Abstract
Originating from observations on similarities between the rheumatoid synovial tissue and skin lesions in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions--similarities as to massive infiltrates of "helper" T lymphocytes close to HLA-DR-expressing macrophage/dendritic cells--a notion is formed on the importance of local macrophage-dependent helper T-cell activation in the rheumatoid joint similar to that in a delayed-type skin reaction. In vitro studies on suspended synovial cells have been used to test and qualify these ideas. It is shown that (i) HLA-DR-expressing cells in normal synovial intima can, like epidermal Langerhans cells, mediate T-cell activation; (ii) the large numbers of rheumatoid synovial HLA-DR-expressing macrophage-like/dendritic cells are heterogeneous and mediate either efficient activation or suppression of T-lymphocyte proliferation, and (iii) specificity of rheumatoid T cells can be analyzed with the help of autologous synovial antigen-presenting cells; a specific anti-collagen type II response is reported in three patients.
Full text
PDF
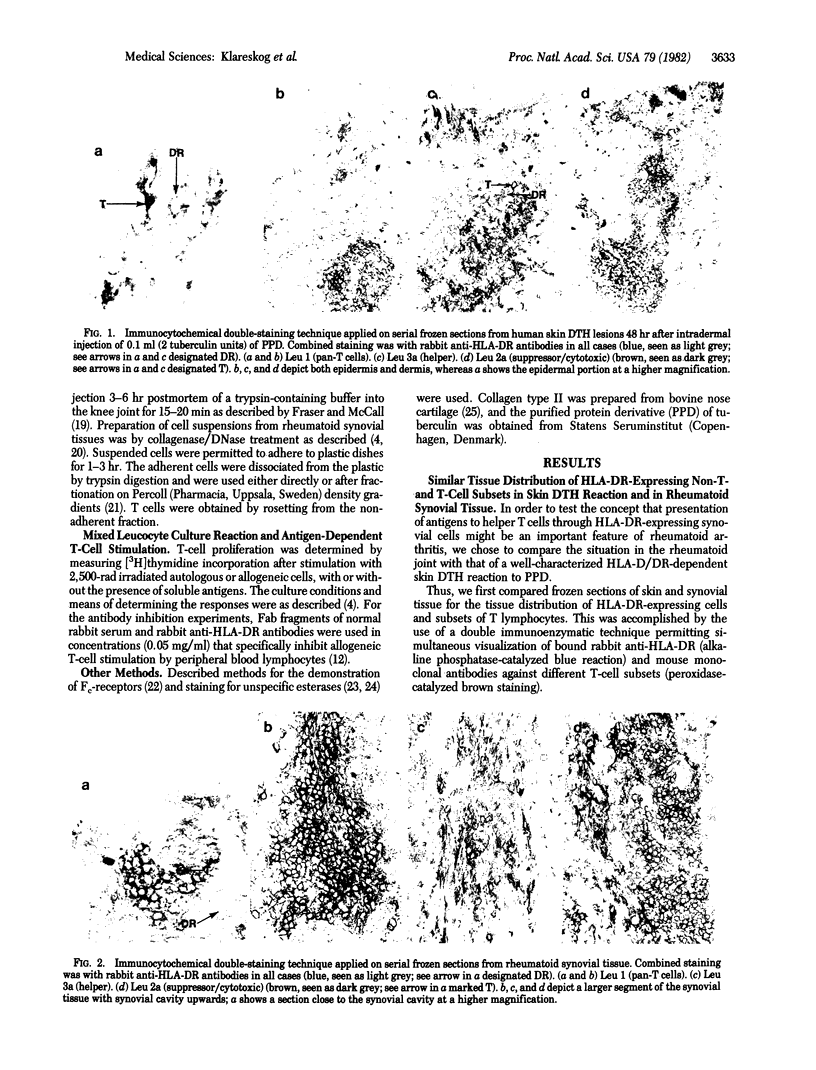
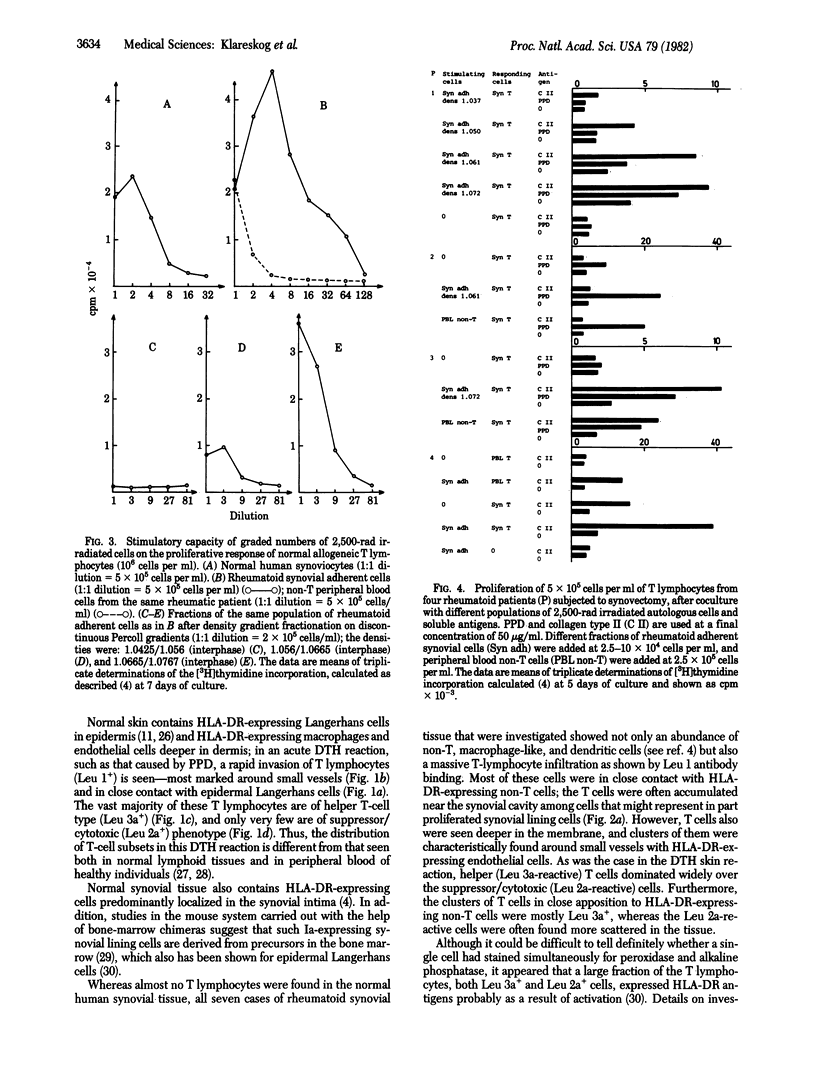


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahamsen T. G., Froland S. S., Natvig J. B., Pahle J. Elution and characterization of lymphocytes from rheumatoid inflammatory tissue. Scand J Immunol. 1975;4(8):823–830. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb03723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsen T. G., Johnson P. M., Natvig J. B. Membrane characteristics of adherent cells dissociated from rheumatoid synovial tissue. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jun;28(3):474–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergholtz B. O., Thorsby E. Macrophage/T-lymphocyte interaction in the immune response to PPD in humans. Scand J Immunol. 1979;9(6):511–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb03279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braathen L. R., Thorsby E. Studies on human epidermal Langerhans cells. I. Allo-activating and antigen-presenting capacity. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(4):401–408. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay C., Chattopadhyay H., Natvig J. B., Michaelsen T. E., Mellbye O. J. Lack of suppressor cell activity in rheumatoid synovial lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(4):309–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Graham R., Russell G., Krane S. M. Collagenase production by rheumatoid synovial cells: stimulation by a human lymphocyte factor. Science. 1977 Jan 14;195(4274):181–183. doi: 10.1126/science.188134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer J. M., Robinson D. R., Krane S. M. Prostaglandin production by rheumatoid synovial cells: stimulation by a factor from human mononuclear Cells. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1399–1404. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Benike C. J., Glickman E., Evans R. L. Antibodies to membrane structures that distinguish suppressor/cytotoxic and helper T lymphocyte subpopulations block the mixed leukocyte reaction in man. J Exp Med. 1981 Jul 1;154(1):193–198. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Warnke R., Fox R. I., Dilley J., Benike C. J., Levy R. Studies of a human T lymphocyte antigen recognized by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1791–1795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. R., McCall J. F. Culture of synovial cells in vitro. Notes on isolation and propagation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Jul;24(4):351–359. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.4.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Panayi G., Duke O., Bofill M., Poulter L. W., Goldstein G. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981 Oct 17;2(8251):839–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Tidman N., Selby W. S., Thomas J. A., Granger S., Kung P. C., Goldstein G. Human T lymphocytes of inducer and suppressor type occupy different microenvironments. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):81–84. doi: 10.1038/288081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Holm G., Wigzell H. Surface markers on human T and B lymphocytes. I. A large population of lymphocytes forming nonimmune rosettes with sheep red blood cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Aug 1;136(2):207–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Tamaki K., Sachs D. H. Epidermal Langerhans cells are derived from cells originating in bone marrow. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):324–326. doi: 10.1038/282324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Forsum U., Malmnäs Tjernlund U. K., Kabelitz D., Wigren A. Appearance of anti-HLA-DR-reactive cells in normal and rheumatoid synovial tissue. Scand J Immunol. 1981 Aug;14(2):183–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1981.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Tjernlund U., Forsum U., Peterson P. A. Epidermal Langerhans cells express Ia antigens. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):248–250. doi: 10.1038/268248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klareskog L., Trägårdh L., Lindblom J. B., Peterson P. A. Reactivity of a rabbit antiserum against highly purified HLA-DR antigens. Scand J Immunol. 1978 Mar;7(3):199–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fu S. M., Winchester R. J., Yu D. T., Kunkel H. G. Ia determinants on stimulated human T lymphocytes. Occurrence on mitogen- and antigen-activated T cells. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):246–255. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert I. A., Suitters A. J., Chisholm P. M. Expression of Ia antigen on epidermal keratinocytes in graft-versus-host disease. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):149–150. doi: 10.1038/293149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. W., Dallman M., Barclay A. N. Graft-versus-host disease induces expression of Ia antigen in rat epidermal cells and gut epithelium. Nature. 1981 Sep 10;293(5828):150–151. doi: 10.1038/293150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason D. Y., Sammons R. Alkaline phosphatase and peroxidase for double immunoenzymatic labelling of cellular constituents. J Clin Pathol. 1978 May;31(5):454–460. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.5.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger Z., Hoffeld J. T., Oppenheim J. J. Macrophage-mediated suppression. I. Evidence for participation of both hdyrogen peroxide and prostaglandins in suppression of murine lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta L., Webb S. R., Grossi C. E., Lydyard P. M., Cooper M. D. Functional analysis of two human T-cell subpopulations: help and suppression of B-cell responses by T cells bearing receptors for IgM or IgG. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):184–200. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller J., Brun del Re G., Buerki H., Keller H. U., Hess M. W., Cottier H. Nonspecific acid esterase activity: a criterion for differentiation of T and B lymphocytes in mouse lymph nodes. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Apr;5(4):270–274. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppema S., Bhan A. K., Reinherz E. L., McCluskey R. T., Schlossman S. F. Distribution of T cell subsets in human lymph nodes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):30–41. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. S. Determinant selection and macrophage function in genetic control of the immune response. Immunol Rev. 1978;40:136–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb00404.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G., Sullivan A. K. Ia antigen expression on human epidermal Langerhans cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):247–248. doi: 10.1038/268247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solinger A. M., Bhatnagar R., Stobo J. D. Cellular, molecular, and genetic characteristics of T cell reactivity to collagen in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3877–3881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P. Association of the B-cell alloantigen DRw4 with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 20;298(16):869–871. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804202981602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stastny P. Mixed lymphocyte cultures in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1148–1157. doi: 10.1172/JCI108382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Moore R. N., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of murine macrophage Ia-antigen expression by products of activated spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1734–1744. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Katz S. I., Shevach E. M., Rosenthal A. S., Green I. Analogous functions of macrophages and Langerhans cells in the initiation in the immune response. J Invest Dermatol. 1978 Jul;71(1):59–64. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12544055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjernlund U. M. Ia-like antigens in lichen planus. Acta Derm Venereol. 1980;60(4):309–314. doi: 10.2340/0001555560309314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjernlund U. M., Scheynius A., Kabelitz D., Klareskog L. Anti-Ia-reactive cells in mycosis fungoides: a study of skin biopsies, single epidermal cells and circulating T lymphocytes. Acta Derm Venereol. 1981;61(4):291–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius R. A., Rocklin R. E., David J. R. Cellular sensitivity to collagen in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 17;299(7):327–332. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197808172990703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Autoimmunity to type II collagen an experimental model of arthritis. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):857–868. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Boxel J. A., Paget S. A. Predominantly T-cell infiltrate in rheumatoid synovial membranes. N Engl J Med. 1975 Sep 11;293(11):517–520. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197509112931101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Luthra H. S., Stuart J. M., David C. S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Major histocompatibility complex (I region) linkage and antibody correlates. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):688–700. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zembala M., Lemmel E. M. Inhibitory factor(s) of lymphoproliferation produced by synovial fluid mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients: the role of monocytes in suppression. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1087–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zvaifler N. J. The immunopathology of joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):265–336. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60299-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]