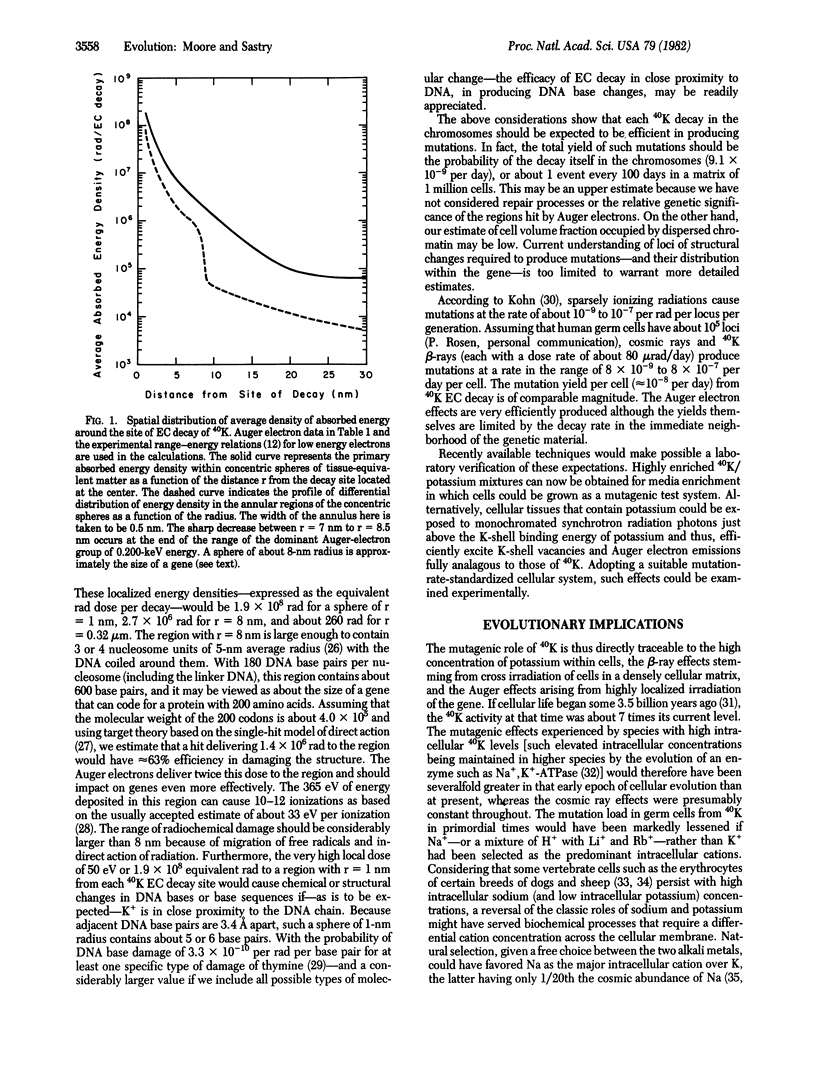
Abstract
We have been interested in the possibility that the low energy electrons (Auger and Coster-Kronig) emitted after the electron capture decay of 40K may have highly localized radiochemical effects on the genetic material--effects dependent upon the intracellular locus of potassium. We report here that these effects are such that the likelihood of mutagenesis by their impact on DNA is substantial. This suggests that intracellular 40K has played a significant role as a mutagenic agent in evolution.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin J. P., Boseley P. G., Bradbury E. M., Ibel K. The subunit structure of the eukaryotic chromosome. Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):245–249. doi: 10.1038/253245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron I. L., Sparks R. L., Horn K. L., Smith N. R. Concentration of elements in mitotic chromatin as measured by x-ray microanalysis. J Cell Biol. 1977 Apr;73(1):193–199. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan P. C., Lisco E., Lisco H., Adelstein S. J. The radiotoxicity of iodine-125 in mammalian cells II. A comparative study on cell survival and cytogenetic responses to 125IUdR, 131TUdR, and 3HTdR. Radiat Res. 1976 Aug;67(2):332–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. Absorption of 20-eV to 50,000-eV electron beams in air and plastic. Radiat Res. 1969 Apr;38(1):7–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Commerford S. L., Bond V. P., Cronkite E. P., Reincke U. Radiotoxicity of intranuclear 125I atoms not bound to DNA. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1980 May;37(5):547–554. doi: 10.1080/09553008014550681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. V. Electrolyte concentrations in red blood cells of British breeds of sheep. Nature. 1954 Nov 13;174(4437):931–932. doi: 10.1038/174931a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodhead D. T., Thacker J., Cox R. Effectiveness of 0.3 keV carbon ultrasoft X-rays for the inactivation and mutation of cultured mammalian cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1979 Aug;36(2):101–114. doi: 10.1080/09553007914550861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer K. G., Hughes W. L. Radiotoxicity of intranuclear tritium, 125 iodine and 131 iodine. Radiat Res. 1971 Jul;47(1):94–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer K. G., Keough G., Smith J. M. Biological toxicity of Auger emitters: molecular fragmentation versus electron irradiation. Curr Top Radiat Res Q. 1978 Jan;12(1-4):335–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis A. I., Adelstein S. J., Haydock C., Sastry K. S. Radiotoxicity of 75Se and 35S: theory and application to a cellular model. Radiat Res. 1980 Dec;84(3):407–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn H. I. X-ray induced mutations, DNA and target theory. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):766–767. doi: 10.1038/263766a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. F., Haseltine W. A. Range of radiochemical damage to DNA with decay of iodine-125. Science. 1981 Aug 21;213(4510):896–898. doi: 10.1126/science.7256283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern M. R., Hariharan P. V., Cerutti P. A. Selective excision of gamma ray damaged thymine from the DNA of cultured mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jun 2;395(1):48–55. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skou J. C. The (Na++K+) activated enzyme system and its relationship to transport of sodium and potassium. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 Jul;7(3):401–434. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


