Abstract
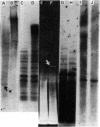
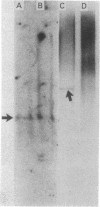
A 2.5-kilobase fragment of a sex-specific satellite DNA from the Colubrid snake species Elaphe radiata has been cloned, and its sequence has been determined. It contains 26 and 12 copies, respectively, of two base quadruplets, G-A-T-A and G-A-C-A, as its sole highly repetitious elements. Southern hybridization experiments with genomic DNA of the chicken, the mouse, and man indicated male sex-specific conservation of at least parts of this cloned DNA. In situ hybridization experiments with metaphase chromosomes of the mouse showed that elements that can cross-hybridize with parts of the cloned snake DNA are concentrated in the pericentric region of the Y chromosome. In blot hybridization experiments with liver poly(A)+ polysomal RNAs of male and female mice, a probe consisting of the first 1,224 bases of the cloned snake DNA singled out a male-specific RNA of 1,250-1,400 bases. Inasmuch as the proximal end of this probe contained an open reading frame (44 consecutive amino acid-specifying codons), the male-specific putative mRNA so detected may specify H-Y antigen. By contrast, a probe consisting of bases 1,480-1,906, containing the simple repeats of the quadruplets, singled out a shorter (approximately 1,000-base) RNA from males and females alike. Although this RNA is poly(A)+, we have yet to establish its attachment to ribosomes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Selby M. J., Rutter W. J. The highly polymorphic region near the human insulin gene is composed of simple tandemly repeating sequences. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):31–35. doi: 10.1038/295031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blattner F. R., Williams B. G., Blechl A. E., Denniston-Thompson K., Faber H. E., Furlong L., Grunwald D. J., Kiefer D. O., Moore D. D., Schumm J. W. Charon phages: safer derivatives of bacteriophage lambda for DNA cloning. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):161–169. doi: 10.1126/science.847462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D., Fry K., Nelson T., Hung P. Synthesis of hybrid bacterial plasmids containing highly repeated satellite DNA. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):509–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. Repeated sequence specific to human males. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):182–186. doi: 10.1038/262182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard C., Doly J., Cortadas J., Bernardi G. The primary structure of bovine satellite 1.715. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6069–6082. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Zehavi-Willner T., Graves P. N., McInnes J., Pestka S. Isolation and cell-free translation of immunoglobulin messenger RNA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):74–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Ullrich A., Saunders G. F. Localization of the human insulin gene to the distal end of the short arm of chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4458–4460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau J., Marcaud L., Maschat F., Kejzlarova-Lepesant J., Lepesant J. A., Scherrer K. A + T-rich linkers define functional domains in eukaryotic DNA. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):260–262. doi: 10.1038/295260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutz G., Kieval S., Groner B., Sippel A. E., Kurtz D., Feigelson P. Isolation of specific messenger RNA by adsorption of polysomes to matrix-bound antibody. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jan;4(1):71–84. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore G. C., Tata J. R. Two fractions of rough endoplasmic reticulum from rat liver. I. Recovery of rapidly sedimenting endoplasmic reticulum in association with mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1977 Mar;72(3):714–725. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.3.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Purdom I. F., Jones K. W. Conserved sex-chromosome-associated nucleotide sequences in eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):805–814. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Purdom I. F., Jones K. W. Satellite DNA and evolution of sex chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1976 Dec 6;59(1):43–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00327708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. In vitro packaging of a lambda Dam vector containing EcoRI DNA fragments of Escherichia coli and phage P1. Gene. 1977 May;1(3-4):255–280. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachtel S. S., Koo G. C., Boyse E. A. Evolutionary conservation of H-Y ('male') antigen. Nature. 1975 Mar 20;254(5497):270–272. doi: 10.1038/254270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock R., Sweet R., Weiss M., Cedar H., Axel R. Intragenic DNA spacers interrupt the ovalbumin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1299–1303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]