Abstract
A method is described for localizing DNA sequences hybridized in situ to Drosophila polytene chromosomes. This procedure utilizes a biotin-labeled analog of TTP that can be incorporated enzymatically into DNA probes by nick-translation. After hybridization in situ, the biotin molecules in the probe serve as antigens which bind affinity-purified rabbit antibiotin antibodies. The site of hybridization is then detected either fluorimetrically, by using fluorescein-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG, or cytochemically, by using an anti-rabbit IgG antibody conjugated to horseradish peroxidase. When combined with Giemsa staining, the immunoperoxidase detection method provides a permanent record that is suitable for detailed cytogenetic analysis. This immunological approach offers four advantages over conventional autoradiographic procedures for detecting in situ hybrids: (i) the time required to determine the site of hybridization is decreased markedly, (ii) biotin-labeled probes are chemically stable and give reproducible results for many months; (iii) biotin-labeled probes appear to produce less background noise than do radiolabeled probes; and (iv) the resolving power is equal to and often greater than that achieved autoradiographically.
Full text
PDF

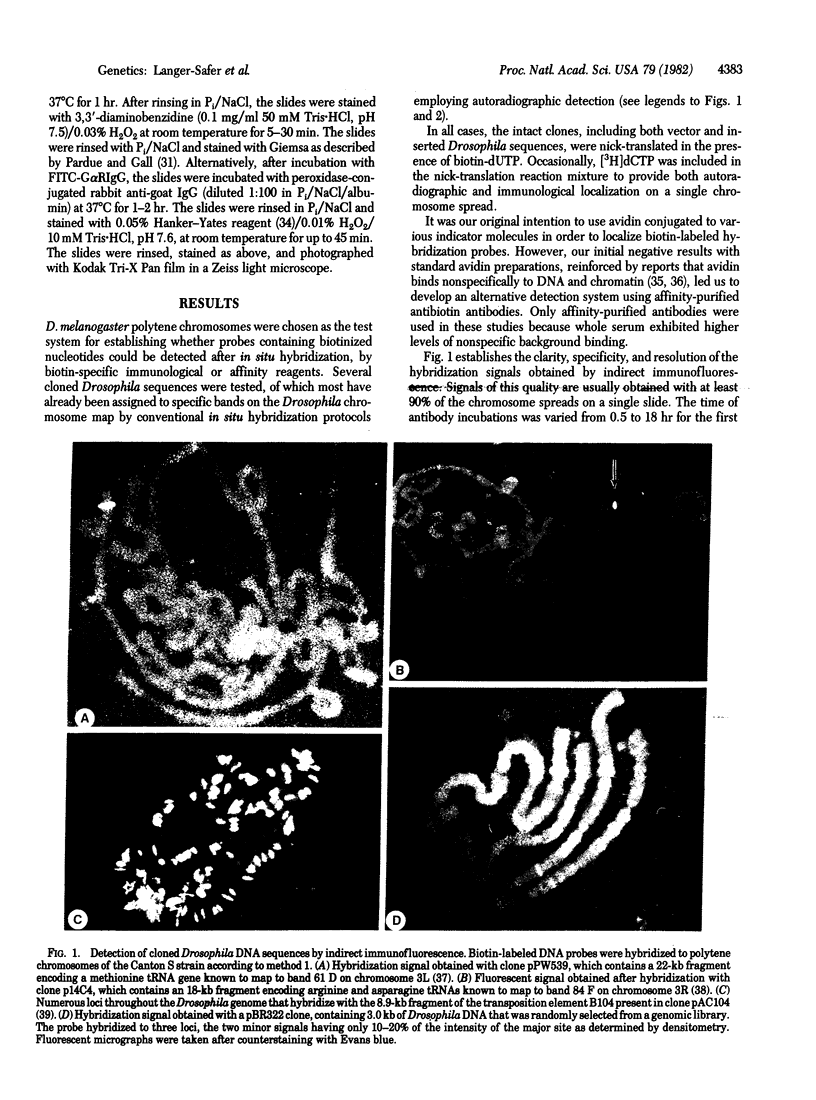


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman J. G., Wiegant J., Borst P., van Duijn P. A new method for fluorescence microscopical localization of specific DNA sequences by in situ hybridization of fluorochromelabelled RNA. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Aug;128(2):485–490. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman J. G., Wiegant J., Van Duijn P., Lubsen N. H., Sondermeijer P. J., Hennig W., Kubli E. Rapid and high resolution detection of in situ hybridisation to polytene chromosomes using fluorochrome-labeled RNA. Chromosoma. 1981;84(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00293359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman J. G., Wiegant J., van Duijn P. Cytochemical hybridization with fluorochrome-labeled RNA. II. Applications. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Feb;29(2):238–246. doi: 10.1177/29.2.6166654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. The use of the avidin-biotin complex as a tool in molecular biology. Methods Biochem Anal. 1980;26:1–45. doi: 10.1002/9780470110461.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. Antibodies that bind biotin and inhibit biotin-containing enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1979;62:319–326. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)62237-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Haase A. T. Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broker T. R., Angerer L. M., Yen P. H., Hershey N. D., Davidson N. Electron microscopic visualization of tRNA genes with ferritin-avidin: biotin labels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):363–384. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung S. W., Tishler P. V., Atkins L., Sengupta S. K., Modest E. J., Forget B. G. Gene mapping by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1977 May;1(3):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(77)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudler R., Egg A. H., Kubli E., Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Gehring W. J., Steward R., Schedl P. Transfer RNA genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2921–2937. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Pardue M. L. Formation and detection of RNA-DNA hybrid molecules in cytological preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):378–383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard D. S., Kawasaki E. S., Bancroft F. C., Szabo P. Localization of a unique gene by direct hybridization in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3755–3759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Avidin. Adv Protein Chem. 1975;29:85–133. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanker J. S., Yates P. E., Metz C. B., Rustioni A. A new specific, sensitive and non-carcinogenic reagent for the demonstration of horseradish peroxidase. Histochem J. 1977 Nov;9(6):789–792. doi: 10.1007/BF01003075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Gillam I. C., Delaney A. D., Tener G. M. Acetylation of chromosome squashes of Drosophila melanogaster decreases the background in autoradiographs from hybridization with [125I]-labeled RNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Aug;26(8):677–679. doi: 10.1177/26.8.99471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H. Avidin binds to condensed chromatin. Stain Technol. 1977 May;52(3):165–169. doi: 10.3109/10520297709116769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitzmann H., Richards F. M. Use of the avidin-biotin complex for specific staining of biological membranes in electron microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3537–3541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann K., Wood S. W., Brinton C. C., Montibeller J. A., Finn F. M. Iminobiotin affinity columns and their application to retrieval of streptavidin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4666–4668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John H. A., Birnstiel M. L., Jones K. W. RNA-DNA hybrids at the cytological level. Nature. 1969 Aug 9;223(5206):582–587. doi: 10.1038/223582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning J. E., Hershey N. D., Broker T. R., Pellegrini M., Mitchell H. K., Davidson N. A new method of in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 24;53(2):107–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00333039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Gall J. G. Nucleic acid hybridization to the DNA of cytological preparations. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;10:1–16. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60727-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudkin G. T., Stollar B. D. High resolution detection of DNA-RNA hybrids in situ by indirect immunofluorescence. Nature. 1977 Feb 3;265(5593):472–473. doi: 10.1038/265472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S., DeFranco D., Silberklang M., Hosbach H. A., Schmidt T., Kubli E., Gergen J. P., Wensink P. C., Söll D. The initiator tRNA genes of Drosophila melanogaster: evidence for a tRNA pseudogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5867–5882. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodja A., Davidson N. Gene mapping and gene enrichment by the avidin-biotin interaction: use of cytochrome-c as a polyamine bridge. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Feb;5(2):385–401. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffensen D. M., Duffey P., Prensky W. Localisation of 5S ribosomal RNA genes on human chromosome 1. Nature. 1974 Dec 20;252(5485):741–743. doi: 10.1038/252741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo P., Elder R., Steffensen D. M., Uhlenbeck O. C. Quantitative in situ hybridization of ribosomal RNA species to polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):539–563. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tereba A., Lai M. M., Murti K. G. Chromosome 1 contains the endogenous RAV-0 retrovirus sequences in chicken cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6486–6490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Davidson N. Transmission electron microscopic method for gene mapping on polytene chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7059–7063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]