Abstract
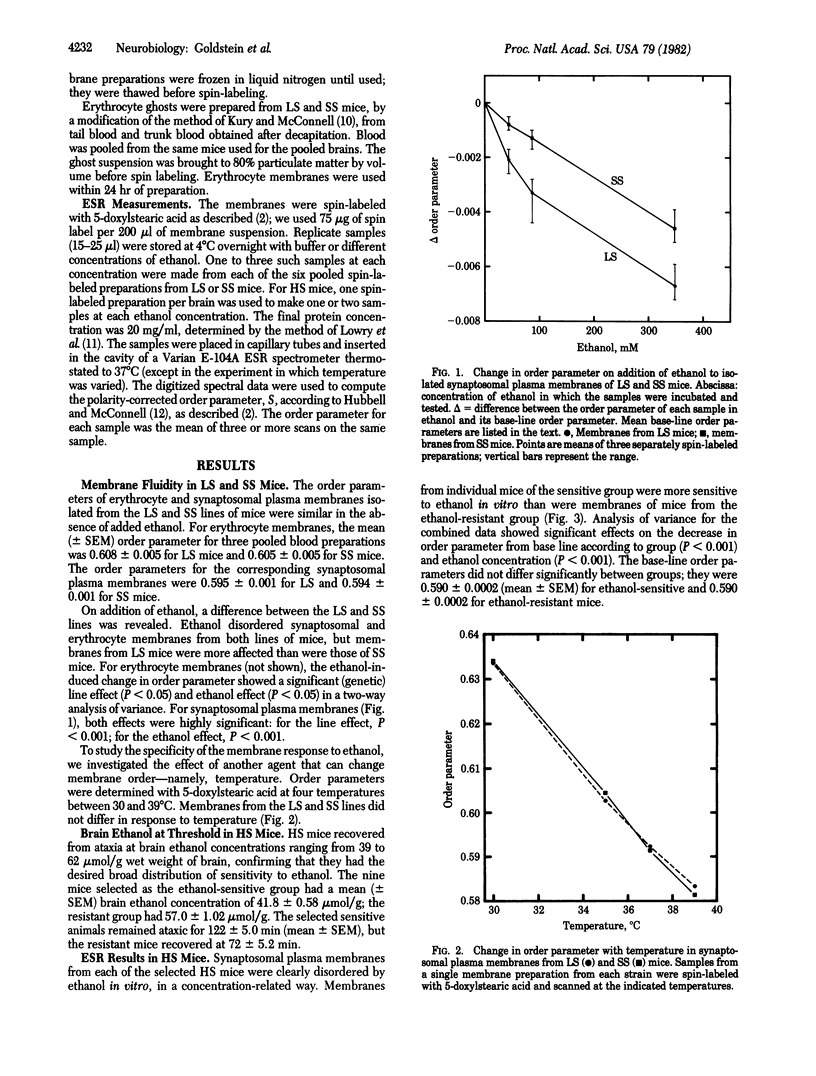
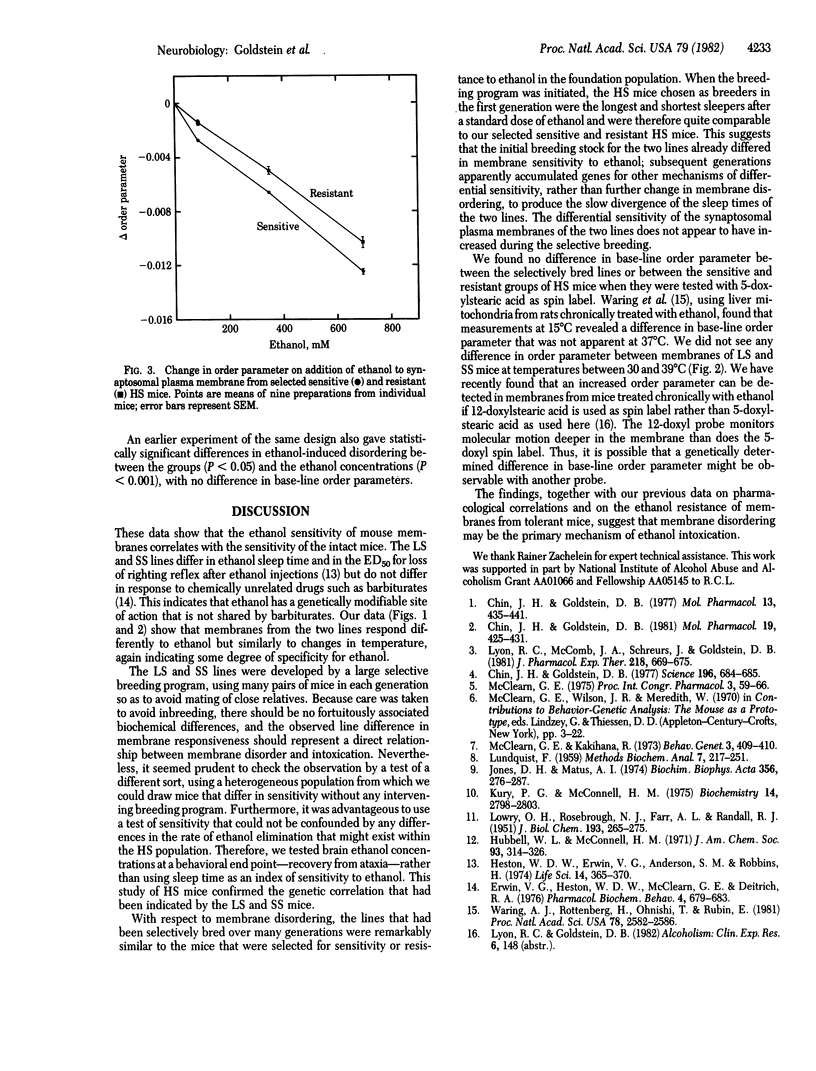
Disordering of brain and erythrocyte membranes by ethanol in vitro was measured by ESR using 5-doxylstearic acid as spin label. Synaptosomal plasma membranes and erythrocyte membranes were isolated from two lines of mice developed, by selective breeding, for differential sensitivity to hypnotic effects of ethanol. Membranes taken from alcohol-sensitive "long-sleep" mice were more strongly disordered by ethanol in vitro than were membranes from alcohol-resistant "short-sleep" mice. Furthermore, within a population of genetically heterogeneous mice, the most ethanol-sensitive animals had the most ethanol-sensitive synaptosomal plasma membranes. In vivo sensitivity of the individual mice was evaluated by measuring brain ethanol levels at a precise behavioral end point, recovery from ataxia. The data extend our previous observations of correlations between in vitro and in vivo effects of ethanol and suggest that membrane disordering may be a primary mechanism of acute effects of ethanol.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin J. H., Goldstein D. B. Drug tolerance in biomembranes: a spin label study of the effects of ethanol. Science. 1977 May 6;196(4290):684–685. doi: 10.1126/science.193186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. H., Goldstein D. B. Effects of low concentrations of ethanol on the fluidity of spin-labeled erythrocyte and brain membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 May;13(3):435–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. H., Goldstein D. B. Membrane-disordering action of ethanol: variation with membrane cholesterol content and depth of the spin label probe. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 May;19(3):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erwin V. G., Heston W. D., McClearn G. E., Deitrich R. A. Effect of hypnotics on mice genetically selected for sensitivity to ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1976 Jun;4(6):679–683. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(76)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston W. D., Erwin V. G., Anderson S. M., Robbins H. A comparison of the effects of alcohol on mice selectively bred for differences in ethanol sleep-time. Life Sci. 1974 Jan 16;14(2):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell W. L., McConnell H. M. Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Jan 27;93(2):314–326. doi: 10.1021/ja00731a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Matus A. I. Isolation of synaptic plasma membrane from brain by combined flotation-sedimentation density gradient centrifugation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 9;356(3):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kury P. G., McConnell M. Regulation of Membrane Flexibility in Human Erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2798–2803. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring A. J., Rottenberg H., Ohnishi T., Rubin E. Membranes and phospholipids of liver mitochondria from chronic alcoholic rats are resistant to membrane disordering by alcohol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2582–2586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


