Abstract
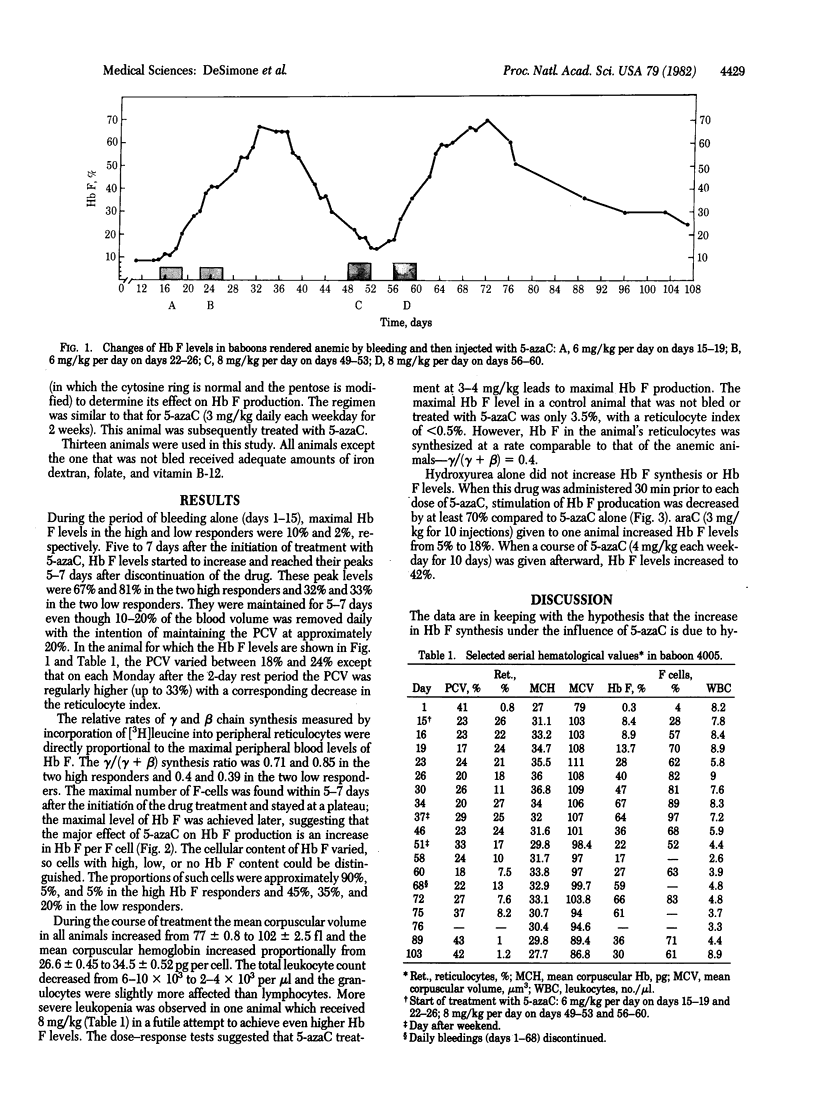
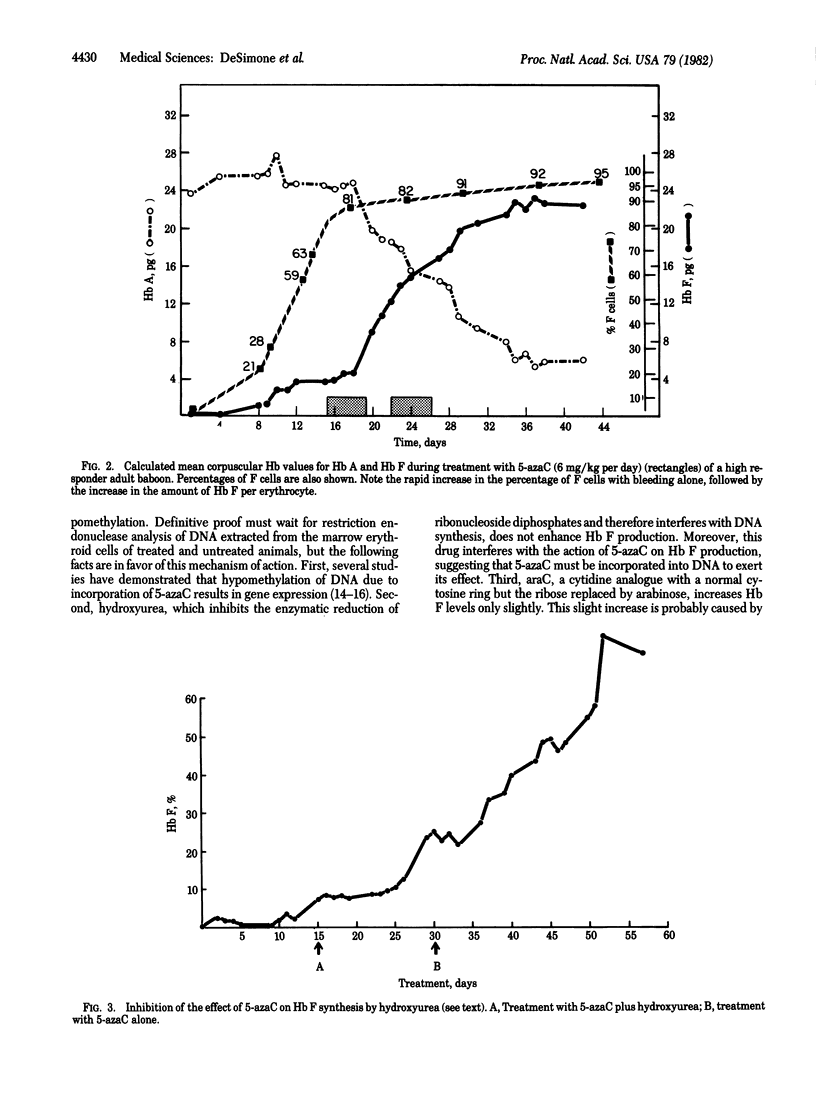
In an attempt to stimulate Hb F synthesis in baboons by means other than erythropoietic stress, we considered the possibility that an agent that inhibits methylation of CpG sequences in DNA may be effective. 5-Azacytidine, a cytosine analogue that cannot be methylated, is such an agent. Animals whose packed red cell volume was maintained at approximately 20% by bleeding were given 10 daily intravenous injections of the drug (6 mg/kg) in 12 days. Hb F levels in these animals started to increase on day 5 of this regimen and peak levels, which were 6-30 times higher than those produced by bleeding alone, occurred 5-7 days after the last dose of the drug. In animals previously identified as genetically "high" or "low" Hb F responders, the maximal Hb F levels were 70-85% and 35-40% respectively. In dose-response studies 5-azacytidine given daily at 3-4 mg/kg produced maximal Hb F increases. The drug did not correlate the percentage (number) of Hb F-containing cells (F cells) beyond the maximal number achieved by bleeding alone and thus its main effect was to increase Hb F per F cell. The finding that Hb F synthesis can be modulated to such a high degree by a drug may have therapeutic implications--e.g., in sickle cell anemia, in which stimulation of Hb F synthesis may prevent sickling.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Compere S. J., Palmiter R. D. DNA methylation controls the inducibility of the mouse metallothionein-I gene lymphoid cells. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Simone J., Mueller A. L. Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) synthesis in baboons, Papio cynocephalus. Analysis of fetal and adult hemoglobin synthesis during fetal development. Blood. 1979 Jan;53(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSimone J., Biel S. I., Heller P. Stimulation of fetal hemoglobin synthesis in baboons by hemolysis and hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2937–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSimone J., Heller P., Amsel J., Usman M. Magnitude of the fetal hemoglobin response to acute hemolytic anemia in baboons is controlled by genetic factors. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):224–226. doi: 10.1172/JCI109654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSimone J., Heller P., Biel M., Zwiers D. Genetic relationship between fetal Hb levels in normal and erythropoietically stressed baboons. Br J Haematol. 1981 Oct;49(2):175–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1981.tb07213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. J., Boyer S. H. Quantitation of hemoglobins within individual red cells: asynchronous biosynthesis of fetal and adult hemoglobin during erythroid maturation in normal subjects. Blood. 1980 Dec;56(6):1082–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich M., Wang R. Y. 5-Methylcytosine in eukaryotic DNA. Science. 1981 Jun 19;212(4501):1350–1357. doi: 10.1126/science.6262918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Eisenman R., Weintraub H. Chromatin structure of endogenous retroviral genes and activation by an inhibitor of DNA methylation. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):311–317. doi: 10.1038/292311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R., Pugh J. E. DNA modification mechanisms and gene activity during development. Science. 1975 Jan 24;187(4173):226–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIHAUER E., BRAUN H., BETKE K. Demonstration von fetalem Hämoglobin in den Erythrocyten eines Blutausstrichs. Klin Wochenschr. 1957 Jun 15;35(12):637–638. doi: 10.1007/BF01481043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Shapiro L. J. Reactivation of an inactive human X chromosome: evidence for X inactivation by DNA methylation. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):393–396. doi: 10.1126/science.6164095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T., Kalmantis T., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Cellular regulation of hemoglobin switching: evidence for inverse relationship between fetal hemoglobin synthesis and degree of maturity of human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6420–6424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrine R. P., Pembrey M. E., John P., Perrine S., Shoup F. Natural history of sickle cell anemia in Saudi Arabs. A study of 270 subjects. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jan;88(1):1–6. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D. X inactivation, differentiation, and DNA methylation. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(1):9–25. doi: 10.1159/000130315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER K., CHERNOFF A. I., SINGER L. Studies on abnormal hemoglobins. I. Their demonstration in sickle cell anemia and other hematologic disorders by means of alkali denaturation. Blood. 1951 May;6(5):413–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Ploeg L. H., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation in the human gamma delta beta-globin locus in erythroid and nonerythroid tissues. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):947–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90086-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




