Abstract
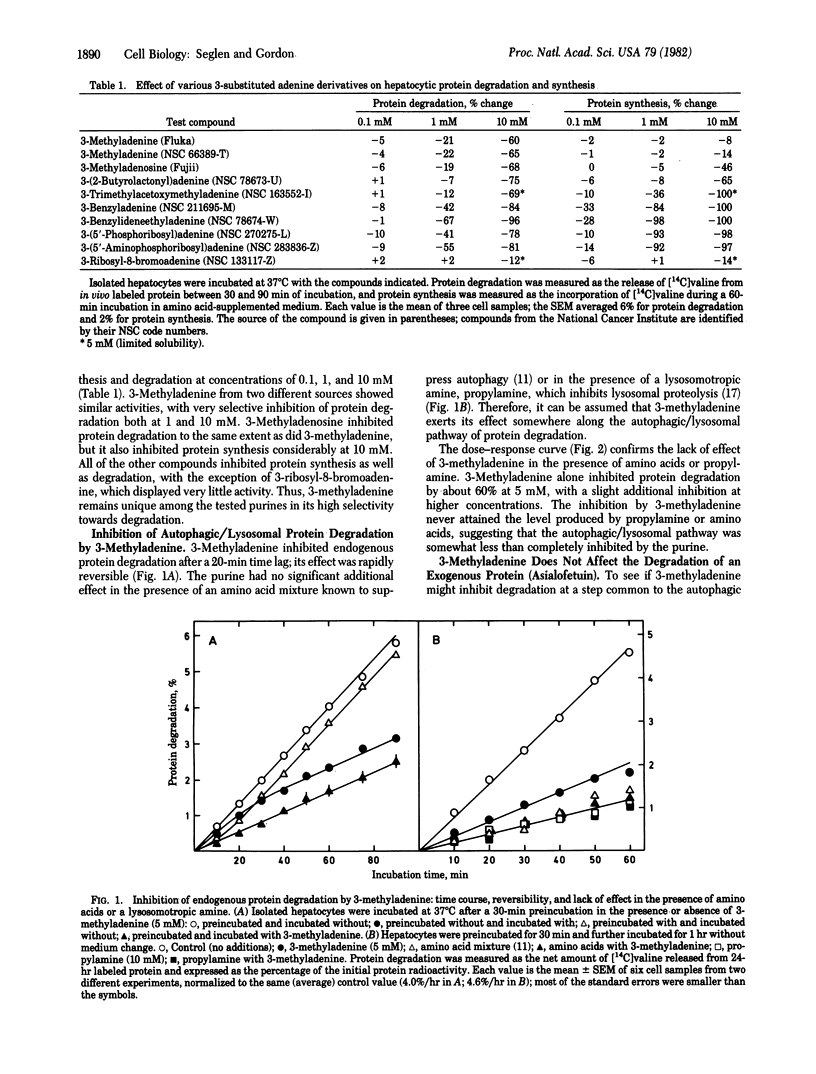
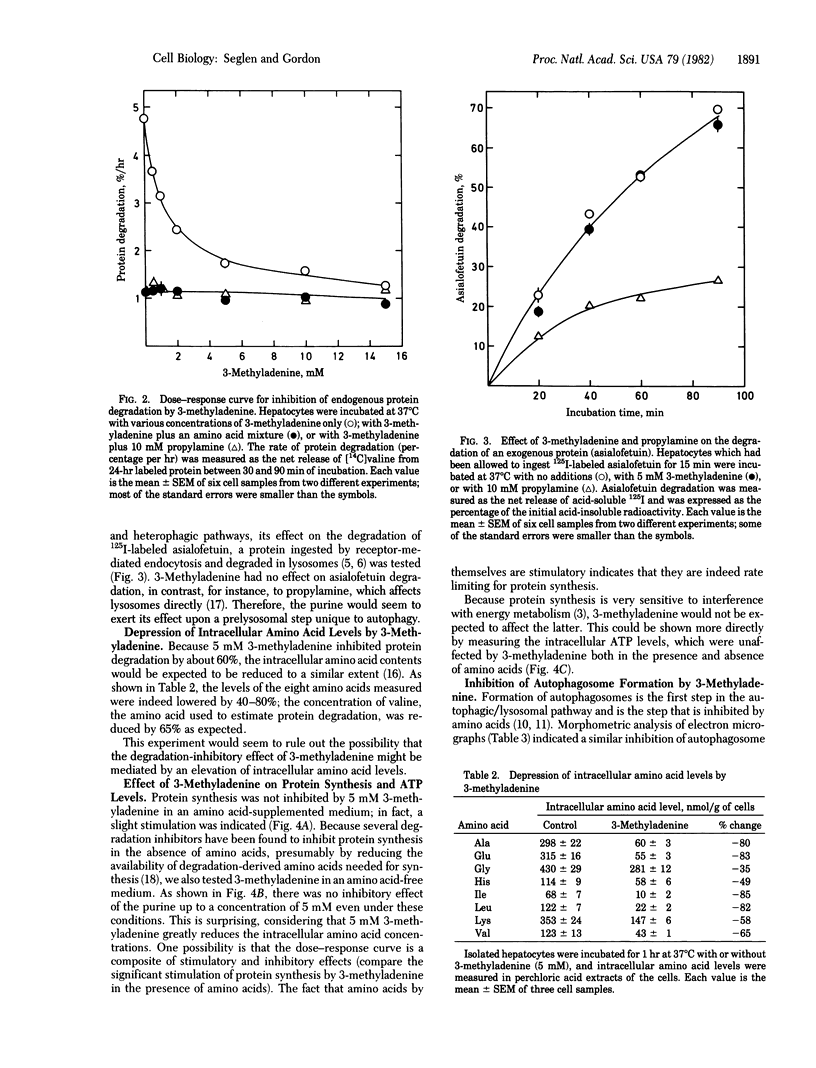
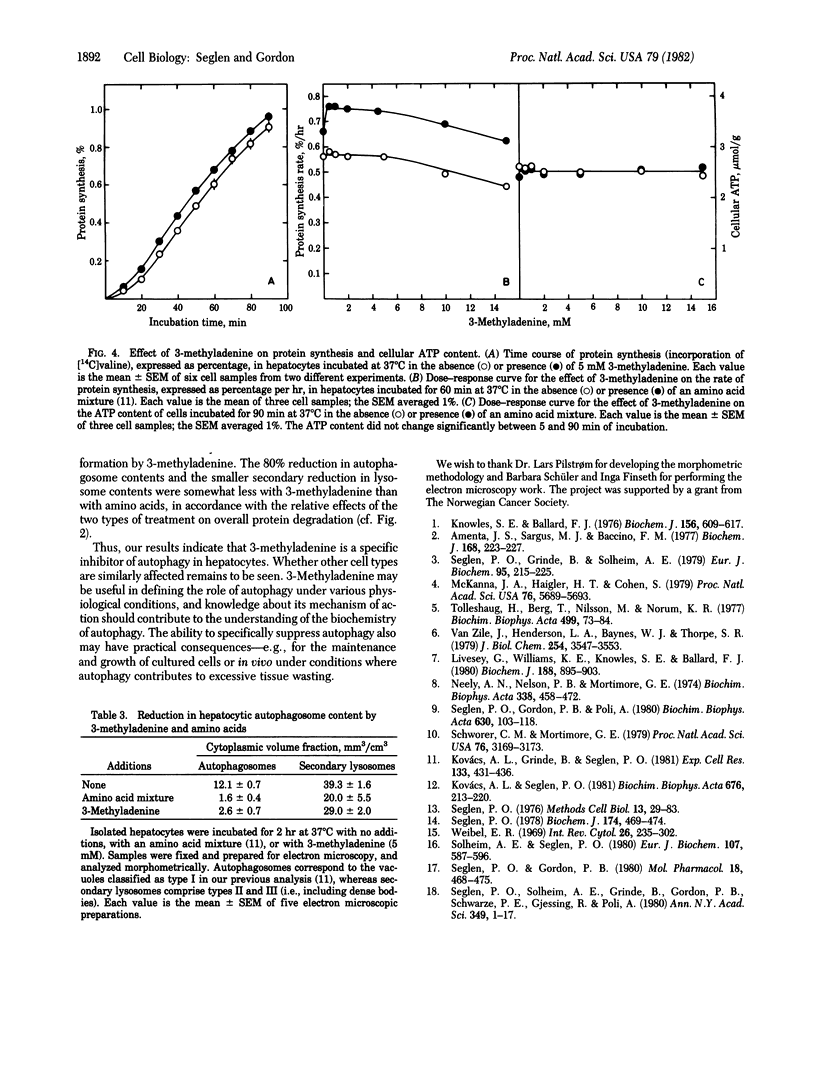
3-Methyladenine (5 mM) inhibits endogenous protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes by about 60%, while having no adverse effect on the degradation of an exogenous protein (asialofetuin), on protein synthesis, or on intracellular ATP levels. 3-Methyladenine appears to act specifically upon the autophagic/lysosomal pathway of degradation, as judged from its lack of effect in the presence of amino acids or a lysosomotropic amine (propylamine). The effect of the purine is not mediated by amino acids because the inhibition of protein degradation is accompanied by a significant depression of intracellular amino acid levels. The ability of 3-methyladenine to suppress the formation of electron microscopically visible autophagosomes suggests that it may be regarded as a specific inhibitor of autophagy.
Keywords: autophagy, lysosomes
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amenta J. S., Sargus M. J., Baccino F. M. Effect of microtubular or translational inhibitors on general cell protein degradation. Evidence for a dual catabolic pathway. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):223–227. doi: 10.1042/bj1680223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles S. E., Ballard F. J. Selective control of the degradation of normal and aberrant proteins in Reuber H35 hepatoma cells. Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):609–617. doi: 10.1042/bj1560609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács A. L., Grinde B., Seglen P. O. Inhibition of autophagic vacuole formation and protein degradation by amino acids in isolated hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Jun;133(2):431–436. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács A. L., Seglen P. O. Inhibition of hepatocytic protein degradation by methylaminopurines and inhibitors of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 17;676(2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livesey G., Williams K. E., Knowles S. E., Ballard F. J. Effects of weak bases on the degradation of endogenous and exogenous proteins by rat yolk sacs. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):895–903. doi: 10.1042/bj1880895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKanna J. A., Haigler H. T., Cohen S. Hormone receptor topology and dynamics: morphological analysis using ferritin-labeled epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5689–5693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schworer C. M., Mortimore G. E. Glucagon-induced autophagy and proteolysis in rat liver: mediation by selective deprivation of intracellular amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3169–3173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Effects of amino acids, ammonia and leupeptin on protein synthesis and degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):469–474. doi: 10.1042/bj1740469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Gordon P. B. Effects of lysosomotropic monoamines, diamines, amino alcohols, and other amino compounds on protein degradation and protein synthesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(3):468–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Gordon P. B., Poli A. Amino acid inhibition of the autophagic/lysosomal pathway of protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 5;630(1):103–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Grinde B., Solheim A. E. Inhibition of the lysosomal pathway of protein degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes by ammonia, methylamine, chloroquine and leupeptin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr 2;95(2):215–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1976;13:29–83. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61797-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O., Solheim A. E., Grinde B., Gordon P. B., Schwarze P. E., Gjessing R., Poli A. Amino acid control of protein synthesis and degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;349:1–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb29510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solheim A. E., Seglen P. O. Subcellular distribution of proteolytically generated valine in isolated rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):587–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Berg T., Nilsson M., Norum K. R. Uptake and degradation of 125I-labelled asialo-fetuin by isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Aug 25;499(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zile J., Henderson L. A., Baynes J. W., Thorpe S. R. [3H]Raffinose, a novel radioactive label for determining organ sites of catabolism of proteins in the circulation. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3547–3553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R. Stereological principles for morphometry in electron microscopic cytology. Int Rev Cytol. 1969;26:235–302. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61637-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



