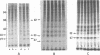Abstract
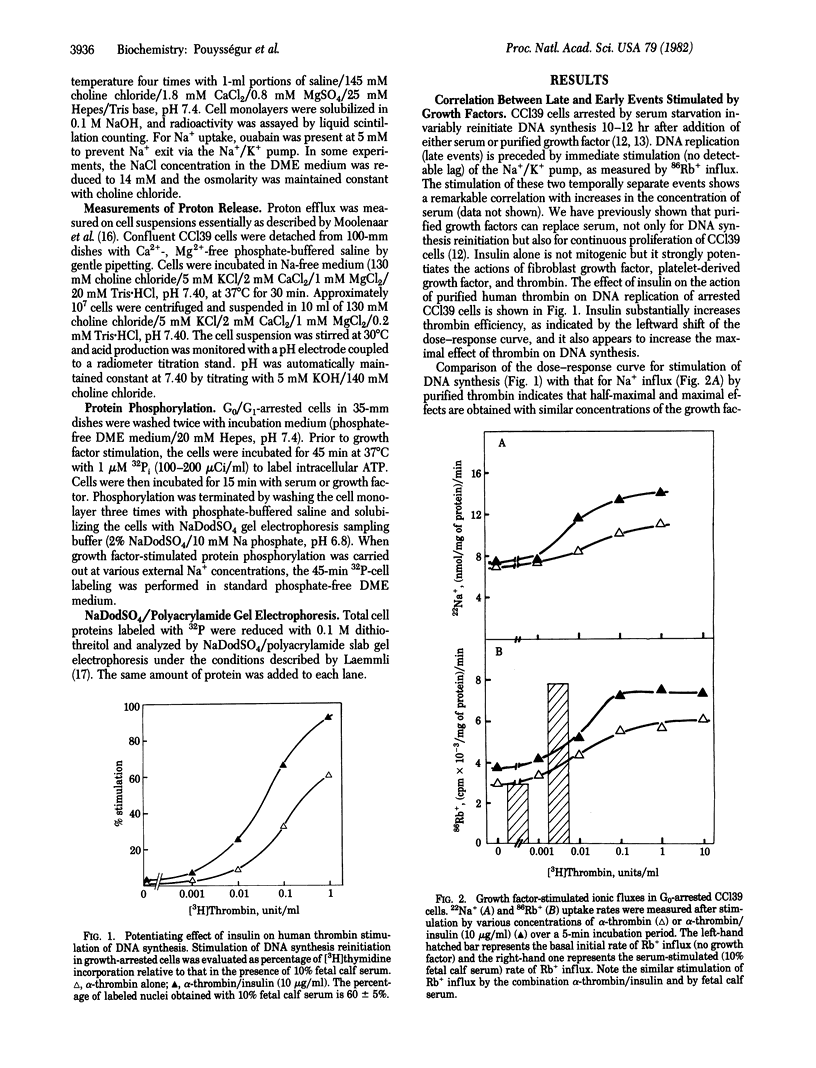
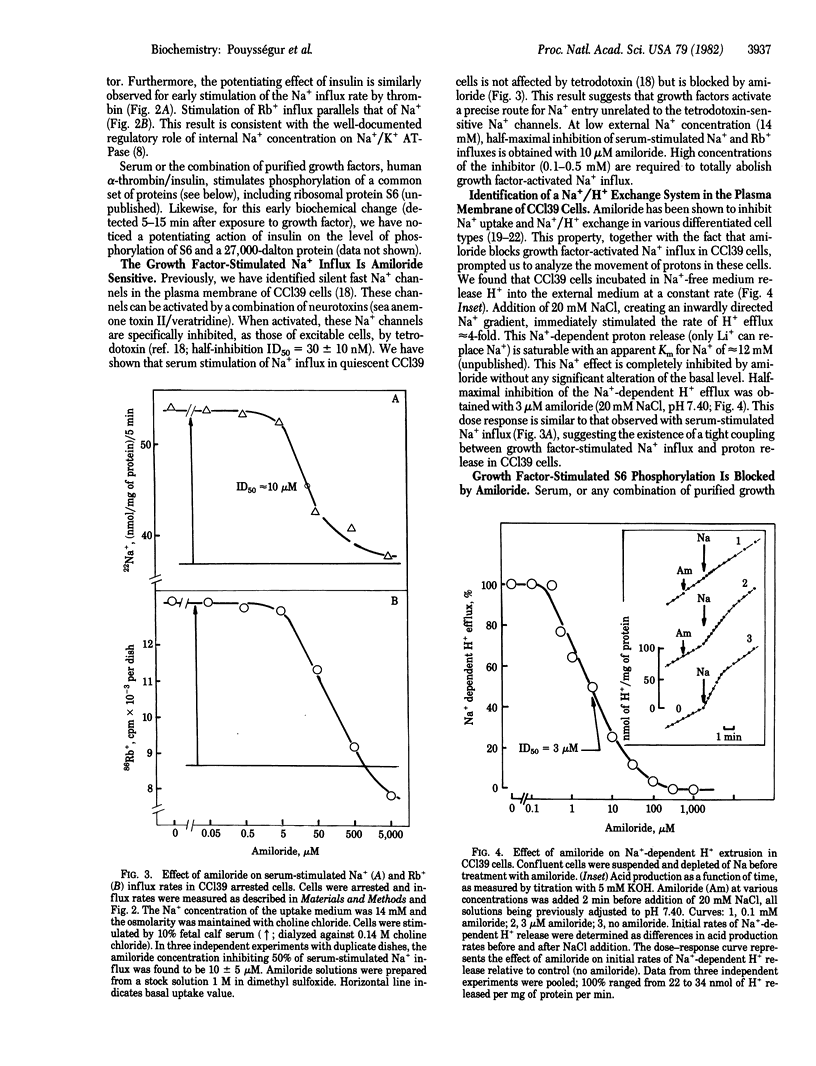
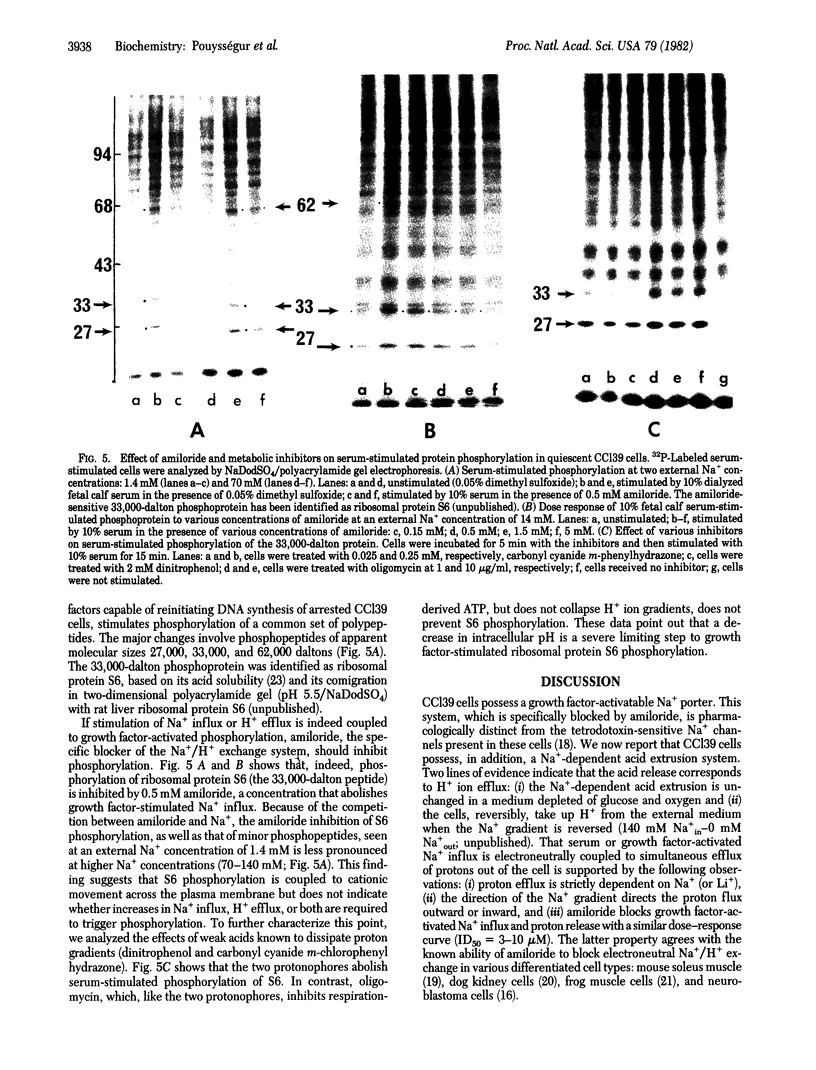
Chinese hamster lung fibroblast cells (CCl39) enter the G0/G1 nonproliferative state after serum deprivation. In this report, we show that reinitiation of DNA synthesis by serum or the combination of purified human thrombin and insulin (1-10 microgram/ml) is preceded by very early stimulation of ionic fluxes (Na+/Rb+) and protein phosphorylation (27,000 daltons, 62,000 daltons, and the ribosomal S6 proteins). The potentiating action of insulin on thrombin-stimulated DNA synthesis is also observed on thrombin-stimulated Na+ influx, Rb+ influx, and protein S6 phosphorylation. Moreover, we demonstrate that CCl39 cells possess a Na+/H+ exchange system sensitive to amiloride. Half-maximal inhibition of growth factor-activated Na+ influx and Na+-dependent H+ efflux is obtained with 3-10 microM amiloride. Two lines of evidence indicate that the extrusion of H+ via the activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger is coupled to protein S6 phosphorylation: serum-stimulated phosphorylation is blocked by (i) amiloride at a concentration that abolishes serum-stimulated Na+ influx and (ii) protonophores that acidify the cell interior. The present data support the idea that the regulation of intracellular pH is a key event in the mechanism of growth factor action.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aickin C. C., Thomas R. C. An investigation of the ionic mechanism of intracellular pH regulation in mouse soleus muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1977 Dec;273(1):295–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger D. G., Hunt T. Fertilization of sea urchin eggs is accompanied by 40 S ribosomal subunit phosphorylation. Dev Biol. 1981 Oct 30;87(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottenstein J., Hayashi I., Hutchings S., Masui H., Mather J., McClure D. B., Ohasa S., Rizzino A., Sato G., Serrero G. The growth of cells in serum-free hormone-supplemented media. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:94–109. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Rapid enhancement of protein phosphorylation in A-431 cell membrane preparations by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4884–4891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Moran J. S. Growth factors in mammalian cell culture. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:531–558. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger J. L., Winkler M. M., Shen S. S., Steinhardt R. A. Intracellular pH controls protein synthesis rate in the sea urchine egg and early embryo. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):396–406. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Patrick J. Nerve growth factor mediates phosphorylation of specific proteins. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):571–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. C., Norman N. E., Schwartz D. B., Simons E. R. Changes in cytoplasmic pH and in membrane potential in thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):295–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. C., Simons E. R. Effects of amiloride on the response of human platelets to bovine alphathrombin. Thromb Res. 1978 Oct;13(4):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Epel D. Intracellular pH and activation of sea urchin eggs after fertilisation. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):661–664. doi: 10.1038/262661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. G. Membrane cation transport and the control of proliferation of mammalian cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1978;40:19–41. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.40.030178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. S., Leffert H. L. Increased sodium ion influx is necessary to initiate rat hepatocyte proliferation. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90364-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Boonstra J., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Sodium/proton exchange in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12883–12887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Mummery C. L., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Rapid ionic events and the initiation of growth in serum-stimulated neuroblastoma cells. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):789–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90443-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., de Laat S. W., van der Saag P. T. Serum triggers a sequence of rapid ionic conductance changes in quiescent neuroblastoma cells. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):721–723. doi: 10.1038/279721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D. Stimulation of Na:H exchange by insulin. Biophys J. 1981 Feb;33(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84881-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen-Hamilton M., Hamilton R. T. Fibroblast growth factor causes an early increase in phosphorylation of a membrane protein in quiescent 3T3 cells. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):444–446. doi: 10.1038/279444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Franchi A., Salomon J. C., Silvestre P. Isolation of a Chinese hamster fibroblast mutant defective in hexose transport and aerobic glycolysis: its use to dissect the malignant phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2698–2701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Franchi A., Silvestre P. Relationship between increased aerobic glycolysis and DNA synthesis initiation studied using glycolytic mutant fibroblasts. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):445–447. doi: 10.1038/287445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pouysségur J., Jacques Y., Lazdunski M. Identification of a tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na+ channel in a variety in fibroblast lines. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):162–164. doi: 10.1038/286162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rodriguez R., Chambard J. C., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Emergence of hamster fibroblast tumors in nude mice--evidence for in vivo selection leading to loss of growth factor requirement. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Dec;109(3):387–396. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041090303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Rodriquez R., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Growth factor requirements of Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts in serum free media: high mitogenic action of thrombin. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1981 Apr;5(4):347–357. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(81)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Taub M., Saier M. H., Jr Uptake of 22Na+ by cultured dog kidney cells (MDCK). J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11431–11439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Stimulation of Na influx, Na-K pump activity and DNA synthesis in quiescent cultured cells. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1980;19:61–85. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(81)90009-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segel G. B., Simon W., Lichtman M. A. Regulation of sodium and potassium transport in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human blood lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Sep;64(3):834–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI109531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Rozengurt E. Serum stimulates the Na+,K+ pump in quiescent fibroblasts by increasing Na+ entry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5560–5564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Siegmann M., Gordon J. Multiple phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during transition of quiescent 3T3 cells into early G1, and cellular compartmentalization of the phosphate donor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]