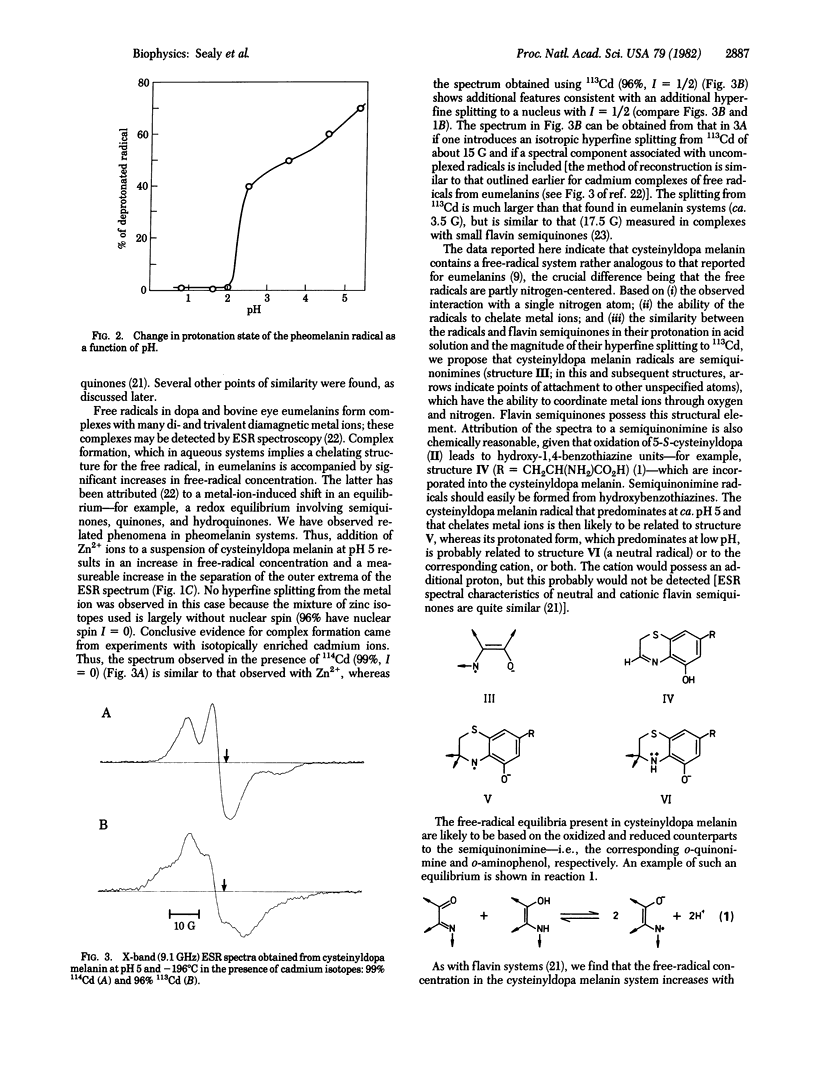
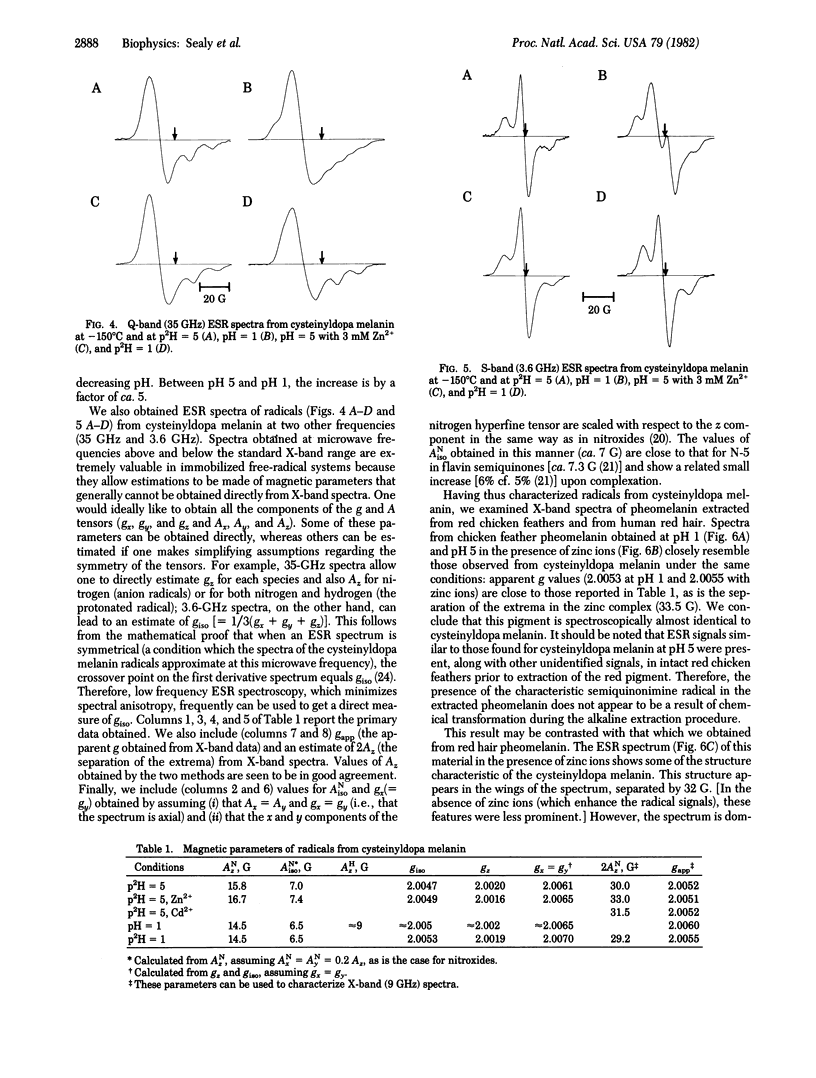
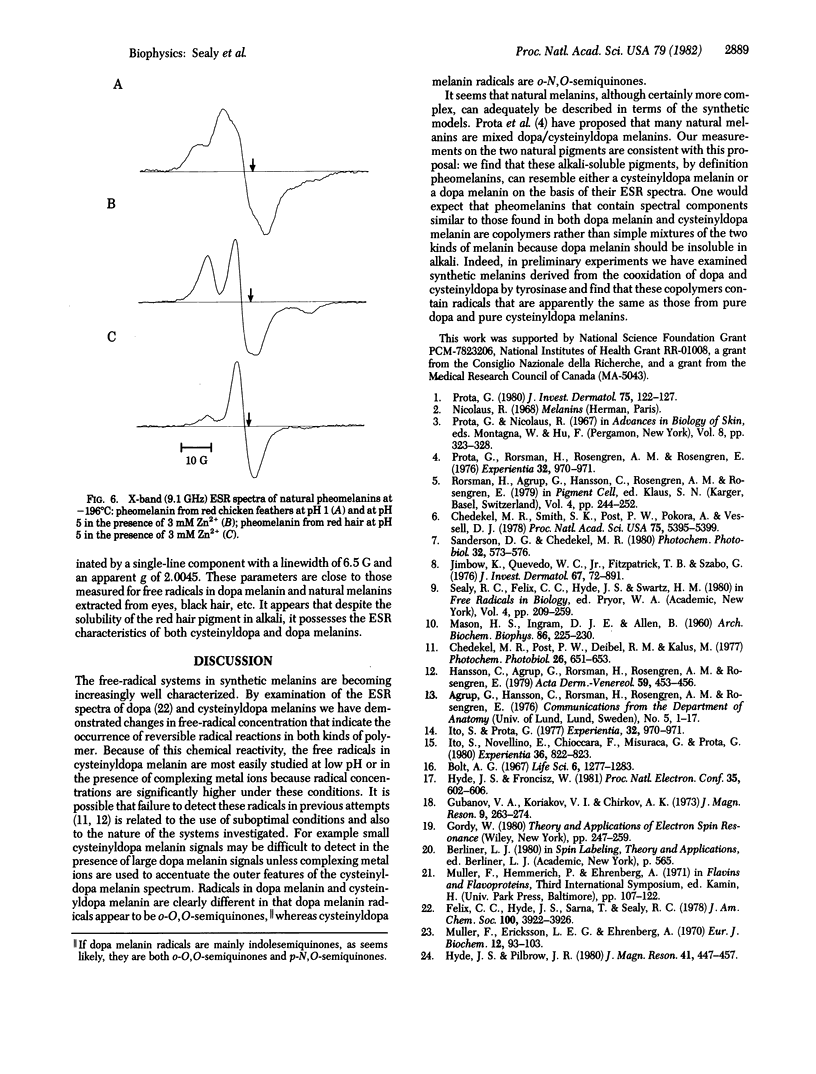
Abstract
Synthetic pheomelanins from enzymic oxidation of the 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (dopa) derivative 5-S-cysteinyldopa have been examined by ESR spectroscopy. These alkalisoluble polymers contain a novel kind of free radical that is spectroscopically distinct from that found in eumelanins. Delocalization of the unpaired electron onto a nitrogen atom and the ability of the radical to chelate complexing metal ions strongly suggest an o-semiquinonimine structure. The synthetic pheomelanin was compared with natural red pigments extracted from human red hair and from red chicken feathers. Spectroscopically, the chicken feather pheomelanin is almost identical to synthetic cysteinyldopa pheomelanin. In contrast, the pigment from red hair has a major spectral component very similar to that found in dopa melanin, with a smaller component corresponding to that found in cysteinyldopa melanin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolt A. G. Interactions between human melanoprotein and chlorpromazine derivatives. I. Isolation and purification of human melanoprotein from hair and melanoma tissue. Life Sci. 1967 Jun 15;6(12):1277–1283. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedekel M. R., Post P. W., Deibel R. M., Kalus M. Photodestruction of phaeomelanin. Photochem Photobiol. 1977 Dec;26(6):651–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1977.tb07546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chedekel M. R., Smith S. K., Post P. W., Pokora A., Vessell D. L. Photodestruction of pheomelanin: role of oxygen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5395–5399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson C., Agrup G., Rorsman H., Rosengren A. M., Rosengren E. Electron spin resonance studies on phaeomelanins. Acta Derm Venereol. 1979;59(5):453–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Novellino E., Chioccara F., Misuraca G., Prota G. Co-polymerization of dopa and cysteinyldopa in melanogenesis in vitro. Experientia. 1980 Jul 15;36(7):822–823. doi: 10.1007/BF01978591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimbow K., Quevedo W. C., Jr, Fitzpatrick T. B., Szabo G. Some aspects of melanin biology: 1950-1975. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Jul;67(1):72–89. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12512500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASON H. S., INGRAM D. J., ALLEN B. The free radical property of melanins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1960 Feb;86:225–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(60)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Eriksson L. E., Ehrenberg A. Flavin radical chelates as studies by electron spin resonance and isotopic substitution. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jan;12(1):93–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prota G. Recent advances in the chemistry of melanogenesis in mammals. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jul;75(1):122–127. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prota G., Rorsman H., Rosengren A. M., Rosengren E. Phaeomelanic pigments from a human melanoma. Experientia. 1976 Aug 15;32(8):970–971. doi: 10.1007/BF01933916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prota G., Rorsman H., Rosengren A. M., Rosengren E. Phaeomelanic pigments from a human melanoma. Experientia. 1976 Aug 15;32(8):970–971. doi: 10.1007/BF01933916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



