Abstract
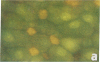
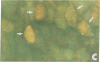
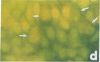
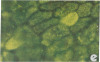
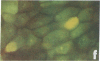
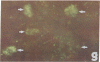
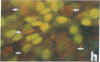
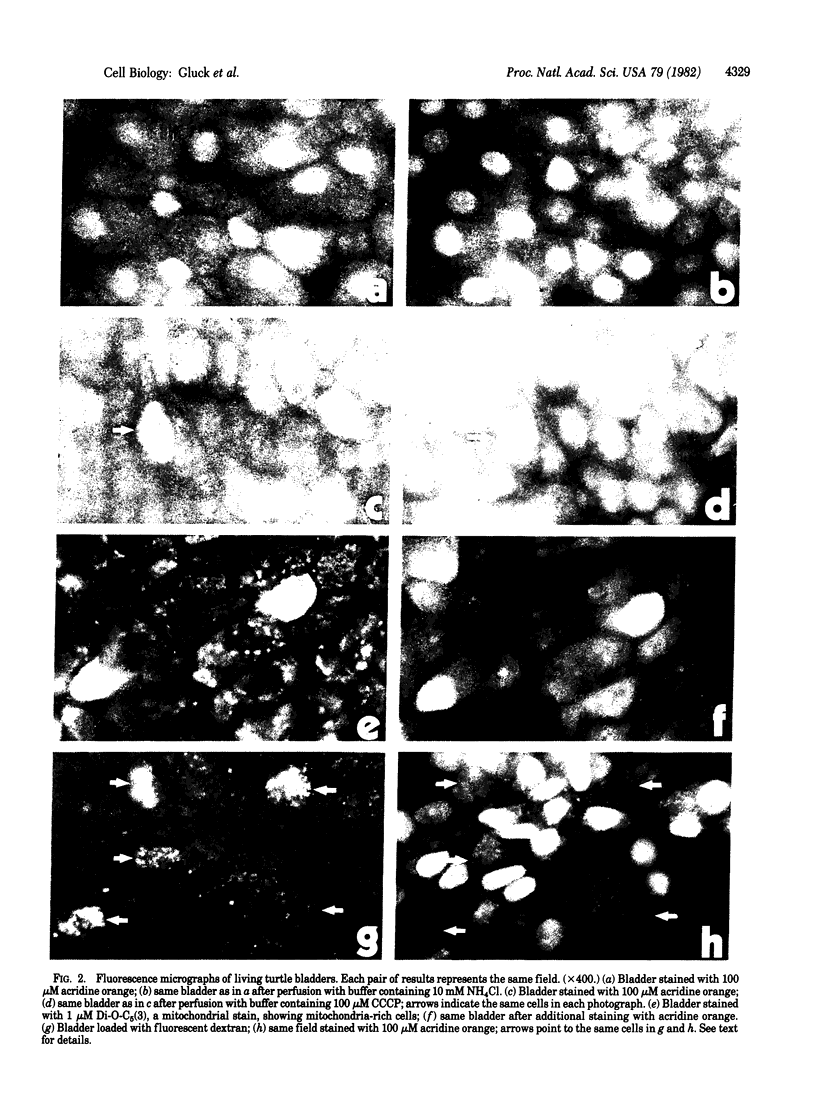
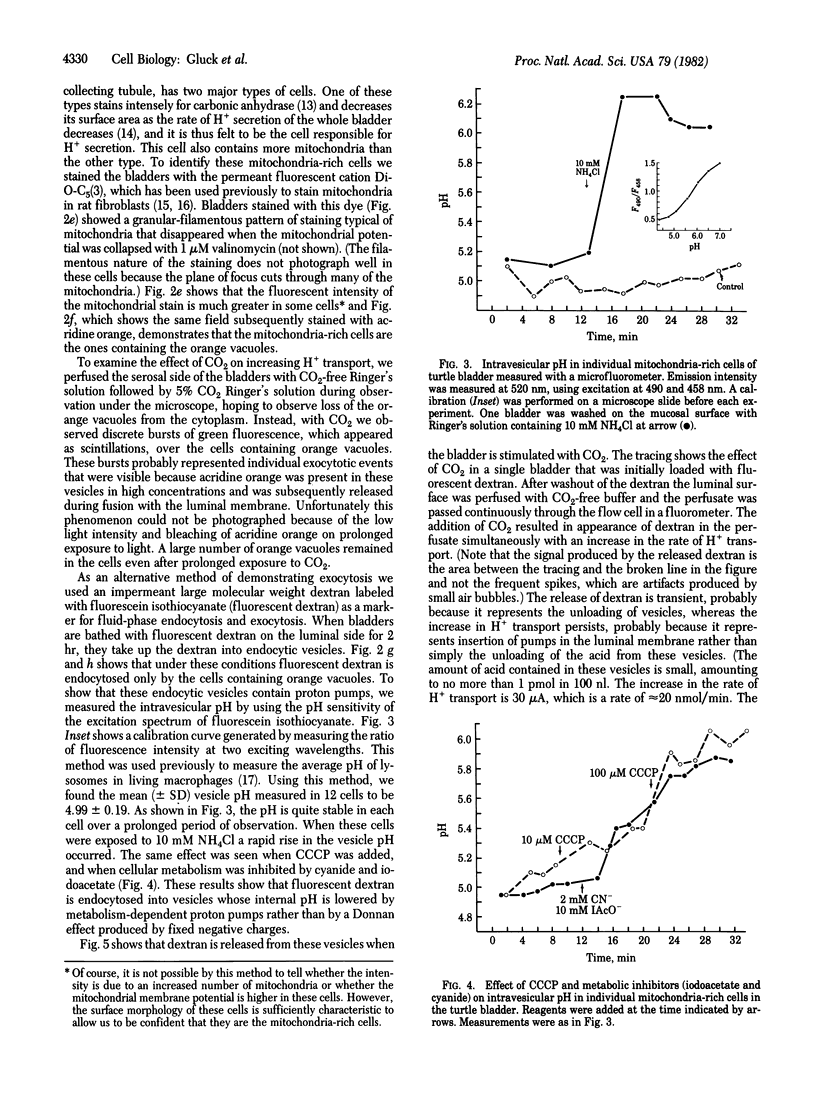
Urinary acidification by the turtle bladder is due to a H+-ATPase that is located in the luminal membrane. The rate of H+ transport is stimulated by an increase in the ambient CO2. Using the fluorescent dye acridine orange, we showed that the mitochondria-rich cell of this equilibrium contains vesicles whose internal pH is acidic. We measured the pH of these vesicles by using endocytosed fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled dextran and found it to be near 5.0. The pH increased after treatment with protonophores or metabolic inhibitors, suggesting that it was due to a H+ pump rather than to a Donnan effect. In bladders preloaded with fluorescent dextran, CO2 stimulated exocytosis and H+ transport measured simultaneously in the same bladder. The increase in the H+ current correlated well with the extent of exocytosis, and both were inhibited by pretreatment with colchicine. We conclude that the turtle bladder contains an intracellular reserve of vesicles containing H+ pumps and CO2 stimulates rapid fusion of these vesicles with the luminal membrane with consequent insertion of H+ pumps, thereby stimulating H+ secretion across the whole epithelium.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-awqati Q., Mueller A., Steinmetz P. R. Transport of H+ against electrochemical gradients in turtle urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):F502–F508. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.6.F502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arruda J. A., Sabatini S., Mola R., Dytko G. Inhibition of H+ secretion in the turtle bladder by colchicine and vinblastine. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Sep;96(3):450–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Honerjäger P. Influence of carbon dioxide on level of ionised calcium in squid axons. Nature. 1978 May 11;273(5658):160–161. doi: 10.1038/273160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauwens R., Al-Awqati Q. Active H+ transport in the turtle urinary bladder. Coupling of transport to glucose oxidation. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Oct;68(4):421–439. doi: 10.1085/jgp.68.4.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berglindh T., Dibona D. R., Ito S., Sachs G. Probes of parietal cell function. Am J Physiol. 1980 Mar;238(3):G165–G176. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1980.238.3.G165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. L., Muirhead K. A., Gill J. E., Waggoner A. S., Horan P. K. A cyanine dye distinguishes between cycling and non-cycling fibroblasts. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):593–595. doi: 10.1038/290593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona D. R., Ito S., Berglindh T., Sachs G. Cellular site of gastric acid secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6689–6693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon T. E., Al-Awqati Q. Urinary acidification in turtle bladder is due to a reversible proton-translocating ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3135–3138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forte T. M., Machen T. E., Forte J. G. Ultrastructural changes in oxyntic cells associated with secretory function: a membrane-recycling hypothesis. Gastroenterology. 1977 Oct;73(4 Pt 2):941–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husted R. F., Mueller A. L., Kessel R. G., Steinmetz P. R. Surface characteristics of carbonic-anhydrase-rich cells in turtle urinary bladder. Kidney Int. 1981 Apr;19(4):491–502. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. V., Walsh M. L., Bockus B. J., Chen L. B. Monitoring of relative mitochondrial membrane potential in living cells by fluorescence microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):526–535. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Carty S. E., Fingerhood B. J., Scarpa A. The internal pH of mast cell granules. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Scarpa A. Internal pH of isolated chromaffin vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):2189–2191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnieli E., Zarnowski M. J., Hissin P. J., Simpson I. A., Salans L. B., Cushman S. W. Insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transport systems in the isolated rat adipose cell. Time course, reversal, insulin concentration dependency, and relationship to glucose transport activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4772–4777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcum J. M., Dedman J. R., Brinkley B. R., Means A. R. Control of microtubule assembly-disassembly by calcium-dependent regulator protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3771–3775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masur S. K., Holtzman E., Walter R. Hormone-stimulated exocytosis in the toad urinary bladder. Some possible implications for turnover of surface membranes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jan;52(1):211–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regula C. S., Pfeiffer J. R., Berlin R. D. Microtubule assembly and disassembly at alkaline pH. J Cell Biol. 1981 Apr;89(1):45–53. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. L. ATP-dependent acidification of intact and disrupted lysosomes. Evidence for an ATP-driven proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3858–3864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. H., Rosen S., Steinmetz P. R. Carbonic anhydrase function and the epithelial organization of H+ secretion in turtle urinary bladder. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2653–2662. doi: 10.1172/JCI107083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]