Abstract
In illuminated rod outer segment membranes, GTP and guanosine 5'-[beta, gamma-imido]triphosphate (p[NH]ppG) have reciprocal effects on cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDEase; 3':5'-cyclic-nucleotide 5'-nucleotidohydrolase, EC 3.1.4.17) activity and cGMP binding to noncatalytic sites on that enzyme. Two micromolar p[NH]ppG increased PDEase activity more than 2-fold while inhibiting cGMP binding more than 40%. Reduction of noncatalytic cGMP binding, which followed addition of p[NH]ppG, was not a result of PDEase activation. Both effects of p[NH]ppG were completely dependent on the presence of bleached rhodopsin. A heat-stable factor has been found to inhibit PDEase activity and also to stimulate cGMP binding to noncatalytic cGMP binding sites. Addition of p[NH]ppG reversed the effects of this factor on both PDEase activity and cGMP binding. During purification of this material, the activity peaks for both PDEase inhibition and activation of noncatalytic cGMP binding comigrated on both Blue Sepharose CL-6B column chromatography and sucrose density gradients centrifugation, suggesting that the same factor could be responsible for both inhibition of PDEase activity and enhancement of noncatalytic cGMP binding. Limited tryptic proteolysis of PDEase, which markedly reduced cGMP binding to the noncatalytic sites, and experiments using highly purified cAMP (free of cGMP) as substrate for PDEase showed that the binding of cGMP to noncatalytic sites was not required for the heat-stable inhibitory factor to inhibit PDEase activity. We discuss possible relationships between the regulation of PDEase and the binding of cGMP to noncatalytic sites.
Full text
PDF

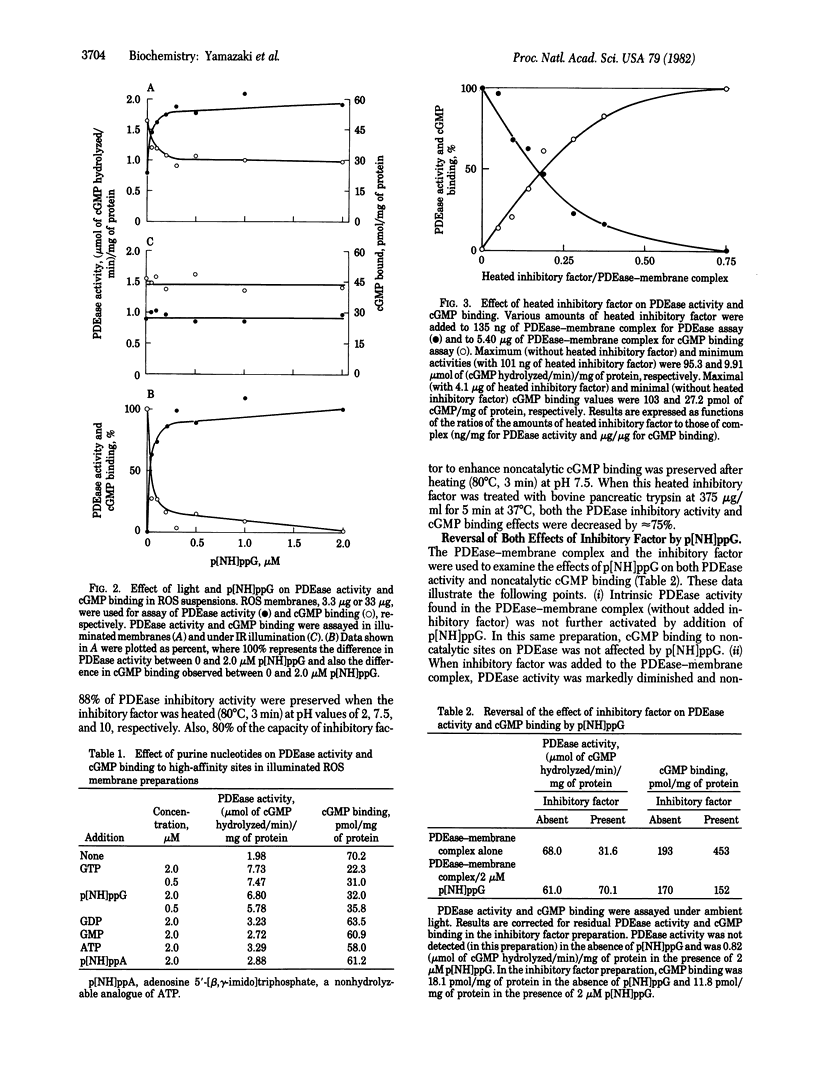

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baehr W., Devlin M. J., Applebury M. L. Isolation and characterization of cGMP phosphodiesterase from bovine rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11669–11677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
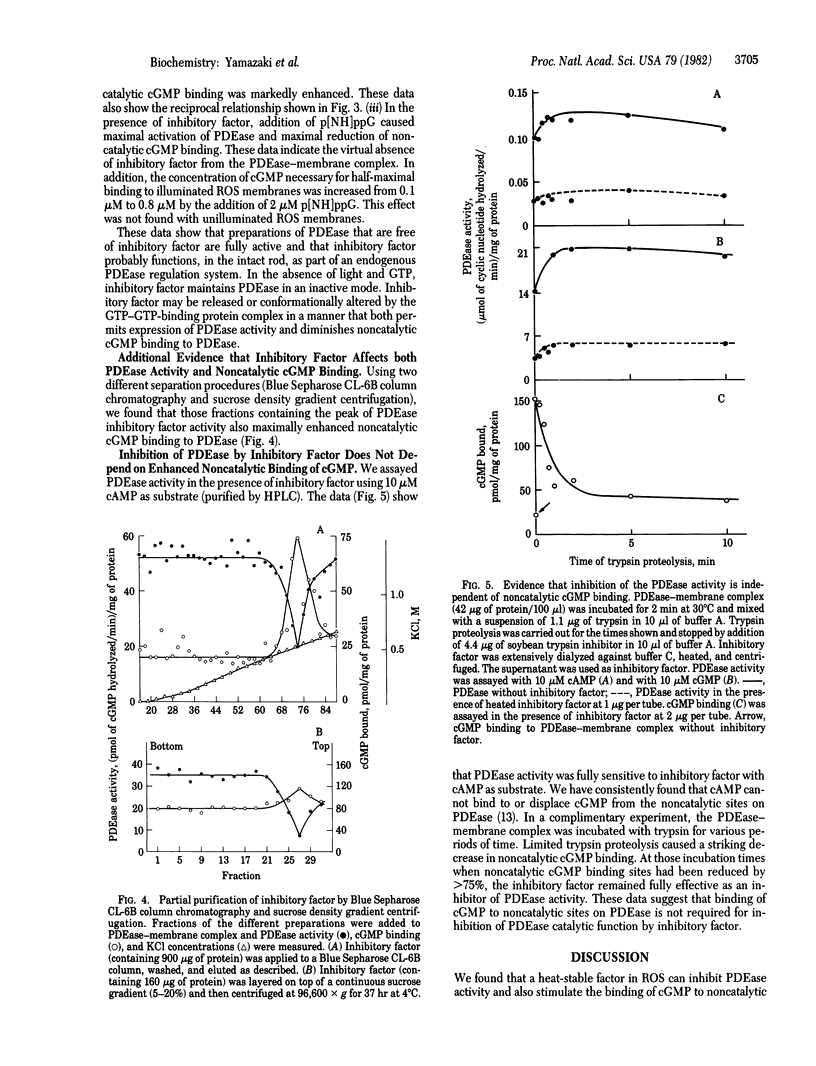
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Ives H. E., Jamieson J. D., Greengard P. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein phosphorylation in intact medial tissue and isolated cells from vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3770–3776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumler I. L., Etingof R. N. Protein inhibitor of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase in retina. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 8;429(2):474–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis S. H., Lincoln T. M., Corbin J. D. Characterization of a novel cGMP binding protein from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):620–626. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamet P., Coquil J. F. Cyclic GMP binding and cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase in rat platelets. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978 Aug;4(4):281–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Barry B., Ebrey T. G. Isolation of an inhibitory protein for the cyclic guanosine 3','5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase of bovine rod outer segments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jul 17;675(3-4):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B. Isolation and recombination of bovine rod outer segment cGMP phosphodiesterase and its regulators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):505–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90362-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. P., Wong V. G. A heat-stable protein inhibitor of cyclic 3',5'-nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Mar 22;583(3):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki N., Baraban J. M., Keirns J. J., Boyce J. J., Bitensky M. W. Purification and properties of the light-activated cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase of rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6320–6327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. R., Kawamura S., Abramson B., Bownds M. D. Control of the cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase of frog photoreceptor membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Nov;76(5):631–645. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.5.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozawa T., Uchida S., Martin E., Cafiso D., Hubbell W., Bitensky M. Additional component required for activity and reconstitution of light-activated vertebrate photoreceptor GTPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1408–1411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Wheeler G. L., Yamazaki A., Bitensky M. W. A GTP-protein activator of phosphodiesterase which forms in response to bleached rhodopsin. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;7(2):95–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler G. L., Bitensky M. W. A light-activated GTPase in vertebrate photoreceptors: regulation of light-activated cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4238–4242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler G. L., Matuto Y., Bitensky M. W. Light-activated GTPase in vertebrate photoreceptors. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):822–824. doi: 10.1038/269822a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki A., Sen I., Bitensky M. W., Casnellie J. E., Greengard P. Cyclic GMP-specific, high affinity, noncatalytic binding sites on light-activated phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11619–11624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]