Abstract
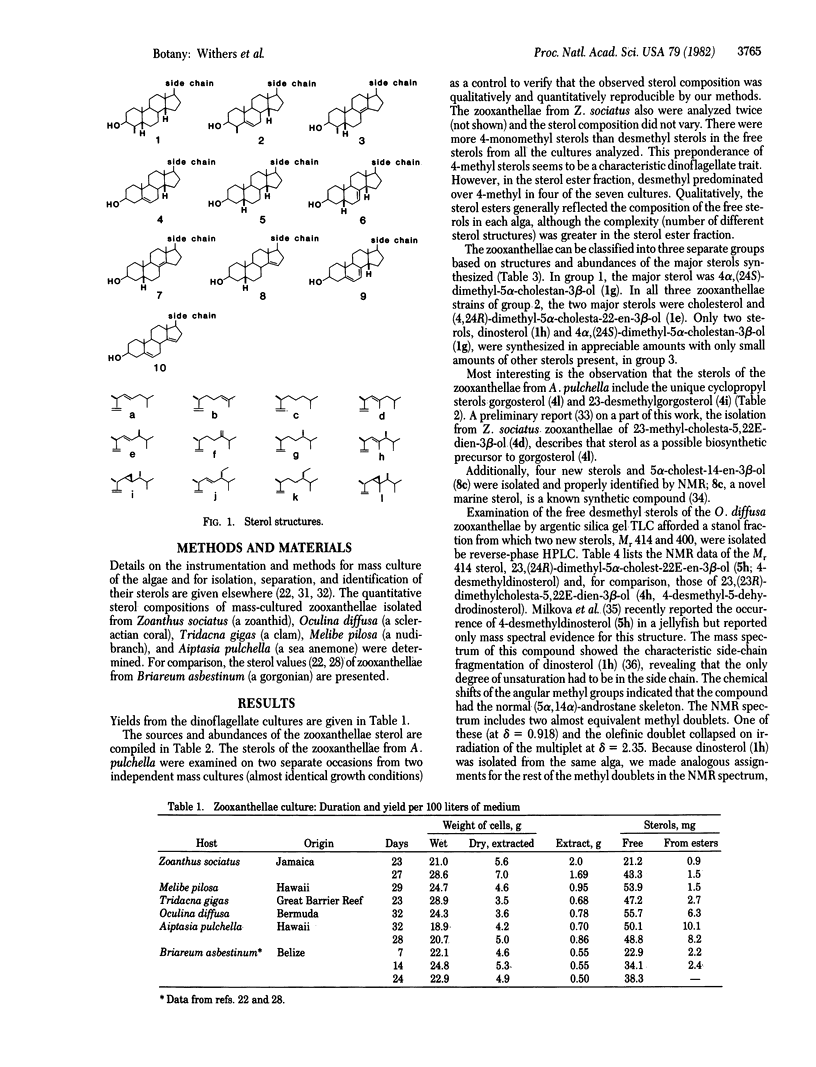
Quantitative sterol compositions of cultured zooxanthellae isolated from various Pacific and Atlantic invertebrate hosts: Zoanthus sociatus (a zoanthid), Oculina diffusa (a scleractian coral), Tridacna gigas (a giant clam), Melibe pilosa (a nudibranch), and Aiptasia pulchella (a sea anemone) are reported. The results clearly demonstrate large differences in sterol patterns of zooxanthellae and that there is no obvious relationship between the taxonomic affiliation of the host and the sterol pattern of its isolated symbiont. The sterols of the zooxanthellae of O. diffusa (Cnidaria) and T. gigas (Mollusca) are qualitatively equivalent. Based on the structures of the two major free sterols synthesized by each alga, the zooxanthellae from different hosts were separated into three distinct groups. It was also found that an aposymbiotic alga can synthesize the unique marine sterols gorgosterol and 23-desmethylgorgosterol. Most of the sterols were identified by using mass spectroscopy and 360-MHz proton magnetic resonance. Spectroscopic data are reported for four novel sterols—(23,24R)-dimethyl-5α-cholest-(22E)-en-3β-o l, 23-methyl-5α-cholest-22E-en-3β-ol, cholesta-5,14-dien-3β-ol, and 4α-methyl-5α-cholesta-8(14)-24-dien-3β-ol.
Keywords: symbiosis, dinoflagellates, algal taxonomy, marine sterols
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alam M., Sansing T. B., Busby E. L., Martiniz D. R., Ray S. M. Dinoflagellate sterols I: Sterol c omposition of the dinoflagellates of Gonyaulax species. Steroids. 1979 Feb;33(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(79)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciereszko L. S., Johnson M. A., Schmidt R. W., Koons C. B. Chemistry of coelenterates. VI. Occurrence of gorgosterol, a C30 sterol, in coelenterates and their zooxanthellae. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1968 Mar;24(3):899–904. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(68)90801-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djerassi C. Applications of mass spectrometry in the steroid field. Pure Appl Chem. 1970;21(2):205–225. doi: 10.1351/pac197021020205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzie R. A., 3rd, Chee G. S. The effect of different zooxanthellae on the growth of experimentally reinfected hosts. Biol Bull. 1979 Jun;156(3):315–327. doi: 10.2307/1540920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N. C., Hale R. L., Djerassi C. The structure and absolute configuration of the marine sterol gorgosterol. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Aug 26;92(17):5281–5282. doi: 10.1021/ja00720a082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popov S., Carlson R. M., Wegmann A., Djerassi C. Minor and trace sterols in marine invertebrates. 1. General methods of analysis. Steroids. 1976 Nov;28(5):699–732. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(76)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. L. Algal symbionts of invertebrates. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:171–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. L. Symbiotic dinoflagellates. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1975;(29):267–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Holt C., Von Holt M. Transfer of photosynthetic products from zooxanthellae to coelenterate hosts. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1968 Jan;24(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(68)90959-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



