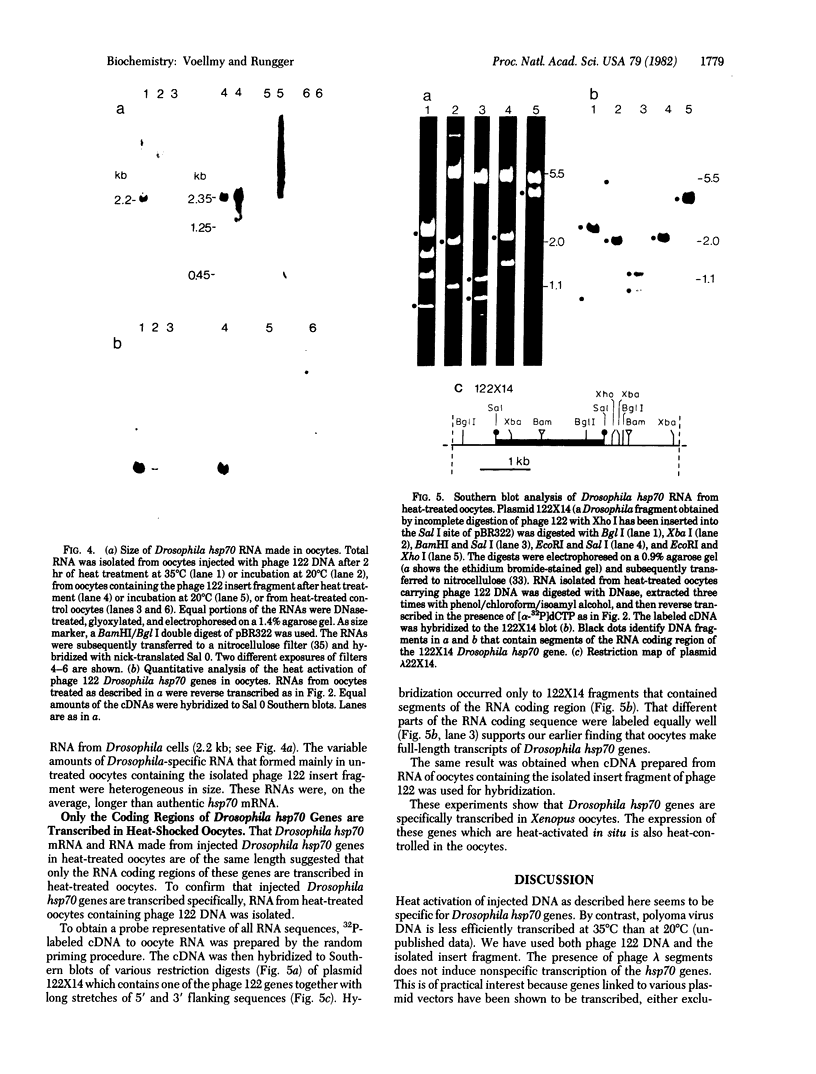

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Schedl P., Mirault M. E., Moran L., Lis J. Genes for the 70,000 dalton heat shock protein in two cloned D. melanogaster DNA segments. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J., Wadsworth S. C. Sequence organization of two recombinant plasmids containing genes for the major heat shock-induced protein of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):575–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Bromley P. A., Spahr P. F. Extensive in vitro transcription of rous sarcoma virus RNA by avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase and concurrent activation of the associated RNase H. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):659–668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.659-668.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Mertz J. E. Coupled transcription-translation of DNA injected into Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppig J. J., Steckman M. L. Comparison of exogenous energy sources for in vitro maintenance of follicle cell-free Xenopus laevis oocytes. In Vitro. 1976 Mar;12(3):173–179. doi: 10.1007/BF02796439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M. Two genes for the major heat-shock protein of Drosophila melanogaster arranged as an inverted repeat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 25;8(2):235–252. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman S. D., Glover C. V., Allis C. D., Gorovsky M. A. Heat shock, deciliation and release from anoxia induce the synthesis of the same set of polypeptides in starved T. pyriformis. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90177-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett R. W., Lis J. T. DNA sequence analysis reveals extensive homologies of regions preceding hsp70 and alphabeta heat shock genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A., McCarthy B. J. Sequence of three copies of the gene for the major Drosophila heat shock induced protein and their flanking regions. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):669–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90430-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karch F., Török I., Tissières A. Extensive regions of homology in front of the two hsp70 heat shock variant genes in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues and heat shock on gene expression in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Clarkson S. G., Telford J. L., Birnstiel M. L. Transcription of xenopus tDNAmet1 and sea urchin histone DNA injected into the Xenopus oocyte nucleus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1077–1082. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüger C., Benecke B. J. In vitro translation of Drosophila heat-shock and non--heat-shock mRNAs in heterologous and homologous cell-free systems. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):595–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90155-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson W., Oppermann H., Jackson J. Transition series metals and sulfhydryl reagents induce the synthesis of four proteins in eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;606(1):170–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livak K. J., Freund R., Schweber M., Wensink P. C., Meselson M. Sequence organization and transcription at two heat shock loci in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5613–5617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Schedl P. Organization of the multiple genes for the 70,000-dalton heat-shock protein in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5254–5258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst E., Kressmann A., Birnstiel M. L. Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):709–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Huber J. P., Türler H. SV40 DNA injected into Xenopus oocyte nuclei is transcribed by RNA polymerase B. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1979 Mar;3(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(79)90125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rungger D., Türler H. DNAs of simian virus 40 and polyoma direct the synthesis of viral tumor antigens and capsid proteins in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6073–6077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl P., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Steward R., Gehring W. J., Mirault M. E., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Moran L., Tissières A. Two hybrid plasmids with D. melanogaster DNA sequences complementary to mRNA coding for the major heat shock protein. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):921–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90346-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Scott M. P., Rich A., Pardue M. L. Translational control of protein synthesis in response to heat shock in D. melanogaster cells. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90559-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török I., Karch F. Nucleotide sequences of heat shock activated genes in Drosophila melanogaster. I. Sequences in the regions of the 5' and 3' ends of the hsp 70 gene in the hybrid plasmid 56H8. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 25;8(14):3105–3123. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.14.3105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Gomer R. H., Lazarides E. Heat shock proteins are methylated in avian and mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. P., Woo S., O'Malley B. W., Gurdon J. B. Expression of a chicken chromosomal ovalbumin gene injected into frog oocyte nuclei. Nature. 1980 Jun 26;285(5767):628–634. doi: 10.1038/285628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Laskey R. A., Finch J., Gurdon J. B. Selective DNA conservation and chromatin assembly after injection of SV40 DNA into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 May;64(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zentgraf H., Trendelenburg M. F., Spring H., Scheer U., Franke W. W., Müller U., Drury K. C., Rungger D. Mitochondrial DNA arranged into chromatin-like structures after injection into amphibian oocyte nuclei. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Sep;122(2):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]