Abstract
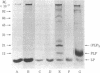
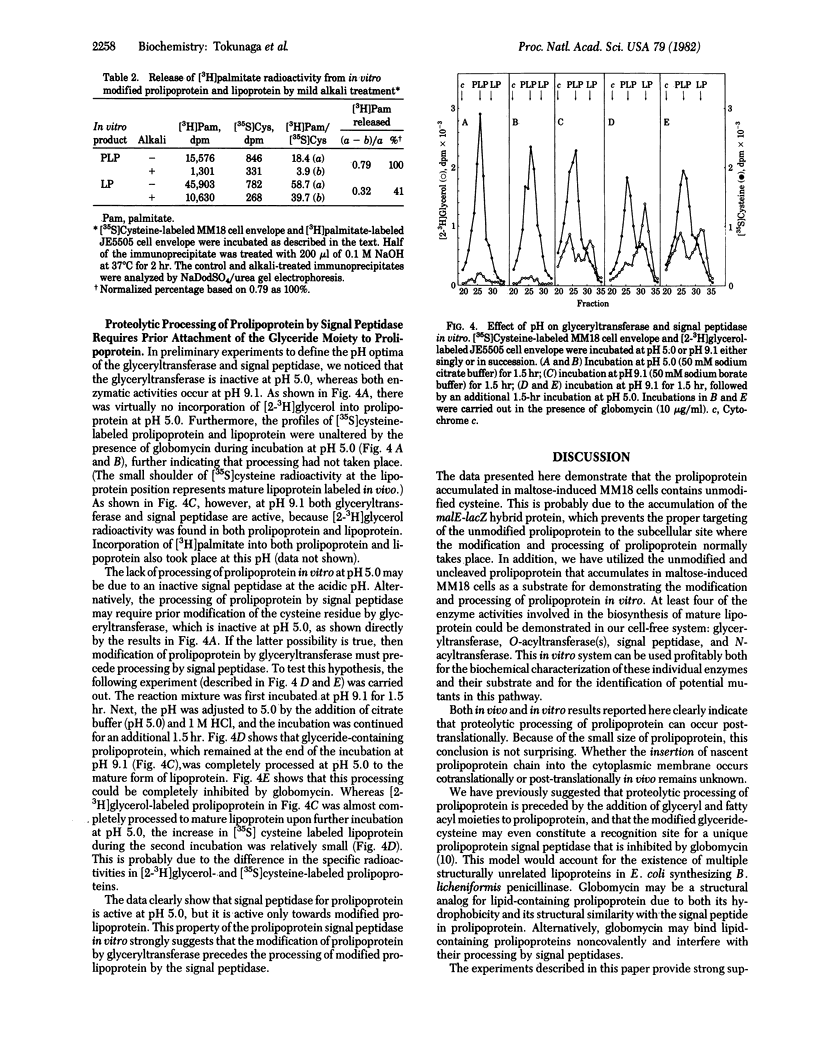
Escherichia coli strain MM18 cells containing malE-lacZ hybrid protein was reported to accumulate prolipoprotein when they were induced with maltose [Ito, K., Bassford, P. J. & Beckwith, J. (1981) Cell 24, 707-717]. We have shown that the prolipoprotein accumulated in maltose-induced MM18 cells is not modified, lacking covalently linked glyceride. When the cell envelope of MM18 containing unmodified prolipoprotein was incubated in the presence of detergent with [2-3H]glycerol-labeled cell envelope of strain JE5505 lacking murein lipoprotein, incorporation of [2-3H]glycerol radioactivity into both prolipoprotein and processed mature lipoprotein was observed. Likewise, when [3H]-palmitate-labeled JE5505 cell envelope was incubated with the MM18 cell envelope containing unmodified prolipoprotein in the presence of detergent, [3H]palmitate radioactivity was incorporated into prolipoprotein by ester linkage and into mature lipoprotein by both ester and amide linkages. These results indicate that our in vitro system contains activities of prolipoprotein modification and processing enzymes, including glyceryltransferase, O-acyltransferase, signal peptidase, and N-acyltransferase. The signal peptidase activity in our in vitro system was completely inhibited by globomycin. At pH 5.0, glyceryltransferase was inactive. Signal peptidase was active at pH 5.0, provided that prolipoprotein had been modified by glyceryltransferase (O-acyl-transferase) during a prior incubation at pH 9.1. These results strongly suggest that the modification of prolipoprotein by glyceryltransferase (and O-acyltransferase) precedes, and may in fact be a prerequisite for, the processing of prolipoprotein by signal peptidase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun V. Covalent lipoprotein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 31;415(3):335–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay P. K., Wu H. C. Biosynthesis of the covalently linked diglyceride in murein lipoprotein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5318–5322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. A mechanism of protein localization: the signal hypothesis and bacteria. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):701–711. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Hirashima A., Sekizawa J., Inouye M. Protein synthesis in toluene-treated Escherichia coli. Exclusive synthesis of membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Oct 1;69(1):163–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirashima A., Wang S., Inouye M. Cell-free synthesis of a specific lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane directed by purified messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4149–4153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Yasuda S. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a mutant of E. coli lacking a murein-lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1417–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M., Ichihara S., Mizushima S. Accumulation of glyceride-containing precursor of the outer membrane lipoprotein in the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli treated with globomycin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3707–3712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihara S., Hussain M., Mizushima S. Characterization of new membrane lipoproteins and their precursors of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3125–3129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye M., Guthrie J. P. A mutation which changes a membrane protein of E. coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):957–961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inukai M., Takeuchi M., Shimizu K., Arai M. Mechanism of action of globomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Nov;31(11):1203–1205. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. Protein localization in E. coli: is there a common step in the secretion of periplasmic and outer-membrane proteins? Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):707–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J. S., Philbrick W. M., Hayashi S., Inukai M., Arai M., Hirota Y., Wu H. C. Globomycin sensitivity of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: effects of mutations affecting structures of murein lipoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):657–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.657-660.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai J. S., Sarvas M., Brammar W. J., Neugebauer K., Wu H. C. Bacillus licheniformis penicillinase synthesized in Escherichia coli contains covalently linked fatty acid and glyceride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3506–3510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai S. H., Philbrick W. M., Wu H. C. Acyl moieties in phospholipids are the precursors for the fatty acids in murein lipoprotein of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5384–5387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Kanazawa H., Ozols J., Wu H. C. An Escherichia coli mutant with an amino acid alteration within the signal sequence of outer membrane prolipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4891–4895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Lai J. S., Wu H. C. Characterization of murein-bound lipoprotein in an Excherichia coli mutant altered in the signal sequence of prolipoprotein. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 1;109(1):50–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Wu H. C. Biosynthesis and assembly of envelope lipoprotein in a glycerol-requiring mutant of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):892–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.892-904.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Glass J., Inouye M. Accumulation of the prolipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane caused by benzyloxycarbonylalanine chloromethyl ketone. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4712–4714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Wu H. C. Proteins of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:369–422. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P., Watts C., Wickner W. Membrane assembly from purified components. I. Isolated M13 procoat does not require ribosomes or soluble proteins for processing by membranes. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):341–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank R. T., Munkres K. D. Molecular weight analysis of oligopeptides by electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate. Anal Biochem. 1971 Feb;39(2):462–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90436-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts C., Silver P., Wickner W. Membrane assembly from purified components. II. Assembly of M13 procoat into liposomes reconstituted with purified leader peptidase. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):347–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. The assembly of proteins into biological membranes: The membrane trigger hypothesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:23–45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Hou C., Lin J. J., Yem D. W. Biochemical characterization of a mutant lipoprotein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1388–1392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Lai J. S., Hayashi S., Giam C. Z. Biogenesis of membrane lipoproteins in Escherichia coli. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):307–315. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84679-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. C., Lin J. J. Escherichia coli mutants altered in murein lipoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):147–156. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.147-156.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwizinski C., Date T., Wickner W. Leader peptidase is found in both the inner and outer membranes of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3593–3597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwizinski C., Wickner W. Purification and characterization of leader (signal) peptidase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7973–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]