Abstract
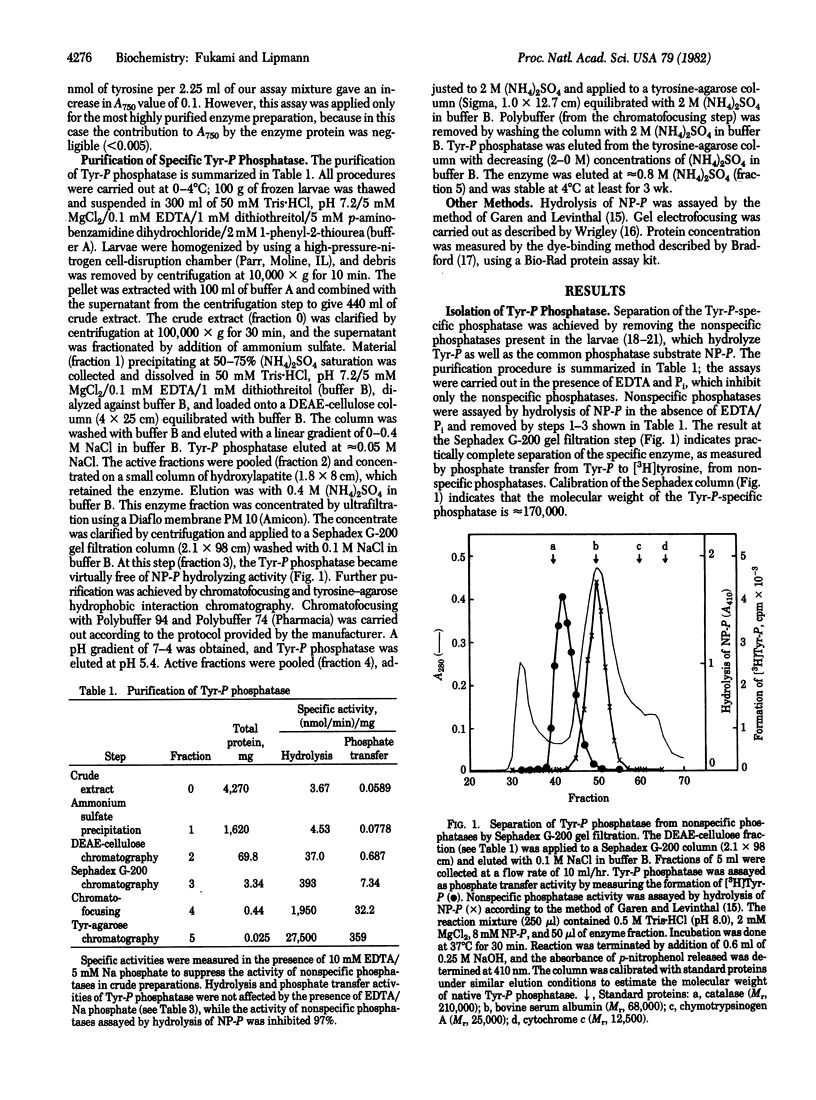
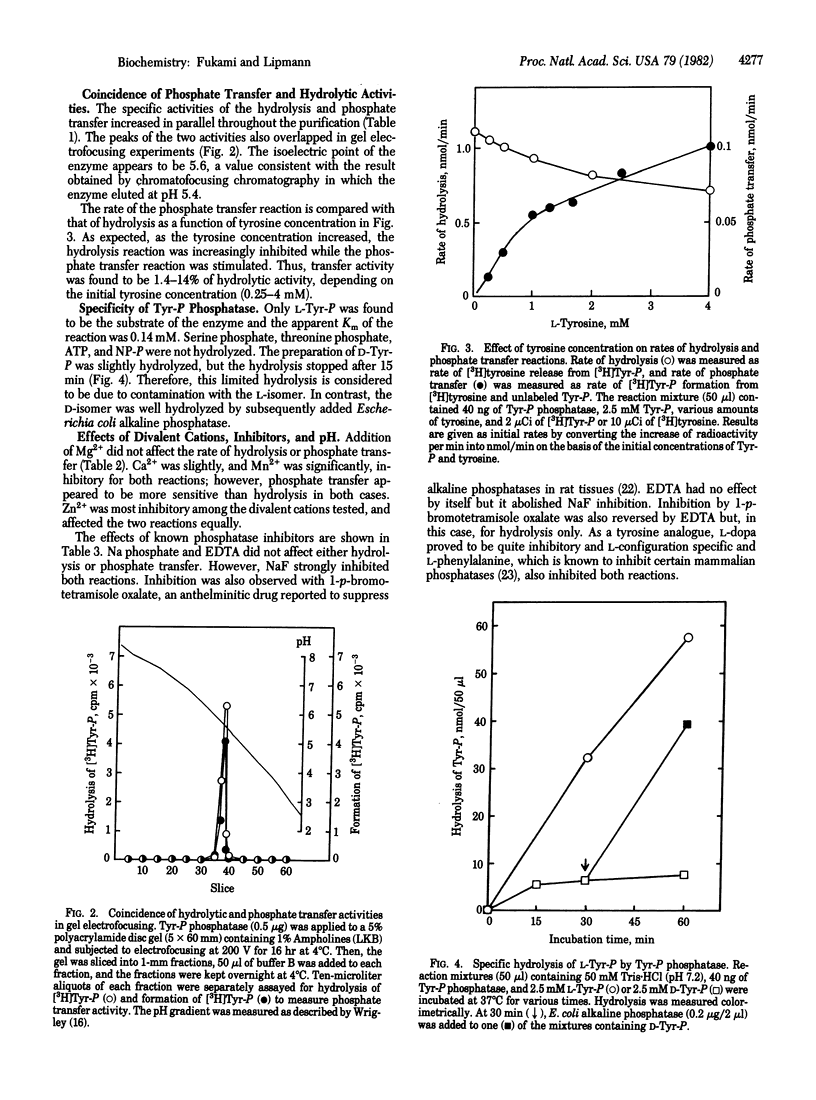
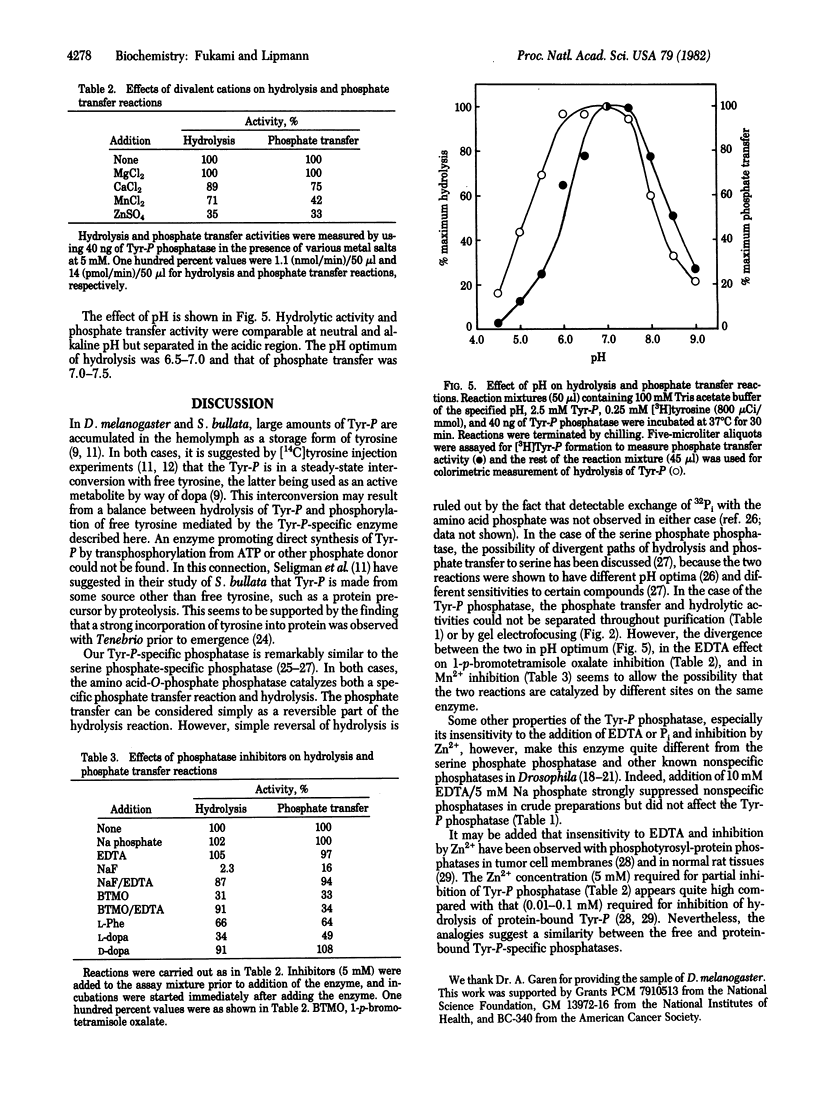
A phosphatase specific for tyrosine-O-phosphate (Tyr-P) was separated from several nonspecific phosphatases present in the third instar larvae of Drosophila melanogaster. The enzyme hydrolyzed L-Tyr-P, with an apparent Km of 0.14 mM, but not D-Tyr-P after being freed from hydrolytic activity toward p-nitrophenyl phosphate, the common phosphatase substrate. Such purified preparations also catalyzed a reversible phosphate transfer reaction from unlabeled Tyr-P to [3H]tyrosine. The transfer activity was L4-14% of the hydrolytic activity, depending on the initial concentration of tyrosine (0.25-4.0 mM). The two activities coincided throughout purification. However, they differed in pH optimum, that of hydrolysis being 6.5-7 and that of phosphate transfer being 7.7.5. The two activities were also differentially inhibited by 1-p-bromotetramisole oxalate in the presence of EDTA and by Mn2+. Addition of Mg2+ did not affect either hydrolysis or phosphate transfer, but 5 mM Zn2+ was 65% inhibitory to both. Sodium fluoride strongly inhibited both reactions, and this inhibition was reversed by EDTA, while EDTA itself had no effect. Pi had no effect and no detectable incorporation of 32Pi into Tyr-P was observed, indicating that the phosphate transfer reaction is not a simple reversal of hydrolysis. No ATP-linked phosphorylation of tyrosine was found.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BORKENHAGEN L. F., KENNEDY E. P. The enzymic equilibration of L-serine with O-phospho-L-serine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Apr;28(1):222–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90463-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgers M., Thoné F. The inhibition of alkaline phosphatase by L-p-bromotetramisole. Histochemistry. 1975 Aug 28;44(3):277–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00491496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brautigan D. L., Bornstein P., Gallis B. Phosphotyrosyl-protein phosphatase. Specific inhibition by Zn. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6519–6522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgers W. F. Mouse brain phosphoserine phosphohydrolase and phosphotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2080–2085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L., Collett M. S., Erikson E., Purchio A. F. Evidence that the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product is a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6260–6264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernley H. N., Walker P. G. Inhibition of alkaline phosphatase by L-phenylalanine. Biochem J. 1970 Feb;116(3):543–544. doi: 10.1042/bj1160543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper R. A., Armstrong F. B. Alkaline phosphatase of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Partial purification and characterization. Biochem Genet. 1972 Feb;6(1):75–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00485968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper R. A., Armstrong F. B. Alkaline phosphatase of Drosophila melanogaster. II. Biochemical comparison among four allelic forms. Biochem Genet. 1973 Sep;10(1):29–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00485746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper R., Armstrong F. B. Alkaline phosphatase of Drosophila melanogaster. 3. Tyrosine-O-phosphate as substrate. Biochem Genet. 1974 Feb;11(2):177–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00485773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilan J., Lipmann F. A cell-free protein synthesis system from pupae of Tenebrio molitor. Acta Biochim Pol. 1966;13(4):353–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunan K. D., Mitchell H. K. The metabolism of tyrosine-O-phosphate in Drosophila. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jul;132(2):450–456. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90388-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL H. K., LUNAN K. D. TYROSINE-O-PHOSPHATE IN DROSOPHILA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul 20;106:219–222. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacIntyre R. J. A method for measuring activities of acid phosphatases separated by acrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochem Genet. 1971 Feb;5(1):45–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00485729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUHAUS F. C., BYRNE W. L. O-Phosphoserine phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Apr;28(1):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90464-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman M., Friedman S., Fraenkel G. Hormonal control of turnover of tyrosine and tyrosine phosphate during tanning of the adult cuticle in the fly, Sarcophaga bullata. J Insect Physiol. 1969 Jun;15(6):1085–1101. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(69)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


