Abstract
H-2 haplotypes were extracted from wild mice of three subspecies, Mus musculus domesticus, M. m. molossinus, and M. m. castaneus, that are known to have been separated from one another for some 1 to 2 million years. Serologically indistinguishable molecules controlled by some of the polymorphic H-2 loci were compared by tryptic peptide mapping, and the maps were found to be identical. In addition, a number of instances of biochemically indistinguishable H-2 molecules were found among wild mice and inbred strains of the M. m. domesticus subspecies. These findings suggest that some of the H-2 alleles have not altered for greater than 1 million years. To reconcile this apparent stability of H-2 genes with their extraordinary polymorphism (some 100 alleles at each of the polymorphic H-2 loci), it is proposed that the H-2 alleles evolve as if they were separate loci.
Full text
PDF
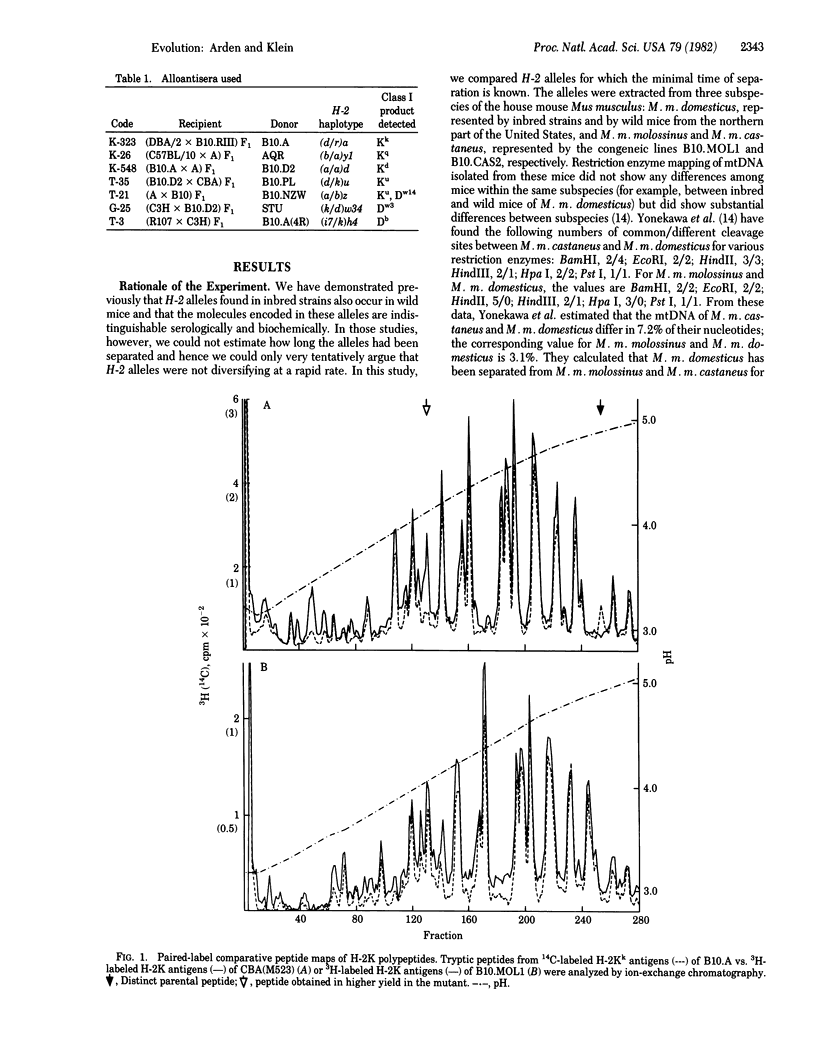
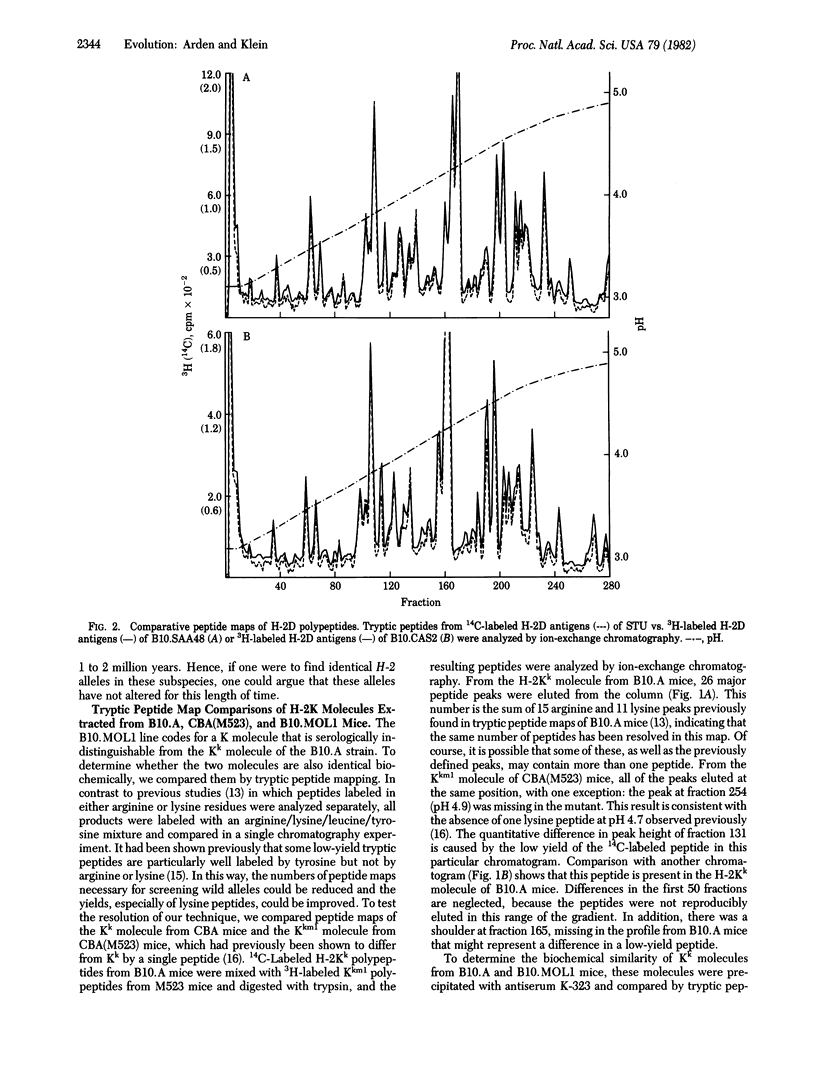
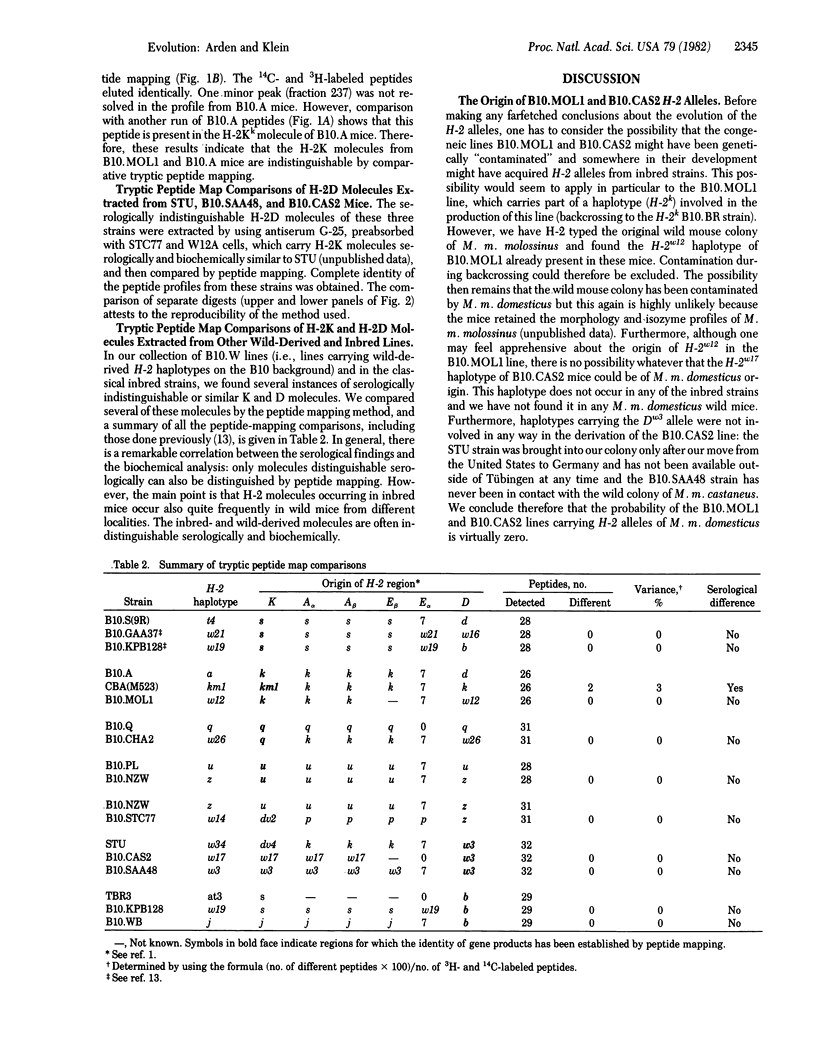

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert E., Kano K., Abeyounis C. J., Milgrom F. Detection of human lymphocyte isoantigens by rabbit homotransplantation sera. Transplantation. 1969 Oct;8(4):466–471. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196910000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arden B., Wakeland E. K., Klein J. Structural comparisons of serologically indistinguishable H-2K-encoded antigens from inbred and wild mice. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2424–2428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. New genetic model for allelism at histocompatibility and other complex loci: polymorphism for control of gene expression. Transplant Proc. 1973 Dec;5(4):1471–1475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cami B., Brégégère F., Abastado J. P., Kourilsky P. Multiple sequences related to classical histocompatibility antigens in the mouse genome. Nature. 1981 Jun 25;291(5817):673–675. doi: 10.1038/291673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iha T. H., Gerbrandt G., Bodmer W. F., McGary D., Stone W. H. Cross-reactions of cattle lymphocytotoxic sera with HL-A and other human antigens. Tissue Antigens. 1973;3(4):291–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1973.tb01006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivăsková E., Dausset J., Iványi P. Cytotoxic reactions of anti-H-2 sera with human lymphocytes. Folia Biol (Praha) 1972;18(3):194–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F. Polymorphism of the mouse H-2 loci. Immunol Rev. 1981;60:23–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Bregegere F., Rask L., Cami B., Garoff H., Daniel F., Wiman K., Larhammar D., Abastado J. P., Gachelin G. cDNA clone coding for part of a mouse H-2d major histocompatibility antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2772–2776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T. Genetic variation in small multigene families. Genet Res. 1981 Apr;37(2):133–149. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300020115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Molecular cloning of a human histocompatibility antigen cDNA fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Hood L. Preliminary amino acid sequences of transplantation antigens: genetic and evolutionary implications. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1976;5:35–68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8142-6_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Frelinger J. G., Fisher D., Hunkapiller T., Pereira D., Weissman S. M., Uehara H., Nathenson S., Hood L. Three cDNA clones encoding mouse transplantation antigens: homology to immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90508-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara H., Ewenstein B. M., Martinko J. M., Nathenson S. G., Coligan J. E., Kindt T. J. Primary structure of murine major histocompatibility complex alloantigens: amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal one hundred and seventy-three residues of the H-2Kb glycoprotein. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 22;19(2):306–315. doi: 10.1021/bi00543a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Capra J. D. The protein products of the murine 17th chromosome: genetics and structure. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:147–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Capra J. D. The protein products of the murine 17th chromosome: genetics and structure. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:147–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaleska-Rutczynska Z., Klein J. Histocompatibility-2 system in wild mice. V. Serologic analysis of sixteen B10.W congenic lines. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):1903–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



