Abstract
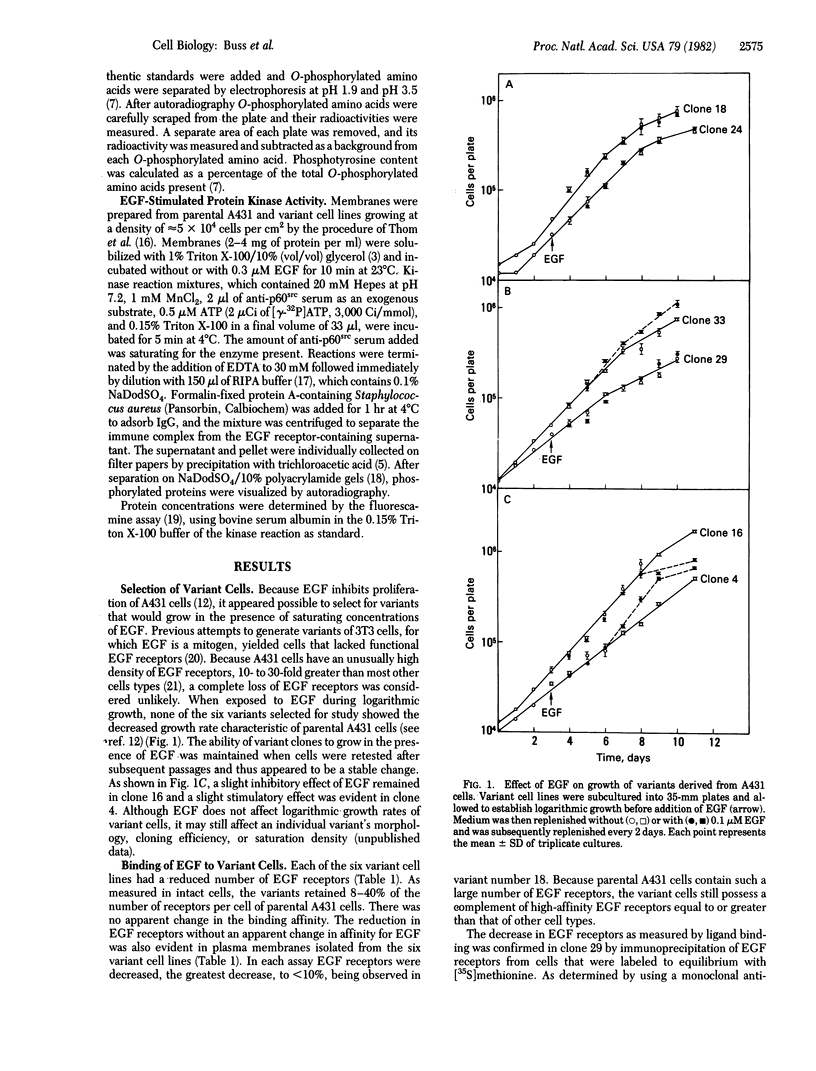
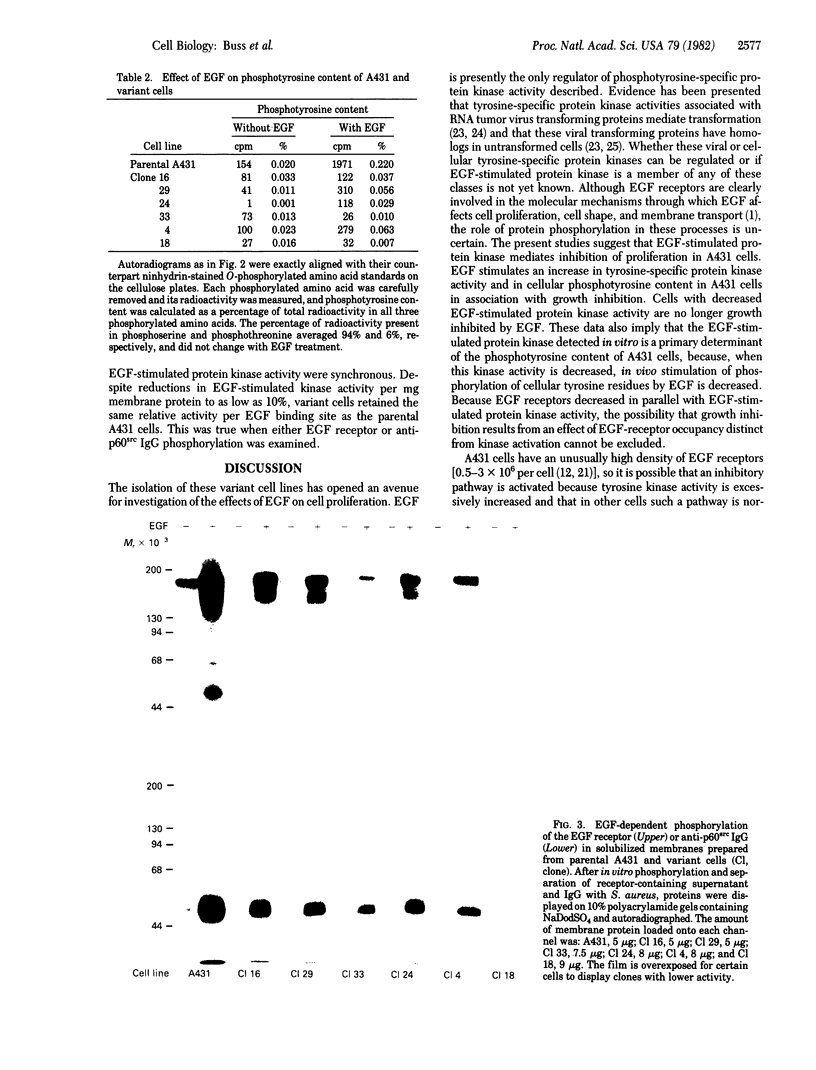
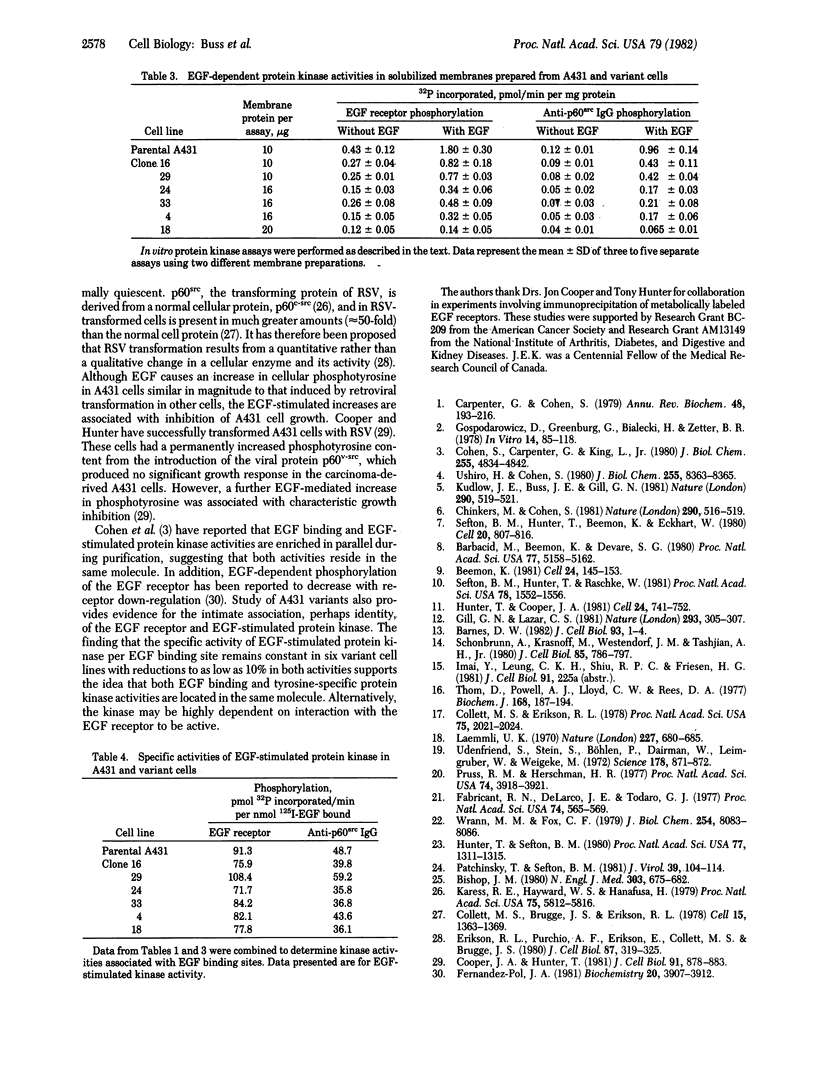
To determine the role of epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated protein kinase in the biological effects caused by EGF, tyrosine-specific kinase activity has been quantitated in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells and six variant cell lines. Because EGF inhibited proliferation of A431 cells, variants resistant to this inhibition were selected by treatment with mutagen and maintenance for 1 month in 0.1 μM EGF. After cloning and growth for 6-20 generations without EGF, the resistance of the variants to the growth-inhibitory effect of EGF was confirmed. Whereas EGF increased cellular phosphotyrosine content ≈10-fold in parental A431 cells, EGF caused smaller or undetectable increases in the six variant cell lines. Solubilized membranes from the six variants displayed diminished EGF-stimulated phosphorylation of the EGF receptor and of antibodies to p60src (the product of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene), which act as an exogenous substrate. The decrease in EGF-stimulated tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity varied from ≈40% (clone 16) to ≈8% (clone 18) of parental A431 activity. Phosphorylated EGF receptors from parental and variant cells migrated identically on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels. The number of EGF receptors in variant cells decreased in parallel with EGF-stimulated protein kinase activity, so that the specific activity of EGF-stimulated protein kinase per EGF receptor remained constant in the six variant cell lines with reductions in both activities to as low as 10%. These results suggest that this tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity mediates the growth-inhibitory effect of EGF on A431 cells and that both EGF binding and kinase activities reside in the same or tightly associated molecules.
Keywords: tyrosine phosphorylation, cell proliferation
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M., Beemon K., Devare S. G. Origin and functional properties of the major gene product of the Snyder-Theilen strain of feline sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5158–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D. W. Epidermal growth factor inhibits growth of A431 human epidermoid carcinoma in serum-free cell culture. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):1–4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K. Transforming proteins of some feline and avian sarcoma viruses are related structurally and functionally. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90510-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular biology of RNA tumor viruses: a physician's guide. N Engl J Med. 1980 Sep 18;303(12):675–682. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198009183031206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Cohen S. Purified EGF receptor-kinase interacts specifically with antibodies to Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):516–519. doi: 10.1038/290516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Characterization of a normal avian cell protein related to the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1363–1369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Similarities and differences between the effects of epidermal growth factor and Rous sarcoma virus. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):878–883. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L., Purchio A. F., Erikson E., Collett M. S., Brugge J. S. Molecular events in cells transformed by Rous Sarcoma virus. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):319–325. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Nerve growth factor receptors on human melanoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Pol J. A. Epidermal growth factor: relationship between receptor down regulation in cultured NRK cells and epidermal growth factor enhancement of phosphorylation of a 170000 molecular weight membrane protein in vitro. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3907–3912. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Lazar C. S. Increased phosphotyrosine content and inhibition of proliferation in EGF-treated A431 cells. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):305–307. doi: 10.1038/293305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Greenburg G., Bialecki H., Zetter B. R. Factors involved in the modulation of cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro: the role of fibroblast and epidermal growth factors in the proliferative response of mammalian cells. In Vitro. 1978 Jan;14(1):85–118. doi: 10.1007/BF02618177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudlow J. E., Buss J. E., Gill G. N. Anti-pp60src antibodies are substrates for EGF-stimulated protein kinase. Nature. 1981 Apr 9;290(5806):519–521. doi: 10.1038/290519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Sefton B. M. Evidence that there exist four classes of RNA tumor viruses which encode proteins with associated tyrosine protein kinase activities. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):104–114. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.104-114.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Variants of 3T3 cells lacking mitogenic response to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3918–3921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonbrunn A., Krasnoff M., Westendorf J. M., Tashjian A. H., Jr Epidermal growth factor and thyrotropin-releasing hormone act similarly on a clonal pituitary cell strain. Modulation of hormone production and inhbition of cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):786–797. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Raschke W. C. Evidence that the Abelson virus protein functions in vivo as a protein kinase that phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1552–1556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thom D., Powell A. J., Lloyd C. W., Rees D. A. Rapid isolation of plasma membranes in high yield from cultured fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):187–194. doi: 10.1042/bj1680187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udenfriend S., Stein S., Böhlen P., Dairman W., Leimgruber W., Weigele M. Fluorescamine: a reagent for assay of amino acids, peptides, proteins, and primary amines in the picomole range. Science. 1972 Nov 24;178(4063):871–872. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4063.871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrann M. M., Fox C. F. Identification of epidermal growth factor receptors in a hyperproducing human epidermoid carcinoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8083–8086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]