Abstract
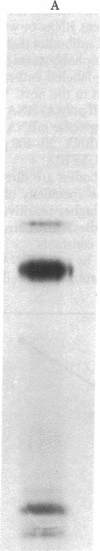
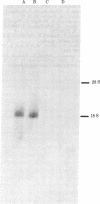
A cDNA clone has been isolated from a trophoblastoma cDNA library. The mRNA complementary to this sequence directs the in vitro synthesis of proteins. The two-dimensional electrophoretic pattern of migration of these proteins is superposable to that of the trophoblastoma intermediate filament proteins recognized by monoclonal antibody (mAb) TROMA-1.This mAb had previously been shown to label trophectoderm cells but not inner cell mass cells. With a sensitive binding assay (ultrasensitive enzymatic radioimmunoassay), these in vitro synthesized proteins were recognized by mAb TROMA-1. The proteins are immunoprecipitated by an antiserum directed against trophoblastoma intermediate filament proteins and by a serum directed against a major cytoskeletal protein found in murine extraembryonic endodermal cell lines (Endo-A) [Oshima R. G. (1981) J. Biol. Chem. 256, 8124-8133]. The cDNA sequence detects specific mRNA(s) migrating with 18S ribosomal RNA in trophoblastoma but not in embryonal carcinoma cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berstine E. G., Hooper M. L., Grandchamp S., Ephrussi B. Alkaline phosphatase activity in mouse teratoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3899–3903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brûlet P., Babinet C., Kemler R., Jacob F. Monoclonal antibodies against trophectoderm-specific markers during mouse blastocyst formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4113–4117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Linnenbach A., Huebner K., Parnes J. R., Margulies D. H., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Control of expression of histocompatibility antigens (H-2) and beta 2-microglobulin in F9 teratocarcinoma stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5754–5758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. C., Yolken R. H., Krokan H., Hsu I. C. Ultrasensitive enzymatic radioimmunoassay: application to detection of cholera toxin and rotavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5336–5339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson B. W., Grund C., Schmid E., Bürki K., Franke W. W., Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. Intermediate filaments of the cytokeratin type and desmosomes in preimplantation embryos. Differentiation. 1980;17(3):161–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1980.tb01093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. Stimulation by cyclic adenosine monophosphate of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid replication and catabolite repression of the plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid-protein relaxation complex. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):577–591. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.577-591.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemler R., Brûlet P., Schnebelen M. T., Gaillard J., Jacob F. Reactivity of monoclonal antibodies against intermediate filament proteins during embryonic development. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1981 Aug;64:45–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R., Evans M. J. Differentiation of clonal lines of teratocarcinoma cells: formation of embryoid bodies in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1441–1445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas J. F., Avner P., Gaillard J., Guenet J. L., Jakob H., Jacob F. Cell lines derived from teratocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1976 Nov;36(11 Pt 2):4224–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima R. G. Identification and immunoprecipitation of cytoskeletal proteins from murine extra-embryonic endodermal cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8124–8133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulin D., Babinet C., Weber K., Osborn M. Antibodies as probes of cellular differentiation and cytoskeletal organization in the mouse blastocyst. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Dec;130(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Mahdavi V. The induction of differentiation in teratocarcinoma stem cells by retinoic acid. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]