Abstract
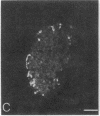
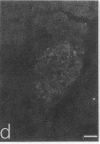
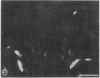
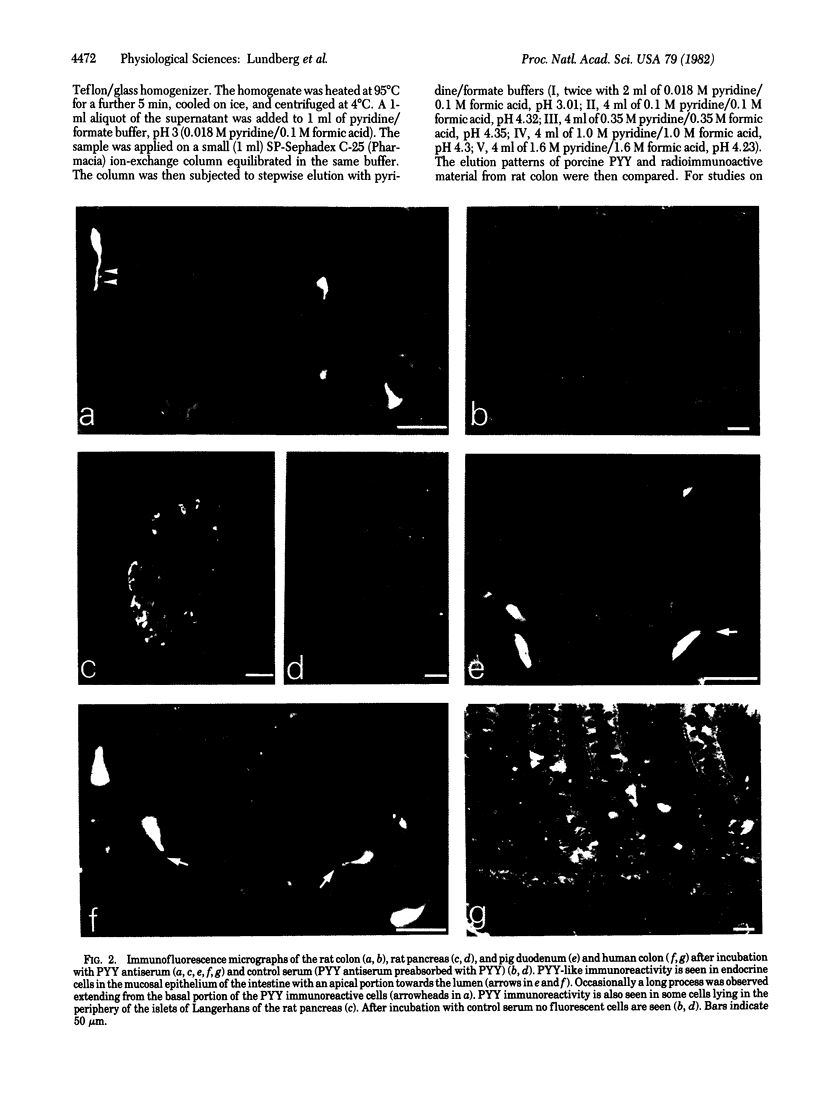
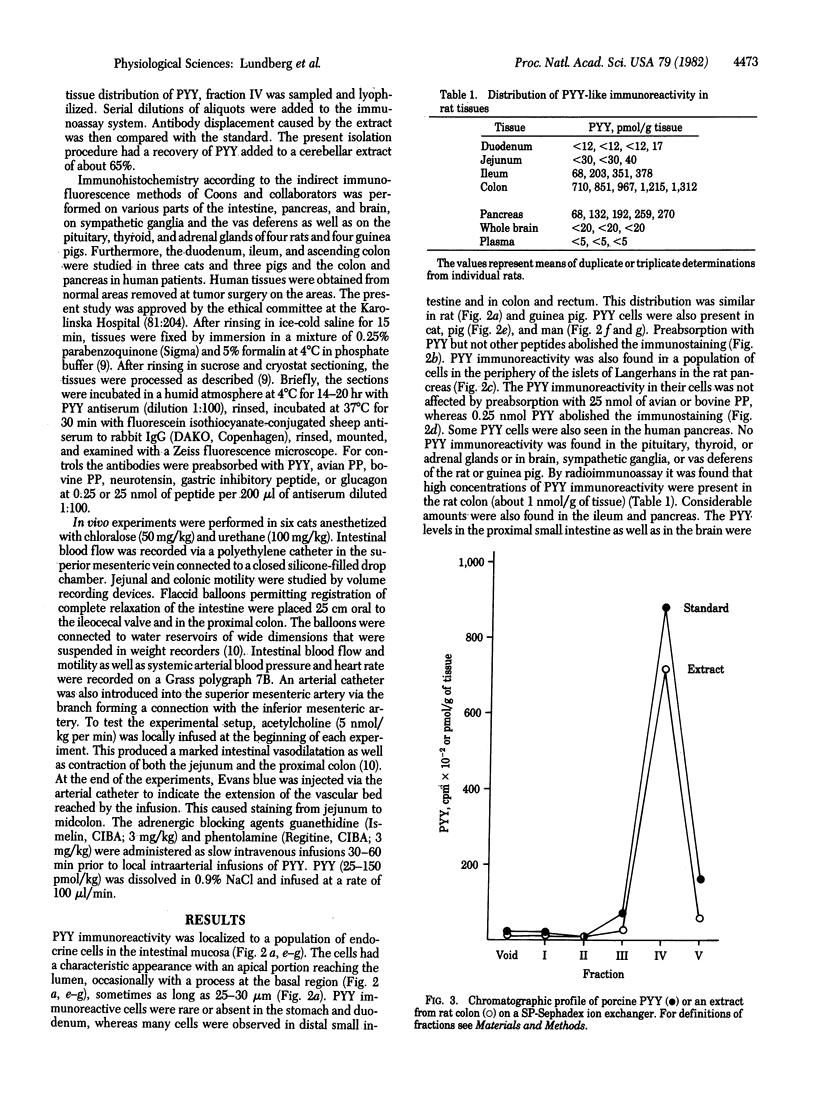
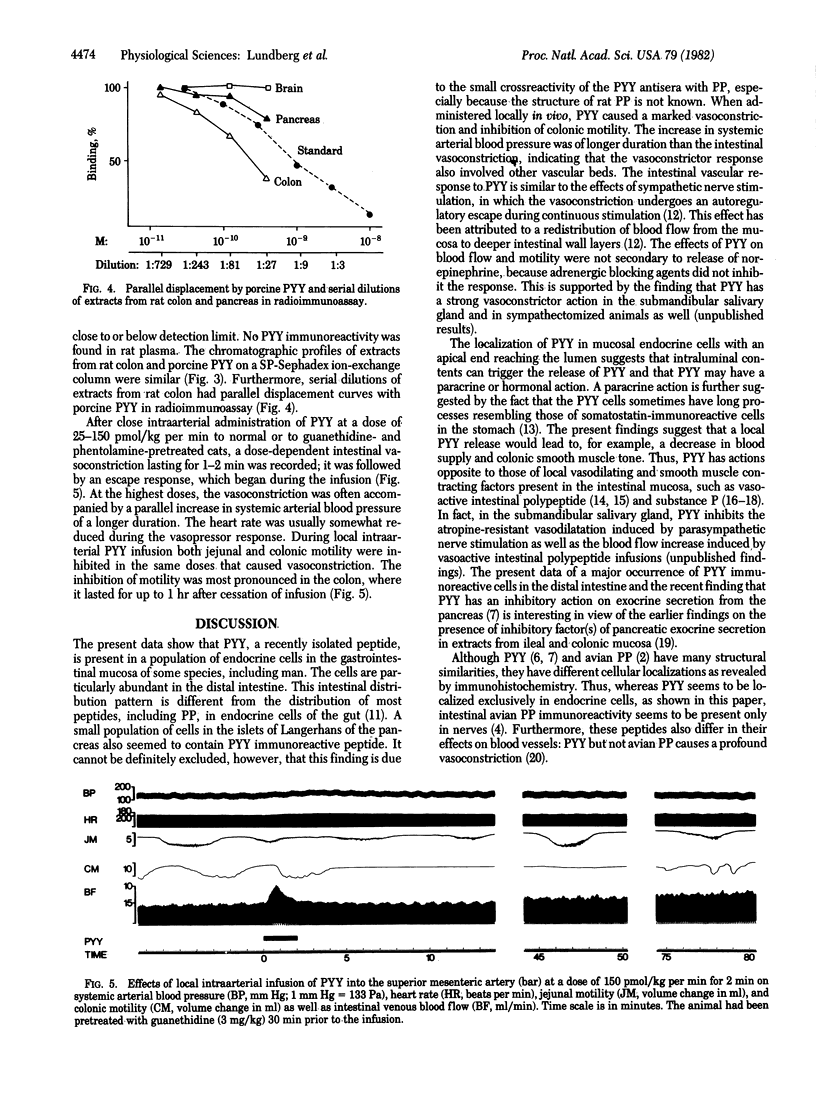
In immunohistochemical studies using antisera to peptide YY (PYY), a 36 amino acid polypeptide isolated from porcine duodenum, it was found that PYY-like immunoreactivity occurred mainly in endocrine cells of the gastrointestinal mucosa. PYY-immunoreactive cells were particularly abundant in the distal intestine and have been observed in five species, including man. By radioimmunoassay it was found that, in the rat, the amount of PYY immunoreactivity was about 100-fold higher in the colon than in the duodenum. The chromatographic profiles of PYY immunoreactivity from the rat colon and porcine PYY on a SP-Sephadex ion exchanger were similar. Furthermore, serial dilutions of extracts from the rat colon and porcine PYY had parallel displacement curves in radioimmunoassay. Close intraarterial administration of PYY in cats caused an intestinal vasoconstriction and an inhibition of jejunal and colonic motility. Simultaneously there was a rise in systemic arterial blood pressure. These effects of PYY were also observed after pretreatment with adrenergic blocking agents. It is concluded that PYY is a gastrointestinal peptide that is present mainly in endocrine cells of distal intestine and that has effect on both intestinal motility and the cardiovascular system.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eklund S., Jodal M., Lundgren O., Sjöqvist A. Effects of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide on blood flow, motility and fluid transport in the gastrointestinal tract of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Apr;105(4):461–468. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., LEWIS D. H., LUNDGREN O., MELLANDER S., WALLENTIN I. THE EFFECT OF GRADED VASOCONSTRICTOR FIBRE STIMULATION ON THE INTESTINAL RESISTANCE AND CAPACITANCE VESSELS. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Aug;61:445–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. A., Hood A. J., Mushens J., Smy J. R. Pancreotone, an inhibitor of pancreatic secretion in extracts of ileal and colonic mucosa. J Physiol. 1979 Jul;292:455–467. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultén L. Extrinsic nervous control of colonic motility and blood flow. An experimental study in the cat. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1969;335:1–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter W. M. Radioimmunoassay and saturation analysis. Preparation and assessment of radioactive tracers. Br Med Bull. 1974 Jan;30(1):18–23. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel J. R., Hayden L. J., Pollock H. G. Isolation and characterization of a new pancreatic polypeptide hormone. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 25;250(24):9369–9376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Fahrenkrug J., Schaffalitzky De Muckadell O., Sundler F., Håkanson R., Rehfeld J. R. Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) to central and peripheral neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3197–3200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L. I., Goltermann N., de Magistris L., Rehfeld J. F., Schwartz T. W. Somatostatin cell processes as pathways for paracrine secretion. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1393–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.382360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorén I., Alumets J., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Immunoreactive pancreatic polypeptide (PP) occurs in the central and peripheral nervous system: preliminary immunocytochemical observations. Cell Tissue Res. 1979 Aug;200(2):179–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00236410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Anggård A., Hökfelt T., Kimmel J. Avian pancreatic polypeptide (APP) inhibits atropine resistant vasodilation in cat submandibular salivary gland and nasal mucosa: possible interaction with VIP. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Oct;110(2):199–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06651.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Anggård A., Kimmel J., Goldstein M., Markey K. Coexistence of an avian pancreatic polypeptide (APP) immunoreactive substance and catecholamine in some peripheral and central neurons. Acta Physiol Scand. 1980 Sep;110(1):107–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1980.tb06638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Anggård A., Terenius L., Elde R., Markey K., Goldstein M., Kimmel J. Organizational principles in the peripheral sympathetic nervous system: subdivision by coexisting peptides (somatostatin-, avian pancreatic polypeptide-, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-like immunoreactive materials). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1303–1307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson G., Larsson L. I., Håkanson R., Brodin E., Pernow B., Sundler F. Localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity in mouse gut. Histochemistry. 1975;43(1):97–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00490158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Isolation and characterization of peptide YY (PYY), a candidate gut hormone that inhibits pancreatic exocrine secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2514–2518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Mutt V. Isolation of two novel candidate hormones using a chemical method for finding naturally occurring polypeptides. Nature. 1980 Jun 5;285(5764):417–418. doi: 10.1038/285417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]