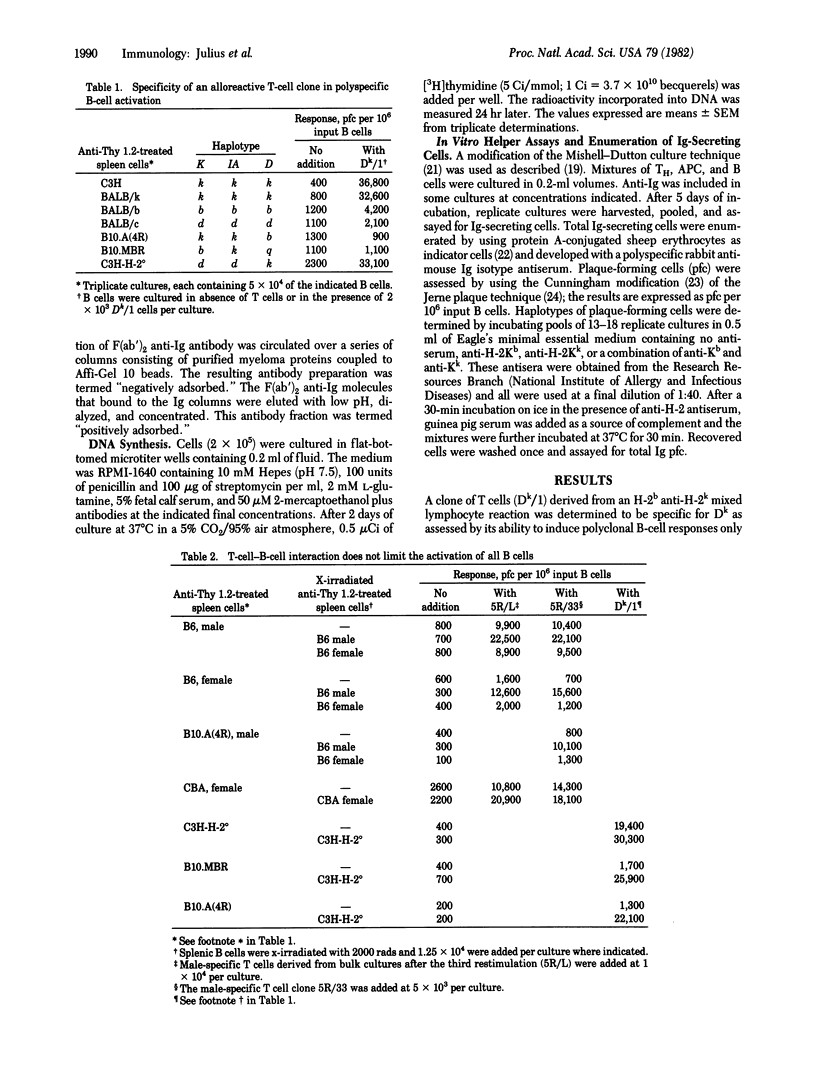
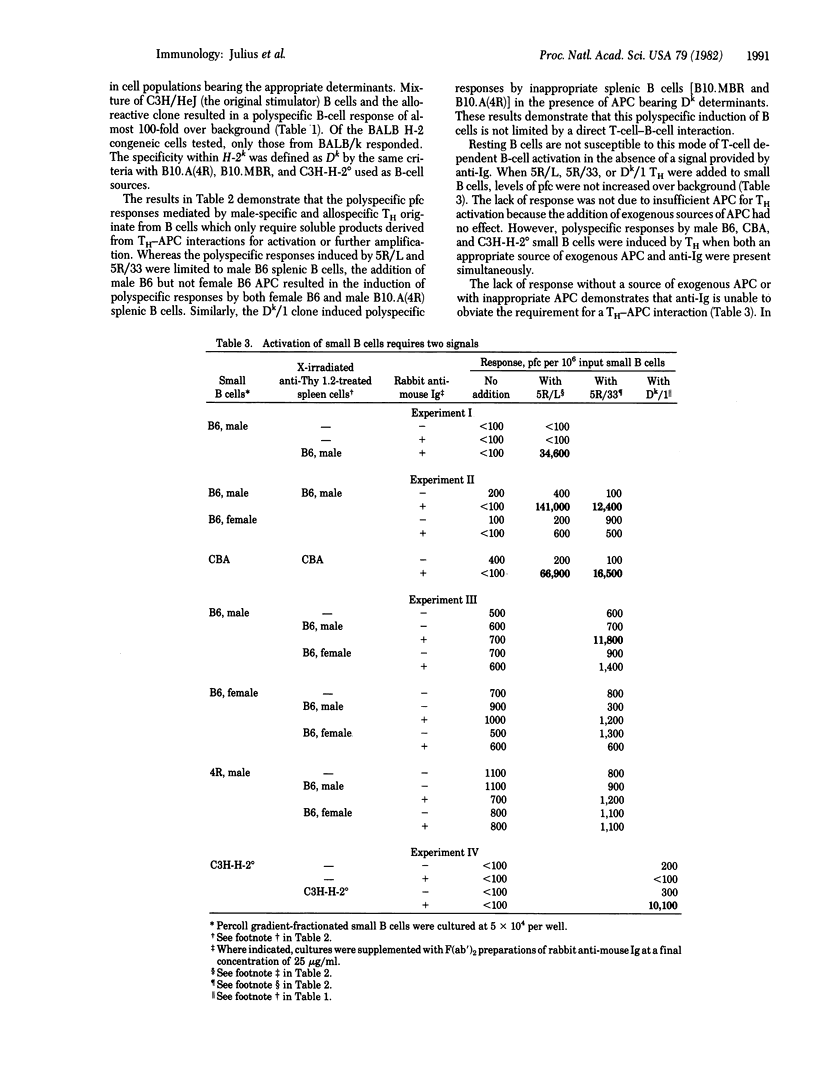
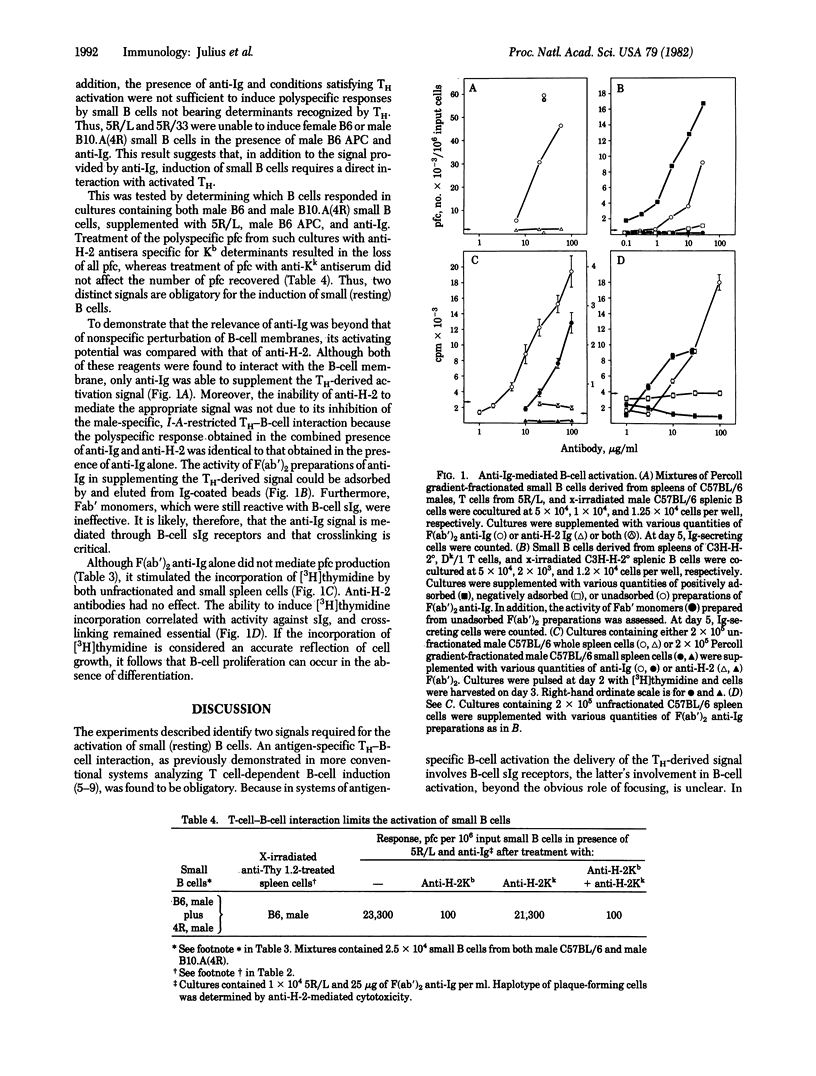
Abstract
Cellular interactions involved in the T cell-dependent activation of B cells were analyzed by using lines and clones of helper T cells specific for determinants expressed on the B cell surface. Activation of male antigen-, M locus-, and H-2-specific T cells was shown to support polyclonal Ig production by a population of B cells that did not require T-cell-B-cell interaction for induction/amplification. However, these T cells alone did not activate gradient-purified small (resting) B cells. The activation of small B cells was shown to require not only a signal derived through an antigen-specific T-helper cell-B cell interaction but in addition a second signal that could be provided by anti-Ig antibodies.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Schreier M. H., Melchers F. T-cell-dependent B-cell stimulation is H-2 restricted and antigen dependent only at the resting B-cell level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1612–1616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustin A. A., Coutinho A. Specific T helper cells that activate B cells polyclonally. In vitro enrichment and cooperative function. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):587–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher P., Cohn M. A theory of self-nonself discrimination. Science. 1970 Sep 11;169(3950):1042–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3950.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesnut R. W., Grey H. M. Studies on the capacity of B cells to serve as antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1075–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Etlinger H. M., Chiller J. M. Lymphocyte specificity to protein antigens. I. Characterization of the antigen-induced in vitro T cell-dependent proliferative response with lymph node cells from primed mice. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1048–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Augustin A. A., Forni L., Fischer-Lindahl K. Genetics of a non-H-2 antigen that stimulates "unrestricted" helper T cells and MLR. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):21–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Möller G. Editorial: Immune activation of B cells: evidence for 'one nonspecific triggering signal' not delivered by the Ig receptors. Scand J Immunol. 1974;3(2):133–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb P., Meier B., Matsunaga T., Feldmann M. Nature of T-cell macrophage interaction in helper-cell induction in vitro. II. Two stages of T-helper-cell differentiation analyzed in irradiation and allophenic chimeras. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):686–701. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronowicz E., Coutinho A., Melchers F. A plaque assay for all cells secreting Ig of a given type or class. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Aug;6(8):588–590. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T., Schimpl A. Studies on the generation and expression of H-2-controlled T helper function in chimeric mice: evidence for two levels of H-2 resitriction. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Sep;9(9):730–736. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERNE N. K., NORDIN A. A. Plaque formation in agar by single antibody-producing cells. Science. 1963 Apr 26;140(3565):405–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Cooperative interaction of B lymphocytes with antigen-specific helper T lymphocytes is MHC restricted. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):547–549. doi: 10.1038/292547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Augustin A. A. Helper activity of T cells stimulated in long-term culture. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Sep;9(9):671–680. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Herzenberg L. A. Isolation of antigen-binding cells from unprimed mice: demonstration of antibody-forming cell precursor activity and correlation between precursor and secreted antibody avidities. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):904–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller D. M., Swierkosz J. E., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Two types of functionally distinct, synergizing helper T cells. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1350–1359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Cort S. P. Generation of T helper cells in vitro. IV. F1 T helper cells primed with antigen-pulsed parental macrophages are genetically restricted in their antigen-specific helper activity. J Immunol. 1978 Feb;120(2):445–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar-Kimber K., Sprent J. Absence of H-2 restriction in primary and secondary mixed-lymphocyte reactions to strong M1s determinants. J Exp Med. 1980 Feb 1;151(2):407–417. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C. Induction and suppression of polyclonal antibody responses by anti-Ig reagents and antigen-nonspecific helper factors: a comparison of the effects of anti-Fab, anti-IgM, and anti IgD on murine B cells. Immunol Rev. 1980;52:115–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00333.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajewsky K., Roelants G. E., Askonas B. A. Carrier specificity and the allogeneic effect in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Dec;2(6):592–598. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S. Determinant selection and macrophage function in genetic control of the immune response. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:136–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Rosenthal A. S. Adherent cell function in murine T lymphocyte antigen recognition. I. A. macrophage-dependent T cell proliferation assay in the mouse. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1991–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier M. H., Andersson J., Lernhardt W., Melchers F. Antigen-specific T-helper cells stimulate H-2-compatible and H-2-incompatible B-cell blasts polyclonally. J Exp Med. 1980 Jan 1;151(1):194–203. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.1.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Unanue E. R. Control of proliferation and differentiation in B lymphocytes by anti-Ig antibodies and a serum-derived cofactor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2401–2405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Unanue E. R. Requirements for mitogenic stimulation of murine B cells by soluble anti-IgM antibodies. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):406–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer A., Hathcock K. S., Hodes R. J. Cellular and genetic control of antibody responses. V. Helper T-cell recognition of H-2 determinants on accessory cells but not B cells. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1208–1226. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J. Restricted helper function of F1 hybrid T cells positively selected to heterologous erythrocytes in irradiated parental strain mice. II. Evidence for restrictions affecting helper cell induction and T-B collaboration, both mapping to the K-end of the H-2 complex. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1159–1174. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt P., Erb P., Keller B., Feldmann M. Nature of macrophage-T cell interaction in secondary helper cell generation in vitro. Genetic restriction of macrophage-T cell interaction, which determines T-B genetic restriction. Eur J Immunol. 1981 May;11(5):377–381. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann H., Pope H., Brent L., Bighouse K. Influence of the major histocompatibility complex on lymphocyte interactions in antibody formation. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):166–168. doi: 10.1038/274166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldron J. A., Jr, Horn R. G., Rosenthal A. S. Antigen-induced proliferation of guinea pig lymphocytes in vitro: obligatory role of macrophages in the recognition of antigen by immune T-lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):58–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H., Haas W. H-2 restricted cytolytic and noncytolytic T cell clones: isolation, specificity and functional analysis. Immunol Rev. 1981;54:27–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



