Abstract
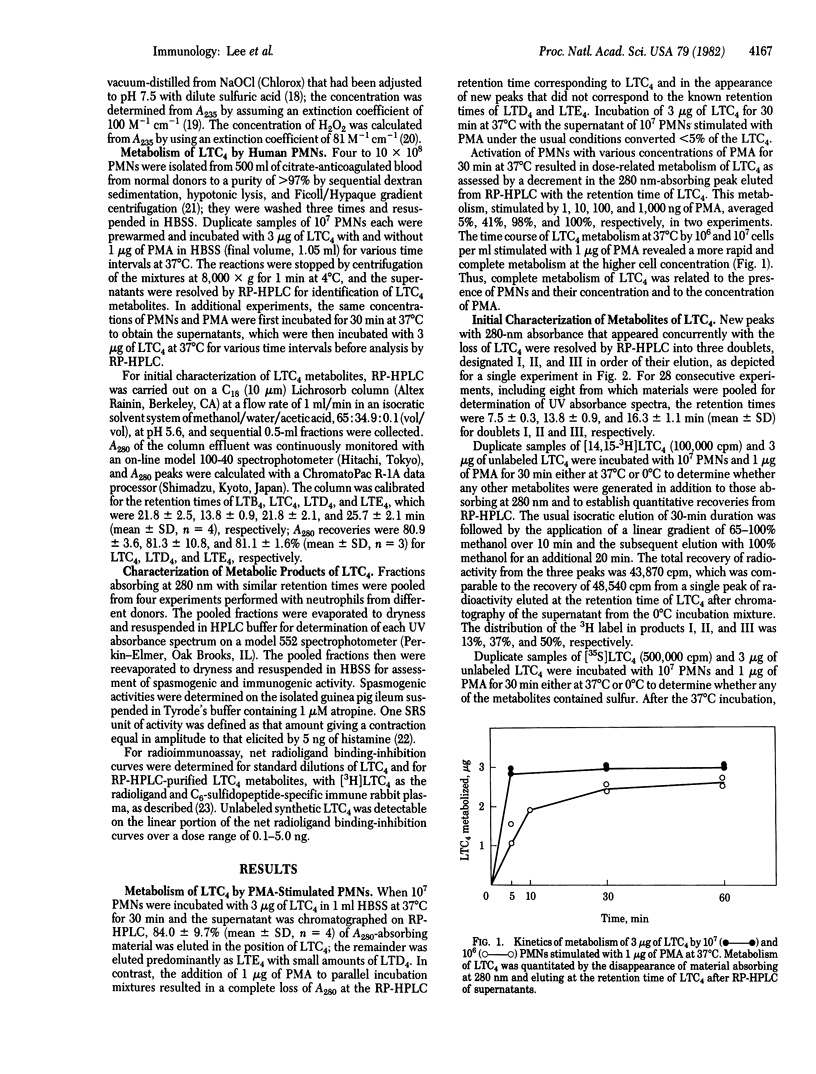
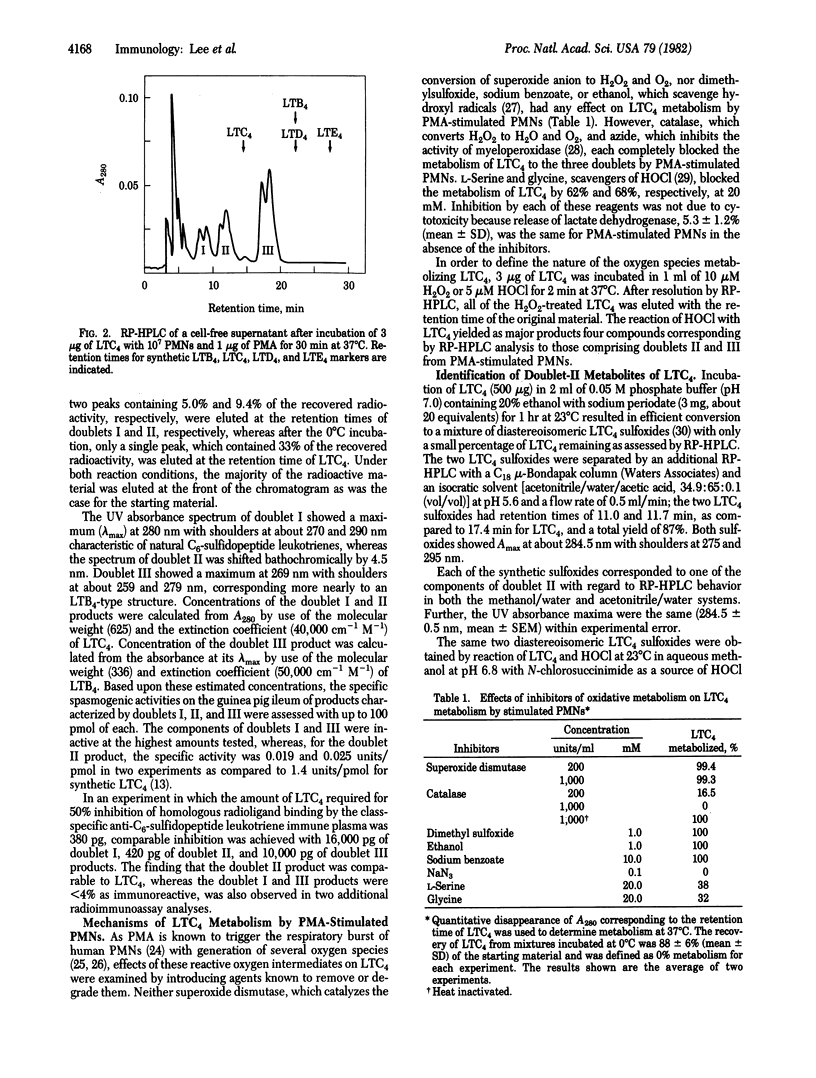
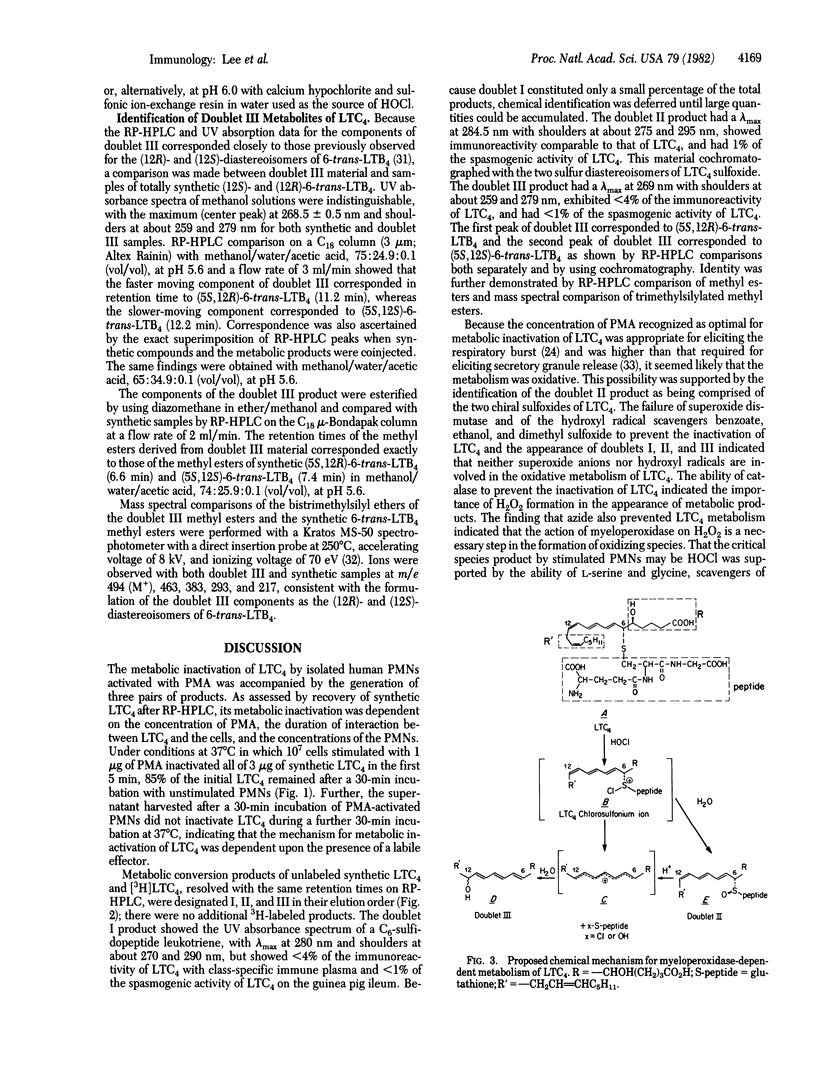
Leukotriene C4 (LTC4) was metabolized by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) into three sets of products. These products differed in mobility on reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP HPLC) from LTC4 and also from leukotriene D4 (LTD4) and leukotriene E4 (LTE4), the sequential products of peptide cleavage of LTC4. Products I, II, and III were eluted as doublets with an average retention time for each doublet of 7.5 ± 0.3, 10.5 ± 0.6, and 16.3 ± 1.1 min (mean ± SD), respectively, as compared with 13.8 min for LTC4. Doublet I material was biologically inactive and showed <5% of the immunoreactivity of LTC4, doublet II material had 1% of the spasmogenic activity of LTC4 on the guinea pig ileum and was equally immunoreactive, and doublet III material was neither biologically active nor immunoreactive. When [14,15-3H]LTC4 and [35S]LTC4 were metabolized, all three doublet products retained the 3H label, whereas only the doublet I and doublet II products retained the 35S label. The UV absorbance spectra of the three sets of metabolites were as follows: doublet I, maximum at 280 nm with shoulders at about 270 and 290 nm; doublet II, maximum at 284.5 nm with shoulders at about 275 and 295 nm; and doublet III, maximum at 269 nm with shoulders at about 259 and 279 nm. The metabolism of LTC4 to the three classes of functionally inactive products by stimulated PMNs was completely blocked by catalase and azide, indicating a requirement for H2O2 and myeloperoxidase. When hypochlorous acid (HOCl)—considered to be a natural product of the interaction of myeloperoxidase, H2O2, and chloride ion—was formed chemically and allowed to react with LTC4, the resulting products were indistinguishable by UV and HPLC analyses from the doublet II and doublet III metabolites of LTC4. The doublet II products were identified as the two diastereoisomeric sulfoxides of LTC4 by comparison with synthetic reference compounds. The doublet III products were shown to be identical with synthetic samples of (5S, 12S)- and (5S, 12R)-6-trans-LTB4. The formation of two diastereoisomeric LTC4 sulfoxides and 6-trans-LTB4 can be explained in terms of an S-chlorosulfonium ion as the initial reactive intermediate, which subsequently undergoes conversion to product II by hydrolysis and product III by carbocation formation.
Keywords: neutrophils, oxidative metabolism
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrich J. M., McCarthy C. A., Hurst J. K. Biological reactivity of hypochlorous acid: implications for microbicidal mechanisms of leukocyte myeloperoxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):210–214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKLEHURST W. E. Occurrence of an unidentified substance during anaphylactic shock in cavy lung. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):16P–17P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 30;298(13):721–725. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803302981305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. K., Brashler J. R., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Identification of a component of rat mononuclear cell SRS as leukotriene D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 29;93(4):1121–1126. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90605-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Transformation of arachidonic acid and homo-gamma-linolenic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Monohydroxy acids from novel lipoxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7816–7820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Arachidonic acid metabolism in polymorphonuclear leukocytes: effects of ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2148–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Metabolism of arachidonic acid in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Structural analysis of novel hydroxylated compounds. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7865–7869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Stone P. J., El Hag A., Calore J. D., Franzblau C. Myeloperoxidase-catalyzed inactivation of alpha 1-protease inhibitor by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3348–3353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Szot S. Chemotactic factor inactivation by stimulated human neutrophils mediated by myeloperoxidase-catalyzed methionine oxidation. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1507–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S., Johnston R. B., Jr Effect of phorbol myristate acetate on the oxidative metabolism of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1976 Apr;47(4):545–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazen J. M., Venugopalan C. S., Austen K. F., Brion F., Corey E. J. Effects of leukotriene E on pulmonary mechanics in the guinea pig. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Mar;125(3):290–294. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.3.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homan-Müller J. W., Weening R. S., Roos D. Production of hydrogen peroxide by phagocytizing human granulocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Feb;85(2):198–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J., Clark R. A. Iodination by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: a re-evaluation. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Mar;89(3):675–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine L., Morgan R. A., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F., Clark D. A., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Radioimmunoassay of the leukotrienes of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7692–7696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Austen K. F., Drazen J. M., Clark D. A., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Slow reacting substances of anaphylaxis: identification of leukotrienes C-1 and D from human and rat sources. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3710–3714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Drazen J. M., Austen K. F., Clark D. A., Corey E. J. Identification of the C(6)-S-conjugate of leukotriene A with cysteine as a naturally occurring slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A). Importance of the 11-cis-geometry for biological activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 16;96(1):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Drazen J. M., Austen K. F., Toda M., Brion F., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Contractile activities of structural analogs of leukotrienes C and D: role of the polar substituents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4579–4583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris H. R., Taylor G. W., Piper P. J., Tippins J. R. Structure of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis from guinea-pig lung. Nature. 1980 May 8;285(5760):104–106. doi: 10.1038/285104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. C., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene C: a slow-reacting substance from murine mastocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orning L., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene D: a slow reacting substance from rat basophilic leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2014–2017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. W., Falkenhein S. F., Huber M. M. Sequential conversion of the glutathionyl side chain of slow reacting substance (SRS) to cysteinyl-glycine and cysteine in rat basophilic leukemia cells stimulated with A-23187. Prostaglandins. 1980 Nov;20(5):863–886. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(80)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Cohn Z. A., Blackburn P., Manning J. M. Mouse peritoneal macrophages release leukotriene C in response to a phagocytic stimulus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4928–4932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Scott W. A., Hamill A. L., Cohn Z. A. Synthesis of leukotriene C and other arachidonic acid metabolites by mouse pulmonary macrophages. J Exp Med. 1982 Mar 1;155(3):720–733. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.3.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rådmark O., Malmsten C., Samuelsson B., Clark D. A., Goto G., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Leukotriene A: stereochemistry and enzymatic conversion to leukotriene B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 12;92(3):954–961. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90795-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rådmark O., Malmsten C., Samuelsson B., Goto G., Marfat A., Corey E. J. Leukotriene A. Isolation from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11828–11831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slivka A., LoBuglio A. F., Weiss S. J. A potential role for hypochlorous acid in granulocyte-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity. Blood. 1980 Feb;55(2):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



