Abstract
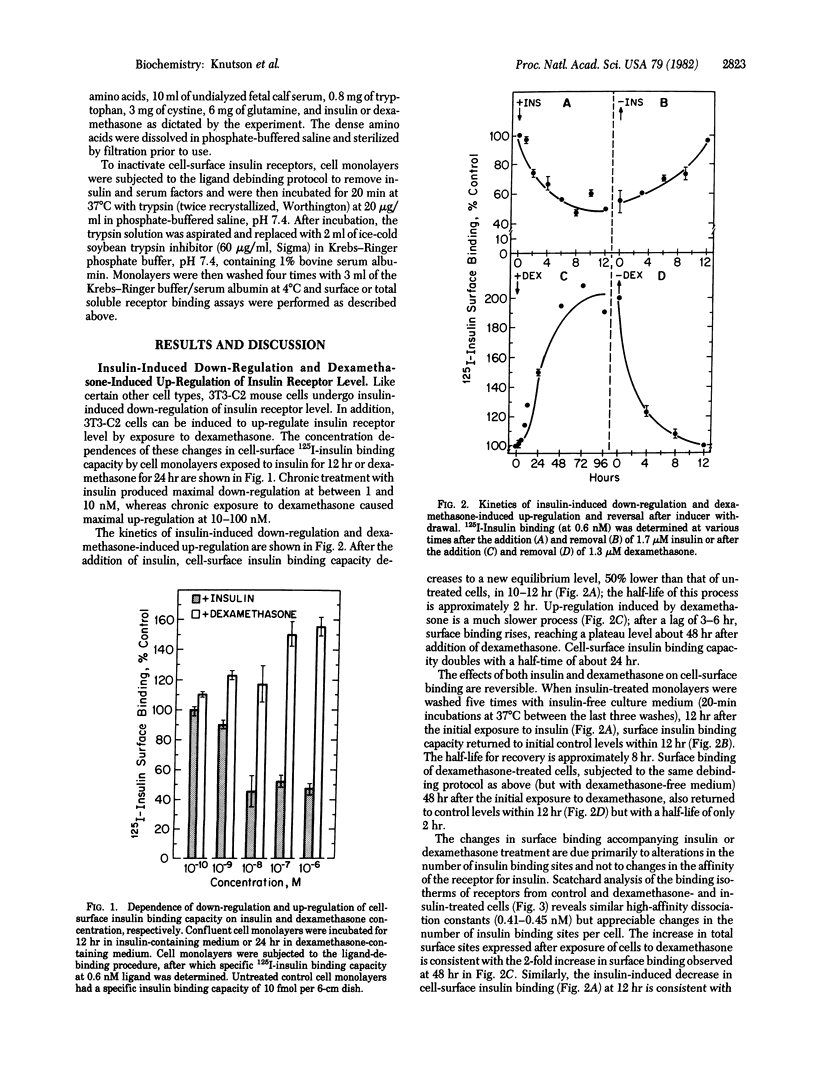
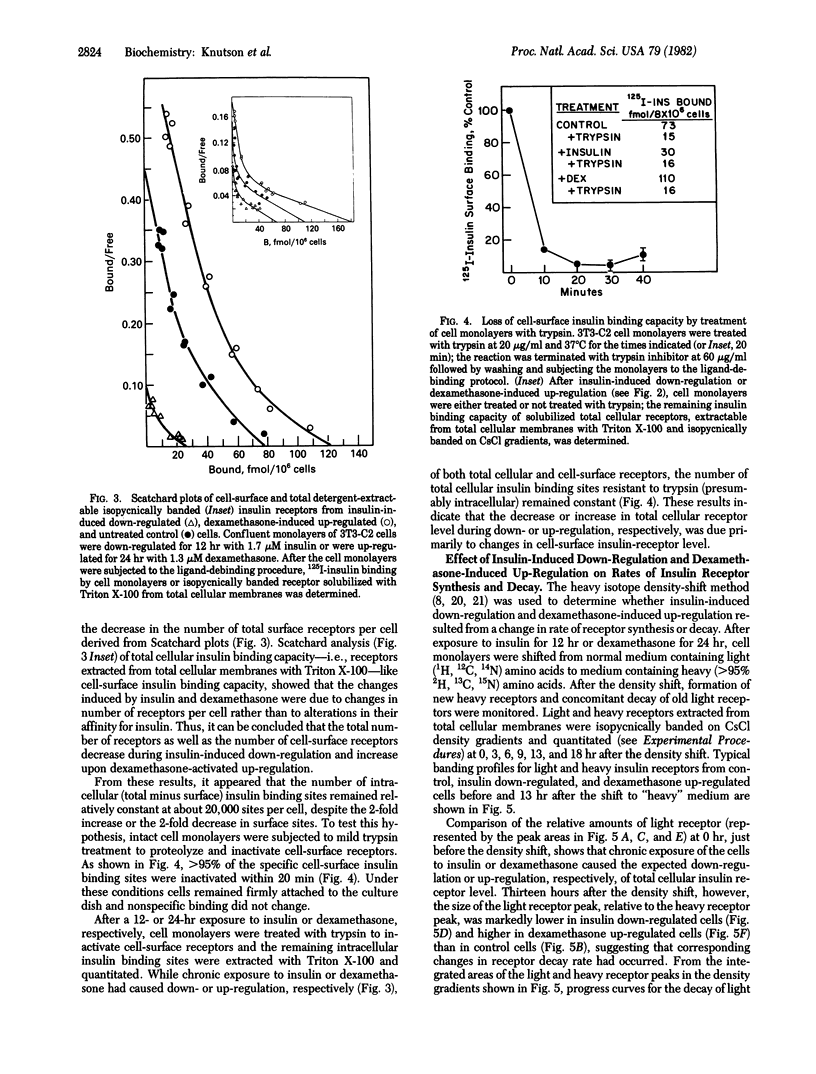
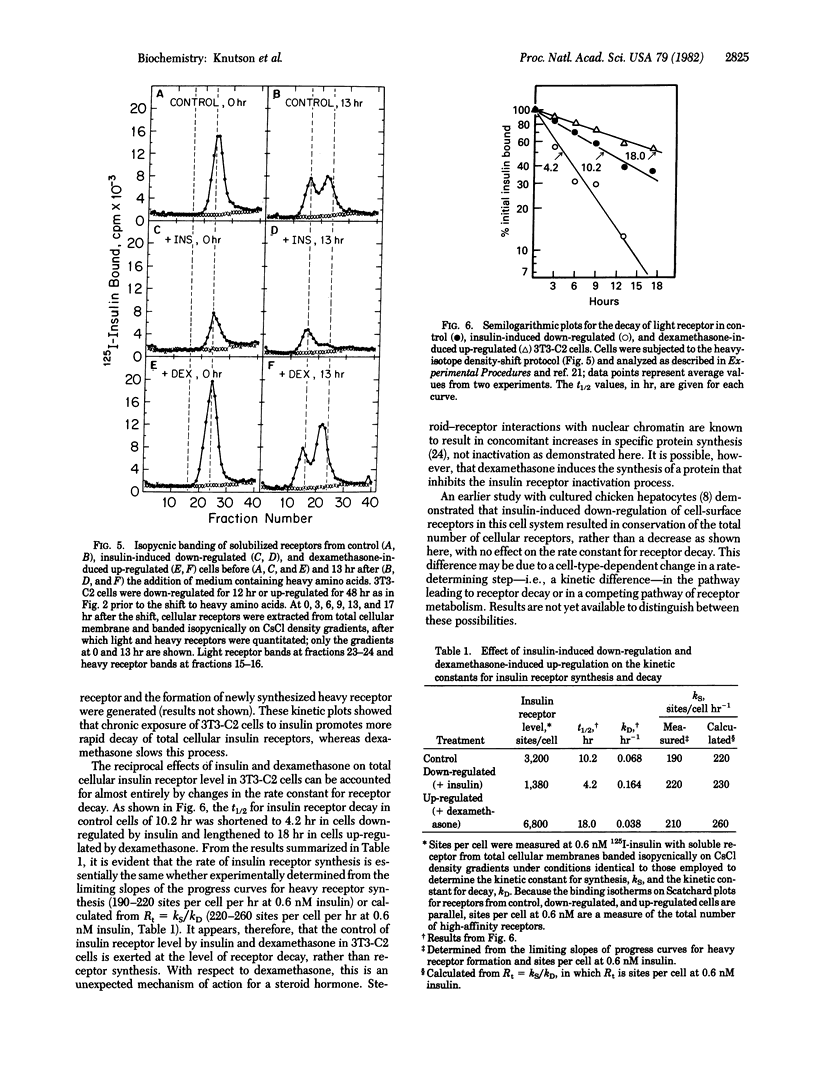
Chronic exposure of 3T3 mouse fibroblasts to insulin or to the glucocorticoid dexamethasone induces down-regulation and up-regulation, respectively, of cell-surface and total cellular insulin binding capacity. Both processes are reversed upon withdrawal of the inducer. Scatchard analysis of insulin binding for receptors in the down- and up-regulated states indicates that the changes in binding capacity result primarily from alterations in insulin receptor level. That these alterations in total receptor level are due to changes in cell-surface receptor level is indicated by the fact that the level of trypsin-insensitive, presumably intracellular, insulin binding sites does not change appreciably upon down- and up-regulation. The effects of insulin-induced down-regulation and dexamethasone-induced up-regulation on the rates of insulin receptor synthesis and decay were assessed by the heavy-isotope density-shift technique. Cells were shifted to medium containing heavy (2H, 13C, 15N) amino acids and, at various times after the shift, light and heavy receptors solubilized from total cellular membranes were resolved by isopycnic banding on density gradients and then quantitated. It was demonstrated that the insulin- and dexamethasone-induced alterations in insulin receptor level were due entirely to changes in the rate constant for receptor inactivation. The decrease in the first-order rate constant for receptor decay caused by dexamethasone is unexpected in view of the known action of steroid hormones in the induction of the synthesis of specific proteins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker J. B., Barsh G. S., Carney D. H., Cunningham D. D. Dexamethasone modulates binding and action of epidermal growth factor in serum-free cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1882–1886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., Gorden P., Roth J., Kahn C. R., De Meyts P. Fluctuations in the affinity and concentration of insulin receptors on circulating monocytes of obese patients: effects of starvation, refeeding, and dieting. J Clin Invest. 1976 Nov;58(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1172/JCI108565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackard W. G., Sherrod J., Ludeman C. Effect of down-regulation of insulin receptors on receptor-antibody binding. Endocrinology. 1981 Feb;108(2):478–483. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-2-478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L., O'Malley B. W. Mechanism of action of the sex steroid hormones (second of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Jun 17;294(25):1372–1381. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197606172942505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigolini M., Smith U. Human adipose tissue in culture. VIII. Studies on the insulin-antagonistic effect of glucocorticoids. Metabolism. 1979 May;28(5):502–510. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Isolation of the insulin receptor of liver and fat-cell membranes (detergent-solubilized-( 125 I)insulin-polyethylene glycol precipitation-sephadex). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantus I. G., Ryan J., Hizuka N., Gorden P. The effect of glucocorticoids on the insulin receptor: an in vivo and in vitro study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 May;52(5):953–960. doi: 10.1210/jcem-52-5-953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr, de Meyts P., Buell D. N. Insulin-dependent regulation of insulin receptor concentrations: a direct demonstration in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Goldfine I. D., Neville D. M., Jr, De Meyts P. Alterations in insulin binding induced by changes in vivo in the levels of glucocorticoids and growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1978 Oct;103(4):1054–1066. doi: 10.1210/endo-103-4-1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson F. A., Grunfeld C., Kahn C. R., Roth J. Regulation of insulin receptors and insulin responsiveness in 3T3-L1 fatty fibroblasts. Endocrinology. 1979 May;104(5):1383–1392. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-5-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Kahn C. R., Hedo J. A., Van Obberghen E., Yamada K. M. Insulin-induced receptor loss in cultured human lymphocytes is due to accelerated receptor degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6917–6921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosmakos F. C., Roth J. Insulin-induced loss of the insulin receptor in IM-9 lymphocytes. A biological process mediated through the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9860–9869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Lane M. D. Evidence for different pathways for the degradation of insulin and insulin receptor in the chick liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1372–1377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M. N., Livingston J. N. Insulin binding to solubilized material from fat cell membranes: evidence for two binding species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp M., Lane M. D. On the mechanism of ligand-induced down-regulation of insulin receptor level in the liver cell. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1689–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Johnson J., Liu F., Jen P., Reaven G. M. The effects of acute and chronic dexamethasone administration on insulin binding to isolated rat hepatocytes and adipocytes. Metabolism. 1975 Apr;24(4):517–527. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen B., Beckner S., Blecher M. Hormone receptors. 7. Characteristics of insulin receptors in a new line of cloned neonatal rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 6;542(3):470–485. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C., Kaufmann S. H., Mackall J. C., Student A. K., Lane M. D. Alterations in insulin binding accompanying differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C., Lane M. D. Expression of insulin receptors during preadipocyte differentiation. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;18:97–117. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(80)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C., Lane M. D. Insulin receptor synthesis and turnover in differentiating 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):285–289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed B. C., Ronnett G. V., Clements P. R., Lane M. D. Regulation of insulin receptor metabolism. Differentiation-induced alteration of receptor synthesis and degradation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3917–3925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Hirsch A., Fung C., Rosen O. M. Development of hormone receptors and hormonal responsiveness in vitro. Insulin receptors and insulin sensitivity in the preadipocyte and adipocyte forms of 3T3-L1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7570–7578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


