Abstract
We report that human leukocyte interferon preparations increase the expression of beta 2-microglobulin by 100-200% on the surface of normal fibroblast and melanoma cell lines sensitive to interferon. This increase in expression can be correlated with an increase in HLA synthesis as measured by incorporation of [35S]methionine in these antigens. This enhanced HLA synthesis, which is 5- to 17-fold, is time dependent and dose related. Synchronized cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle appear to be more sensitive to this interferon action. Neither an increase in surface expression nor in HLA synthesis is observed in a melanoma cell line resistant to the antiviral and antigrowth effects of interferon. Furthermore, there appears to be a stronger correlation between this increased HLA synthesis and the antiviral function than between it and the antiproliferative action of interferon.
Full text
PDF
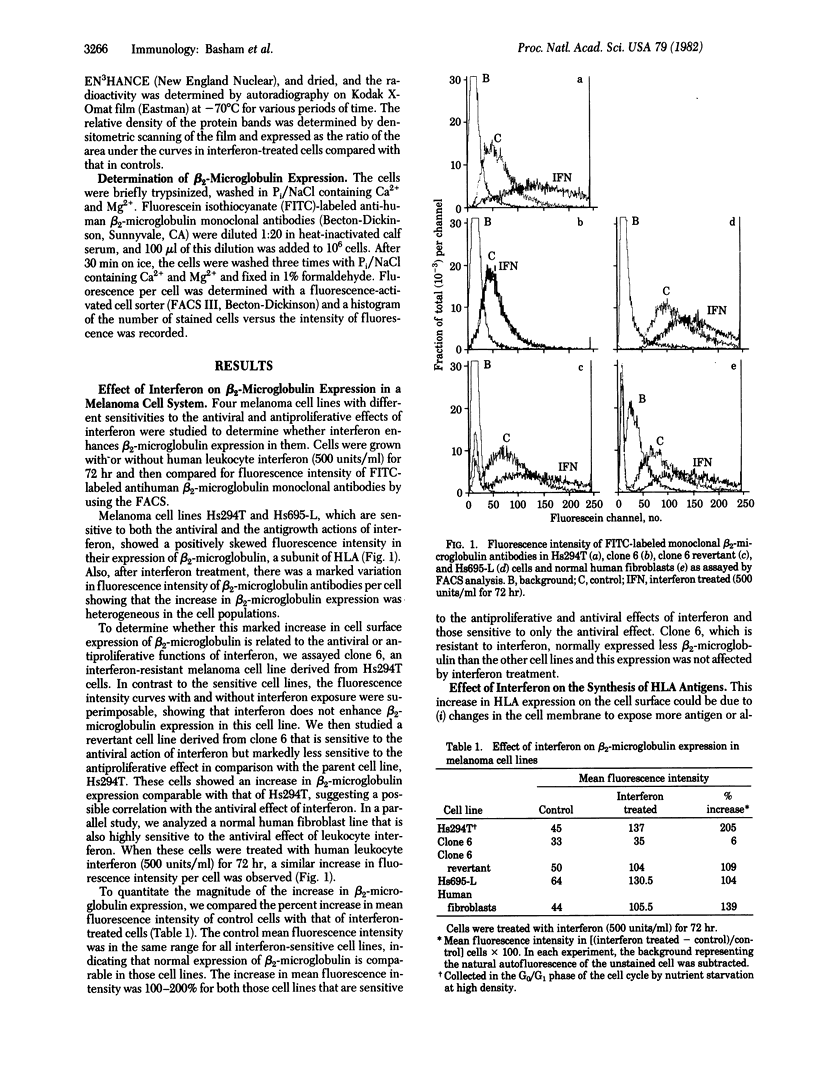
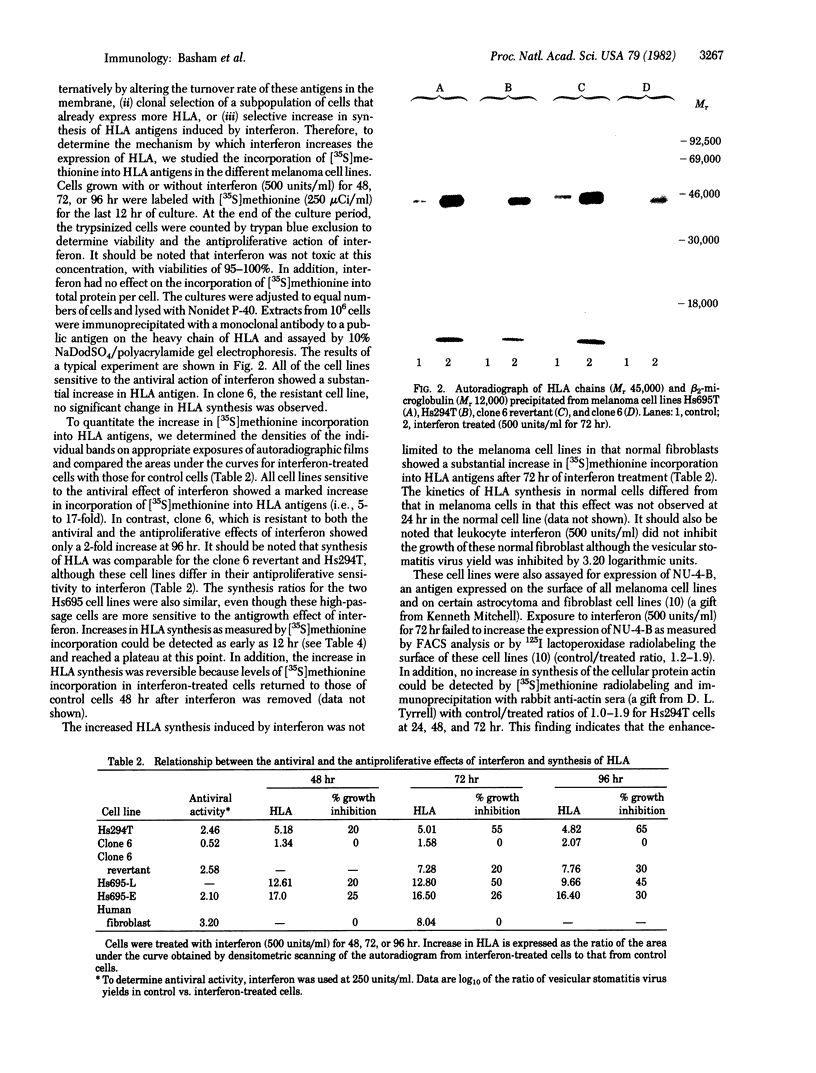


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attallah A. M., Strong D. M. Differential effects of interferon on the MHC expression of human lymphocytes. Enhanced expression of HLA without effect on Ia. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;60(1):101–105. doi: 10.1159/000232328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouty-Boyé D., Macieira-Coelho A., Fiszman M., Gresser I. Interferon and cell division. 8. Effect of interferon on macromolecular synthesis in L1210 Cells in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1973 Jul 15;12(1):250–258. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910120126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasey A. A., Bartholomew J. C., Merigan T. C. Role of G0-G1 arrest in the inhibition of tumor cell growth by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1471–1475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creasey A. A., Bartholomew J. C., Merigan T. C. Role of G0-G1 arrest in the inhibition of tumor cell growth by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1471–1475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Broeze R. J., Lengyel P. Accumulation of an mRNA and protein in interferon-treated Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Nature. 1979 Jun 7;279(5713):523–525. doi: 10.1038/279523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Bono R., Hyafil F., Gresser I. Interferon enhances the amount of membrane-bound beta2-microglobulin and its release from human Burkitt cells. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jun;11(6):524–526. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Kamoun M., Gresser I., Bono R. Enhanced expression of HLA antigens and beta 2-microglobulin on interferon-treated human lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):446–449. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuse A., Kuwata T. Effects of interferon on the human clonal cell line, RSa: inhibition of macromolecular synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1976 Oct;33(1):17–24. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-1-17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S. L., Rubin B. Y., Holmes S. L. Interferon action: induction of specific proteins in mouse and human cells by homologous interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4817–4821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heron I., Hokland M., Berg K. Enhanced expression of beta2-microglobulin and HLA antigens on human lymphoid cells by interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6215–6219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K., Ng A. K., Glassy M. C., Ferrone S. Differential effect of interferon on the expression of tumor-associated antigens and histocompatibility antigens on human melanoma cells: relationship to susceptibility to immune lysis mediated by monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killander D., Lindahl P., Lundin L., Leary P., Gresser I. Relationship between the enhanced expression of histocompatibility antigens on interferon-treated L 1210 cells and their position in the cell cycle. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jan;6(1):56–59. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P., Leary P., Gresser I. Enhancement by interferon of the expression of surface antigens on murine leukemia L 1210 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2785–2788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Glassy M. C., Ferrone S., Jones O. W. Cell cycle and the differential expression of HLA-A,B and HLA-DR antigens on human B lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignaux F., Gresser I. Differential effects of interferon on the expression of H-2K, H-2D, and Ia antigens on mouse lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):721–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]