Abstract
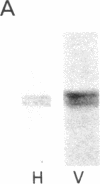
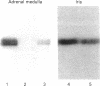
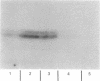
The cellular and subcellular distribution of protein I, a major brain phosphoprotein, has been studied in the peripheral nervous system. The levels of protein I in various peripheral nerves and innervated peripheral tissues were determined by radioimmunoassay and radioimmunolabeling of polyacrylamide gels. The results indicated tha protein I is present throughout the peripheral nervous system. Denervation studies of adrenal medulla and iris suggested that the protein I contained in peripheral tissues is localized to the neuronal elements innervating those tissues. Protein I was found to be enriched in neurotransmitter vesicle fractions of peripheral nervous tissue. Moreover, protein I appeared to be transported from cell bodies to axons terminals at least partly in association with neurotransmitter vesicles.
Full text
PDF

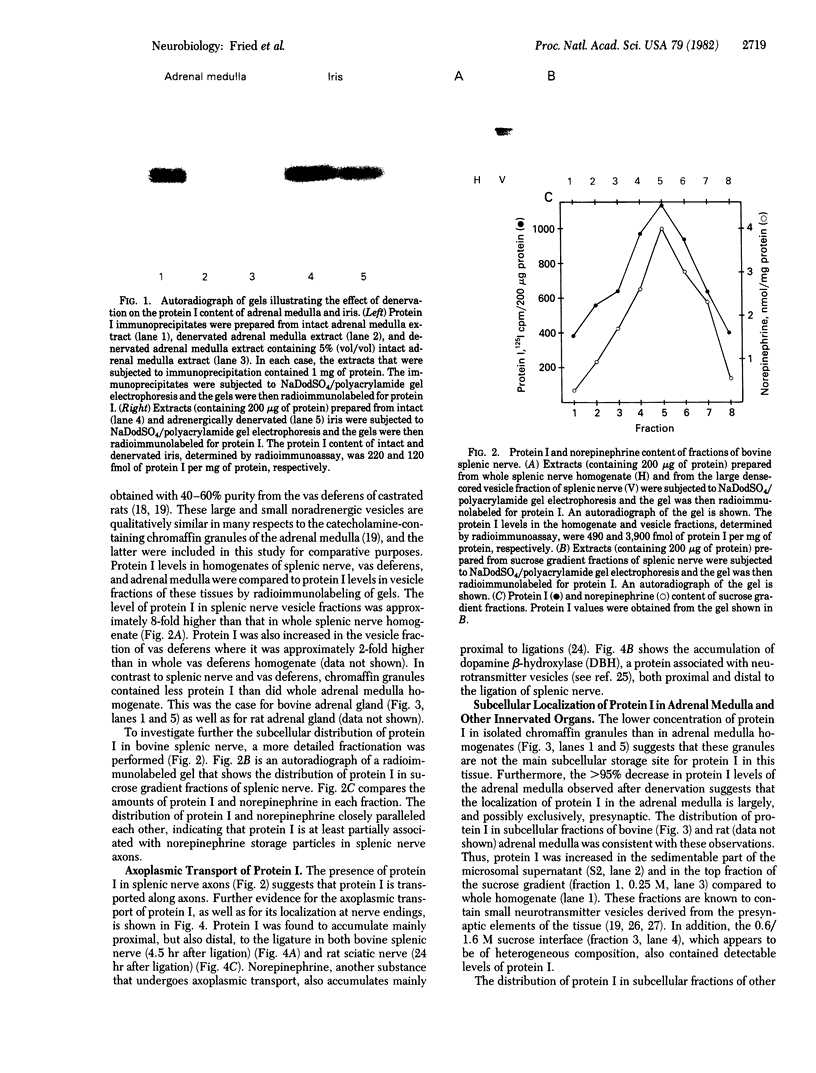
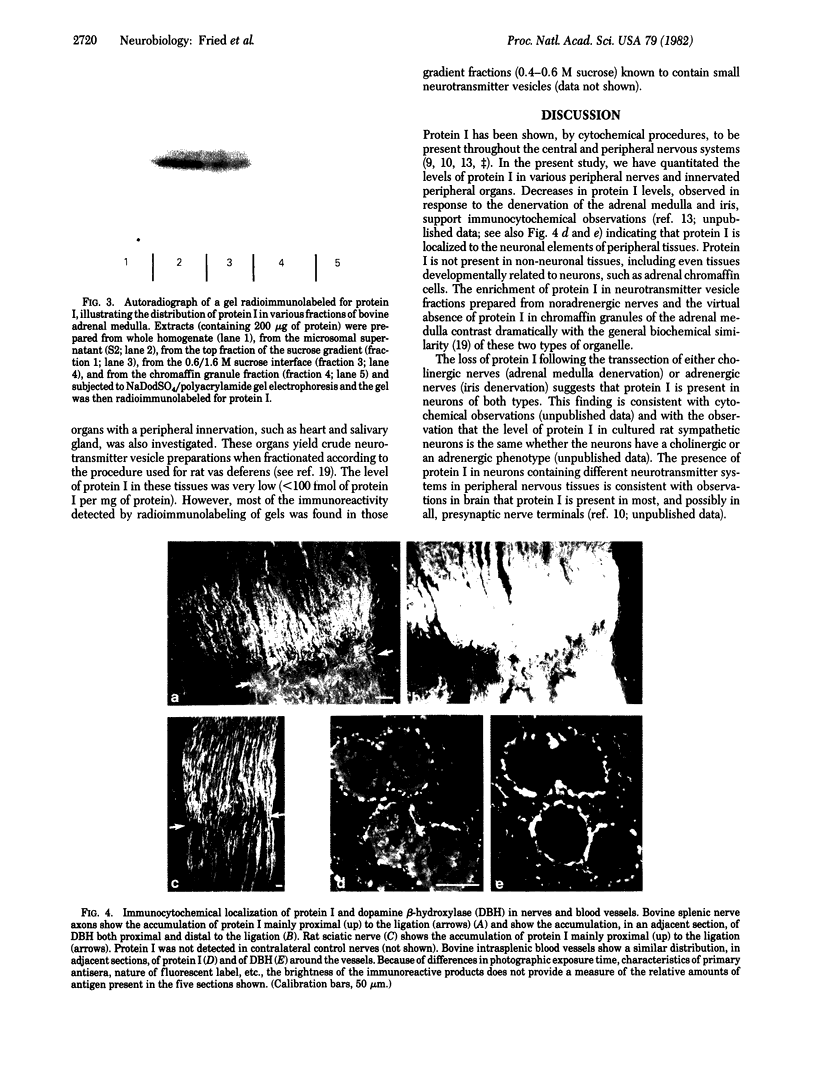

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair W. S., Jurivich D., Goodenough U. W. Localization of cellular antigens in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. J Cell Biol. 1978 Oct;79(1):281–285. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedeczky I., Smith A. D. Ultrastructural studies on the adrenal medulla of golden hamster: origin and fate of secretory granules. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;124(3):367–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00355037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom F. E., Ueda T., Battenberg E., Greengard P. Immunocytochemical localization, in synapses, of protein I, an endogenous substrate for protein kinases in mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5982–5986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragg B. G. The density of synapses and neurones in the motor and visual areas of the cerebral cortex. J Anat. 1967 Sep;101(Pt 4):639–654. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlström A. Observations on the accumulation of noradrenaline in the proximal and distal parts of peripheral adrenergic nerves after compression. J Anat. 1965 Oct;99(Pt 4):677–689. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Ueda T., Bloom F. E., Battenberg E., Greengard P. Widespread distribution of protein I in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5977–5981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Greengard P. Serotonin stimulates phosphorylation of protein I in the facial motor nucleus of rat brain. Nature. 1981 Jan 1;289(5793):76–79. doi: 10.1038/289076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehinger B., Falck B. Concomitant adrenergic and parasympathetic fibres in the rat iris. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966 Jun;67(2):201–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1966.tb03301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarizing agents and cyclic nucleotides regulate the phosphorylation of specific neuronal proteins in rat cerebral cortex slices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5195–5199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G., Lagercrantz H., Hökfelt T. Improved isolation of small noradrenergic vesicles from rat seminal ducts following castration. A density gradient centrifugation and morphological study. Neuroscience. 1978;3(12):1271–1291. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(78)90147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried G. Small noradrenergic storage vesicles isolated from rat vas deferens--biochemical and morphological characterization. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1980;493:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelz S. E., Nestler E. J., Chehrazi B., Greengard P. Distribution of protein I in mammalian brain as determined by a detergent-based radioimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helle K. B., Serck-Hanssen G. The adrenal medulla: a model for studies of hormonal and neuronal storage and release mechanisms. Mol Cell Biochem. 1975 Feb 28;6(2):127–146. doi: 10.1007/BF01732006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjemdahl P., Daleskog M., Kahan T. Determination of plasma catecholamines by high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: comparison with a radioenzymatic method. Life Sci. 1979 Jul 9;25(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90384-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Multiple phosphorylation sites in protein I and their differential regulation by cyclic AMP and calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. B., Greengard P. Two calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases, which are highly concentrated in brain, phosphorylate protein I at distinct sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. L., Thureson-Klein A. K., Yen S. H., Baggett J. M., Gasparis M. S., Kirksey D. F. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase distribution in density gradients: physiological and artefactual implications. J Neurobiol. 1979 May;10(3):291–307. doi: 10.1002/neu.480100308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Forn J., Greengard P. Depolarization-induced phosphorylation of specific proteins, mediated by calcium ion influx, in rat brain synaptosomes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2764–2773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagercrantz H. On the composition and function of large dense cored vesicles in sympathetic nerves. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmfors T., Sachs C. Direct studies on the disappearance of the transmitter and changes in the uptake-storage mechanisms of degenerating adrenergic nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Jul;64(3):211–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler E. J., Greengard P. Dopamine and depolarizing agents regulate the state of phosphorylation of protein I in the mammalian superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7479–7483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostberg A. J., Raisman G., Field P. M., Iversen L. L., Zigmond R. E. A quantitative comparison of the formation of synapses in the rat superior cervical sympathetic ganglion by its own and by foreign nerve fibres. Brain Res. 1976 May 14;107(3):445–470. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Mueller R. A., Axelrod J. Trans-synaptic induction of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Oct;169(2):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P., Berzins K., Cohen R. S., Blomberg F., Grab D. J., Siekevitz P. Subcellular distribution in cerebral cortex of two proteins phosphorylated by a cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):308–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]