Sir,
Clear cell meningioma (CCM) is a rare variant of meningioma with an aggressive clinical course and usually occurs in the cerebello pontine angle (CPA) or cauda equina.[2,3] We report a case of CCM occurring in CPA that mimicked a trigeminal schawannoma by the virtue of its dumbbell shape and erosion of petrous bone.
A 14-year-old female presented with left-sided facial numbness and heaviness for 2.5 months, followed by left-sided hearing loss and features of raised intracranial pressure for 2 months. A month later she developed left facial paresis of lower motor neuron type along with difficulty in swallowing and imbalance while walking with right lower limb weakness. Clinical examination revealed bilateral papilledema with left-sided trigeminal (both sensory and motor), facial (LMN type) involvement. The left glossopharyngeal, vagus, and hypoglossal nerves were involved. She had left-sided cerebellar signs with subtle right hemiparesis. Contrast-enhanced CT [Figure 1] and magnetic resonance imaging [Figures 2 and 3] of brain revealed a lobulated mass in the left cerebro-pontine angle cistern with extension of the tumor in the middle cranial fossa in the region of Meckel's cave. Radiology showed truncation of the petrous suggesting a trigeminal schwannoma.
Figure 1.
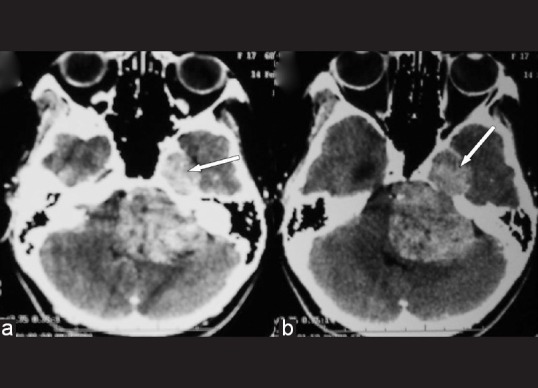
Contrast-enhanced axial sections showing large lobulated dumbbell-shaped extra-axial mass in the left cerebro-pontine angle cistern with extension into middle cranial fossa in the parasellar region (white arrows). There is also erosion destruction of the petrous apex
Figure 2.
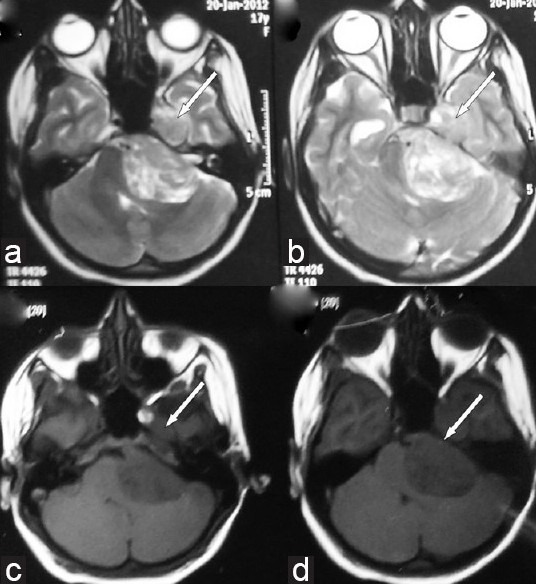
Axial T2 (a, b) and T1-weighted (c, d) images demonstrates large lobulated extra-axial mass in the left cerebro-pontine angle with component in the middle cranial fossa (white arrows). It is heterogeneously hyperintense on T2 and hypointense on T1-weighted images
Figure 3.
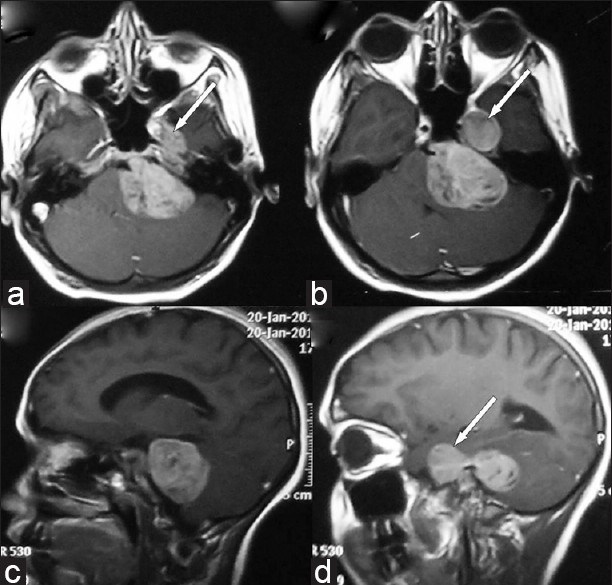
Postgadolinium axial (a, b) and sagittal (c, d) images showing heterogeneous enhancement of the tumor with a tongue of tumor (white arrow) extending forward into the region of the Meckel cave
She underwent a subtotal excision of the tumor through the left retromastoid approach. The lesion was grayish in color and was relatively firm and less suckable. However, CUSA was helpful. The capsule of the lesion was left. There was injury to the superior petrosal sinus and the patient succumbed to venous infarction a week later. Unfortunately, autopsy was not performed.
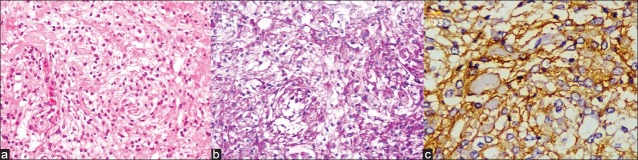
Histopathological examination showed round to polygonal cells arranged in whorls, showing clear cytoplasm and round to oval nuclei with dispersed chromatin and insconspicuous nucleoli. There was perivascular and interstitial deposition of collagenous material in a block manner. Tumor cells tested positive for PAS and epithelial membrane antigen [Figure 4]. Features suggested clear cell meningioma, WHO grade II. Ki 67 labelling index was 2.5%.
Figure 4.
Clear cell meningioma (a) consisting of patternless growth of clear cells (H and E, ×200) (b) containing glycogen (PAS, ×200). (c) Tumor cells express epithelial membrane antigen. (Immunoperoxidase stain, ×400)
Trigeminal schwannoma typically grows from posterior fossa into the middle cranial fossa as the lesion grows along the nerve fibers. The truncation of petrous apex suggests chronic compression and is usually seen with trigeminal schwannoma. Occasionally lymphoma or lymphohistiocytic inflammation may spread along the nerve fibers to occupy both the posterior and the middle cranial fossa thereby, mimicking a schwannoma.[1,5]
Clear cell meningioma is a rare variant that is often seen in the CPA and is seen in relatively younger patients. The behavior of this variant is aggressive and is included in Grade II WHO.[2,3] Gross total resection followed by radiotherapy is the treatment for these lesions. However, lesions in the meckel's cave meningiomas in particular, are associated with more deficits following total excision.[4]
Our patient had rapidly worsening symptoms over 2 months and was relatively young. The clinical features suggested an aggressive lesion rather than a schwannoma. However, the radiology showed a lesion straddling across the petrous to occupy both the middle cranial fossa and posterior fossa along with truncation of petrous suggesting a trigeminal schwannoma.
The above case highlights the potential of meningiomas to grow along the nerve fibers straddling across the petrous to occupy both middle cranial and posterior fossa along with erosion of petrous mimicking a trigeminal schwannoma. Whether, such a phenomenon is limited to more aggressive meningiomas like clear cell variant remains unclear.
Footnotes
Available FREE in open access from: http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com/text.asp?2012/3/1/93/99940
Contributor Information
Pravin Salunke, Email: drpravin_salunke@yahoo.co.uk.
Barun K. Pal, Email: drbarunpal@gmail.com.
Sameer Vyas, Email: sameer574@yahoo.co.in.
Bishan D. Radotra, Email: bishanradotra@hotmail.com.
REFERENCES
- 1.Abdel Aziz KM, van Loveren HR. Primary lymphoma of Meckel's cave mimicking trigeminal schwannoma: Case report. Neurosurgery. 1999;44:859–62. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199904000-00096. discussion 862-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen H, Li XM, Chen YC, Wu JS, Dou YF, Wang Y, et al. Intracranial clear cell meningioma: A clinicopathologic study of 15 cases. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2011;153:1769–80. doi: 10.1007/s00701-011-1052-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jain D, Sharma MC, Sarkar C, Suri V, Garg A, Singh M, et al. Clear cell meningioma, an uncommon variant of meningioma: A clinicopathologic study of nine cases. J Neurooncol. 2007;81:315–21. doi: 10.1007/s11060-006-9237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Muto J, Kawase T, Yoshida K. Meckel's cave tumors: Relation to the meninges and minimally invasive approaches for surgery: Anatomic and clinical studies. Neurosurgery. 2010;67(Suppl Operative 3):ons291–8. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000382967.84940.52. discussion ons298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tronnier V, Pannier G, Gottschalk S, Petersen D, Reusche E, Merz H. Isolated lympho-histiocytic inflammation of the Gasserian ganglion mimicking trigeminal schwannoma. Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2010;71:99–103. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1237714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]