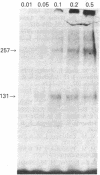
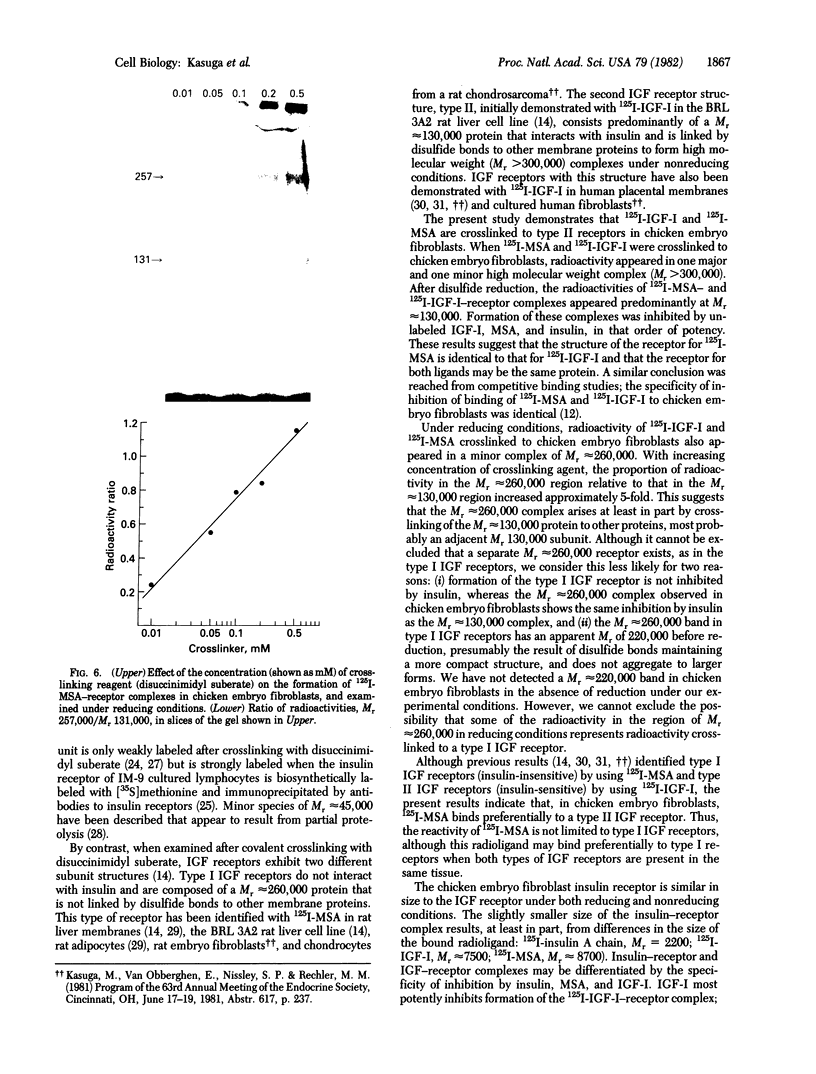
Abstract
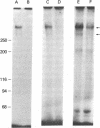
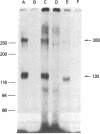
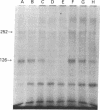
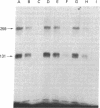
The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and insulin stimulate DNA synthesis and cell multiplication in chicken embryo fibroblasts in culture. This response appears to be mediated by interaction with a single type of IGF receptor. The present study examines the subunit structure of this receptor by covalently crosslinking two 125I-labeled IGFs, IGF-I and multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA), to chicken embryo fibroblasts by using disuccinimidyl suberate. After solubilization, NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and autoradiography, IGF receptor complexes of appropriate specificity were identified; they had Mr approximately 130,000 (major band) and approximately 260,000 (minor band) under reducing conditions and Mr greater than 300,000 without disulfide reduction. The proportion of the Mr 260,000 component increased with increasing concentration of crosslinking agent, suggesting that it was formed from smaller proteins during the crosslinking procedure. The IGF receptor in chicken embryo fibroblasts resembles the insulin receptor in size and structure but can be distinguished by a higher affinity for IGF-I and MSA than for insulin. Although IGF receptors with different structure and specificity have been recognized in other tissues, the function of these binding sites is unknown. The present study demonstrates that the IGF receptor of chicken embryo fibroblasts that appears to mediate the growth-promoting effects of the IGFs contains a Mr approximately 130,000 binding subunit and exists as a native receptor complex of Mr greater than 300,000.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bala R. M., Bhaumick B. Purification of a basic somatomedin, from human plasma Cohn fraction IV-1, with physicochemical and radioimmunoassay similarity to somatomedin-C and insulin-like growth factor. Can J Biochem. 1979 Nov;57(11):1289–1298. doi: 10.1139/o79-172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhaumick B., Bala R. M., Hollenberg M. D. Somatomedin receptor of human placenta: solubilization, photolabeling, partial purification, and comparison with insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4279–4283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernausek S. D., Jacobs S., Van Wyk J. J. Structural similarities between human receptors for somatomedin C and insulin: analysis by affinity labeling. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7345–7350. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughaday W. H., Mariz I. K., Trivedi B. A preferential binding site for insulin-like growth factor II in human and rat placental membranes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Aug;53(2):282–288. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-2-282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: structure and function. Endocr Rev. 1981 Summer;2(3):251–263. doi: 10.1210/edrv-2-3-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Hazum E., Shechter Y., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin receptor: covalent labeling and identification of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4918–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Van Obberghen E., Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Demonstration of two subtypes of insulin-like growth factor receptors by affinity cross-linking. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5305–5308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., van Obberghen E., Yamada K. M., Harrison L. C. Autoantibodies against the insulin receptor recognize the insulin binding subunits of an oligomeric receptor. Diabetes. 1981 Apr;30(4):354–357. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.4.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Todaro G. J., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Purification and primary structure of a polypeptide with multiplication-stimulating activity from rat liver cell cultures. Homology with human insulin-like growth factor II. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6859–6865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Guillette B. J., Czech M. P. Affinity labeling of multiplication stimulating activity receptors in membranes from rat and human tissues. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2122–2125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. A unique proteolytic cleavage site on the beta subunit of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3182–3190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Electrophoretic resolution of three major insulin receptor structures with unique subunit stoichiometries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7137–7141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M., Moses A. C., Short P. A., Podskalny J. M. Proinsulin binds to a growth peptide receptor and stimulates DNA synthesis in chick embryo fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1977 Sep;101(3):708–716. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-3-708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissley S. P., Rechler M. M. Multiplication-stimulating activity (MSA): a somatomedin-like polypeptide from cultured rat liver cells. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1978 May;(48):167–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. The subunit structure of the high affinity insulin receptor. Evidence for a disulfide-linked receptor complex in fat cell and liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1722–1731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Fryklund L., Nissley S., Hall K., Podskalny J. M., Skottner A., Moses A. C. Purified human somatomedin A and rat multiplication stimulating activity. Mitogens for cultured fibroblasts that cross-react with the same growth peptide receptors. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jan 2;82(1):5–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb11991.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Nissley S. P., King G. L., Moses A. C., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Romanus J. A., Knight A. B., Short P. A., White R. M. Multiplication stimulating activity (MSA) from the BRL 3A rat liver cell line: relation to human somatomedins and insulin. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;15(3):253–286. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380150305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Nissley S. P. Characterization of the binding of multiplication-stimulating activity to a receptor for growth polypeptides in chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3898–3910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Nissley S. P. Interaction of multiplication-stimulating activity with chick embryo fibroblasts demonstrates a growth receptor. Nature. 1976 Jan 15;259(5539):134–136. doi: 10.1038/259134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Zapf J., Nissley S. P., Froesch E. R., Moses A. C., Podskalny J. M., Schilling E. E., Humbel R. E. Interactions of insulin-like growth factors I and II and multiplication-stimulating activity with receptors and serum carrier proteins. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1451–1459. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel T. W., Ganguly S., Jacobs S., Rosen O. M., Rubin C. S. Purification and properties of the human placental insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9266–9273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Temin H. M. Purified multiplication-stimulating activity from rat liver cell conditioned medium: comparison of biological activities with calf serum, insulin, and somatomedin. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):181–192. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Klapper D. G., Fellows R. E., Grissom F. E., Schlueter R. J. Purification of somatomedin-C from human plasma: chemical and biological properties, partial sequence analysis, and relationship to other somatomedins. Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 19;19(4):790–797. doi: 10.1021/bi00545a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Ksauga M., Le Cam A., Hedo J. A., Itin A., Harrison L. C. Biosynthetic labeling of insulin receptor: studies of subunits in cultured human IM-9 lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1052–1056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Yeung C. W., Moule M. L. Photoaffinity labeling of insulin receptor proteins of liver plasma membrane preparations. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 8;19(1):70–76. doi: 10.1021/bi00542a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Morell B., Walter H., Laron Z., Froesch E. R. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and its carrier protein in various metabolic disorders. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1980 Dec;95(4):505–517. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0950505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) from human serum: recent accomplishments and their physiologic implications. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12):1803–1828. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90267-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II: some biological actions and receptor binding characteristics of two purified constituents of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]