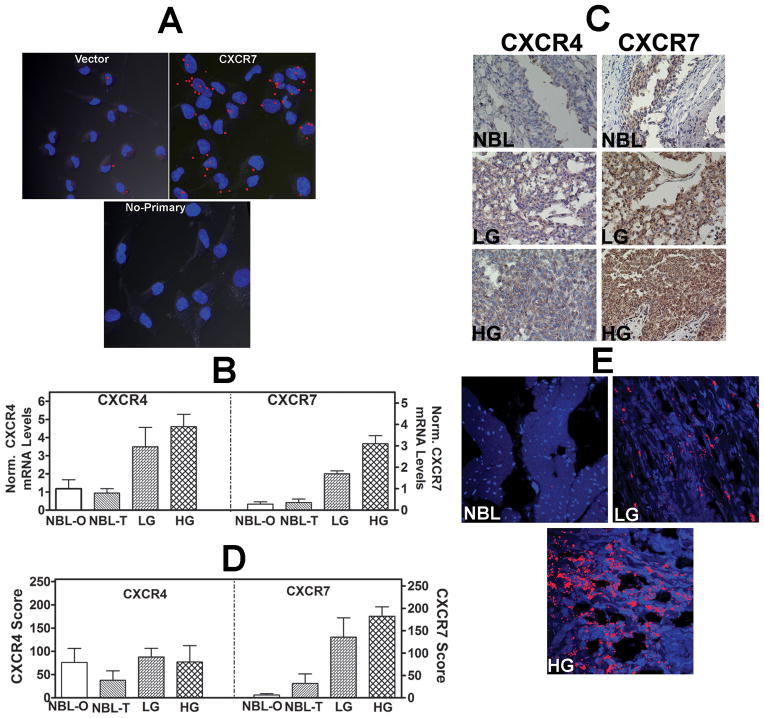
Figure 2. Analysis of CXCR7 transfectants and expression of CXCR4 and CXCR7 in bladder tissues.
A: In-cell co-IP of 253J-Lung vector and CXCR7 transfectants using the anti-CXCR7 and anti-EGFR antibodies; lower panel, no primary antibody control for the CXCR7 transfectant. Red dots indicate co-localization of CXCR7 and EGF-R. Magnification: 400×. B: CXCR4 and CXCR7 transcript levels in bladder tissues. NBL: normal bladder; NBL-O: NBL tissue obtained from organ donors; NBL-T: NBL tissue obtained from BCa patients at the time of cystectomy. LG: low-grade BCa; HG: high-grade BCa. The mean±sd levels are shown. C: CXCR4 and CXCR71 were localized in normal bladder, LG and HG BCa tissues by IHC. Representative specimens from each category are shown. D: Mean±sd staining scores of CXCR4 and CXCR7 in bladder specimens are shown. Due to poor fixation which resulted in the loss of tissues during staining, 22 high-grade, 7 low-grade tissues and 15 NBL tissues could be stained. E: Localization of CXCR7 in bladder endothelial cells. Bladder tissues were stained with anti-CD31 (endothelial cell marker) and CXCR7 using the in-cell co-IP technique. Red staining represents co-localization of CD31 and CXCR7, i.e., localization of CXCR7 in endothelial cells. Magnification: 400×.