Abstract
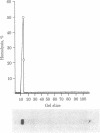
The interaction of homogeneous preparations of mouse submandibular gland nerve growth factor (NGF) with the classical complement pathway was studied. NGF was found to be capable of carrying out the enzyme activities of the first component (C1-) of the classical complement pathway (i.e., the cleavage of zymogen C4 and C2). NGF would not substitute for any other classical pathway component, C2-C9. The C1(-)-like activity of NGF was inhibited by human C1- inactivator. This interaction of NGF with the complement system may account for the previously described ability of NGF to accelerate the rate of contraction of experimentally induced wounds.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austen K. F. Hageman-factor-dependent coagulation, fibrinolysis, and kinin generation. Transplant Proc. 1974 Mar;6(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Immune hemolysis: a simplified method for the preparation of EAC'4 with guinea pig or with human complement. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle M. D., Langone J. J. A simple procedure to use whole serum as a source of either IgG- or IgM-specific antibody. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson V. H. Blood coagulation and related plasma enzymes in inflammation. Ser Haematol. 1970;3(1):39–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee A. P., Borsos T., Boyle M. D. Interaction between components of the human classical complement pathway and immobilized Cibacron Blue F3GA. J Immunol Methods. 1979;30(2):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(79)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Shooter E. M., Varon S. Enzymatic activities of mouse nerve growth factor and its subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1383–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson J. M., Niall M., Evans D., Fowler R. Effect of salivary glands on wound contraction in mice. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):793–795. doi: 10.1038/279793a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Assay and properties of serum inhibitor of C'l-esterase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:608–611. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li A. K., Koroly M. J., Schattenkerk M. E., Malt R. A., Young M. Nerve growth factor: acceleration of the rate of wound healing in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4379–4381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M., Borsos T., Rapp H. J. Immune hemolysis and the functional properties of the second (C2) and fourth (C4) components of complement. IV. Formation of EAC42 by treatment of C2 with trypsin in the presence of EAC4. J Immunol. 1972 Sep;109(3):434–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Saide J. D., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Molecular properties of the nerve growth factor secreted in mouse saliva. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2672–2676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. A., Saide J. D., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Nerve growth factor in mouse serum and saliva: role of the submandibular gland. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2330–2333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenstein N. S., Dvorak H. F., Blanchard M. H., Young M. Nerve growth factor: a protease that can activate plasminogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5497–5500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace L. J., Partlow L. M. alpha-Adrenergic regulation of secretion of mouse saliva rich in nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4210–4214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Koroly M. J. Nerve growth factor zymogen. Stoichiometry of the active-site serine and role of zinc(II) in controlling autocatalytic self-activation. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5316–5321. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Oger J., Blanchard M. H., Asdourian H., Amos H., Arnason B. G. Secretion of a nerve growth factor by primary chick fibroblast cultures. Science. 1975 Jan 31;187(4174):361–362. doi: 10.1126/science.1167427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M., Saide J. D., Murphy R. A., Blanchard Nerve growth factor: multiple dissociation products in homogenates of the mouse submandibular gland. Purification and molecular properties of the intact undissociated form of the protein. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1490–1498. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]