Abstract
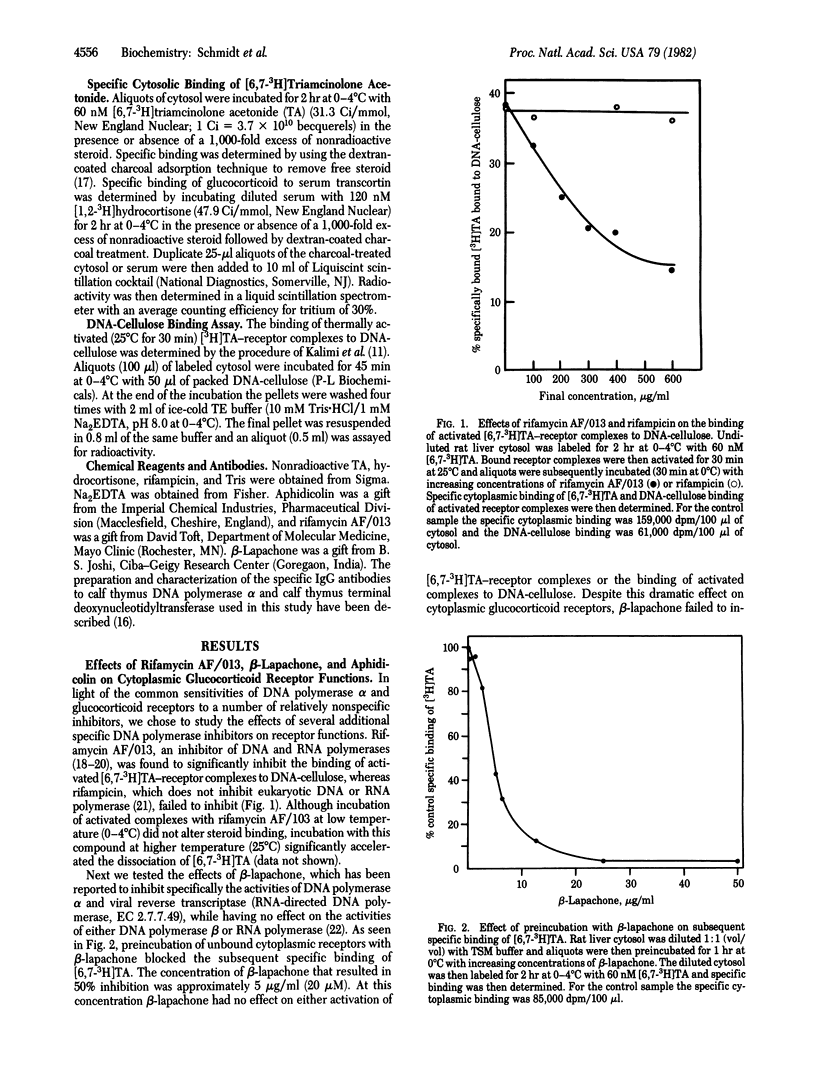
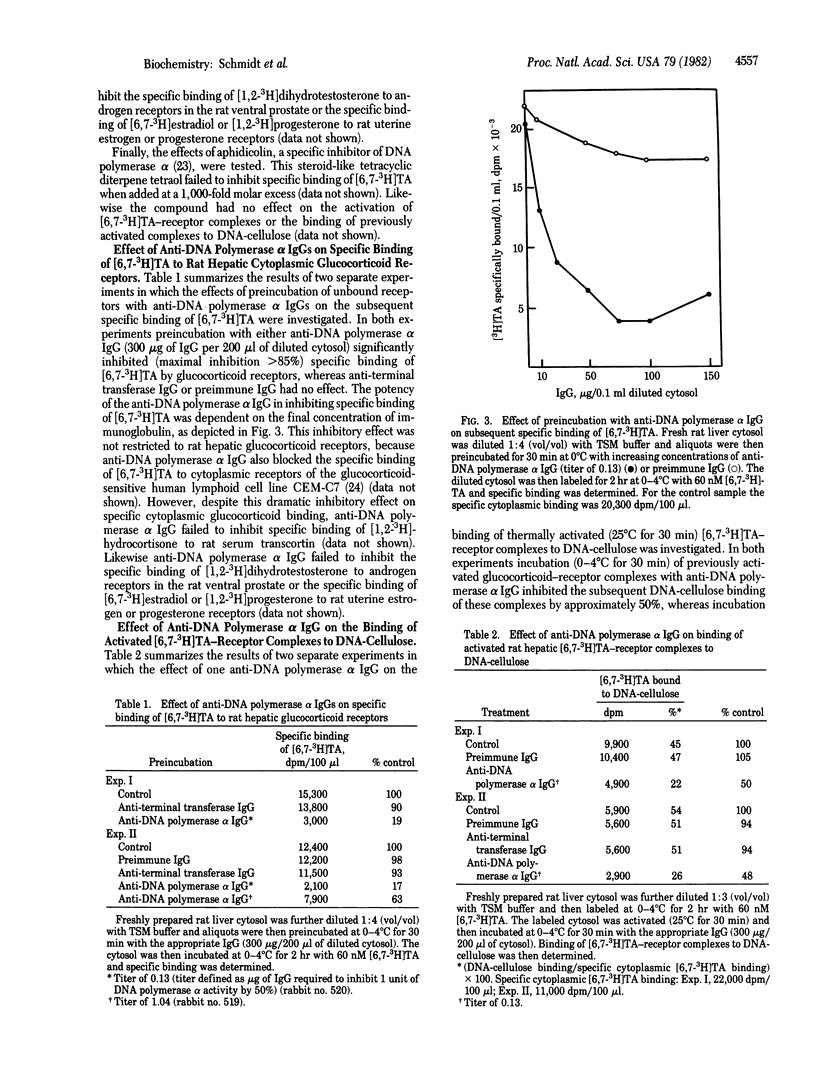
Specific inhibitors and anti-DNA polymerase alpha IgG have been utilized to probe for similarities between cytoplasmic rat hepatic glucocorticoid receptors and DNA polymerase alpha [DNA nucleotidyltransferase (DNA-directed), EC 2.7.7.7]. Rifamycin AF/013, an inhibitor of RNA and DNA polymerase activities, significantly inhibited the binding of activated [6,7-3H]-triamcinolone acetonide (TA) receptor complexes to DNA-cellulose. beta-Lapachone, an inhibitor of DNA polymerase alpha and reverse transcriptase activities, inhibited the specific binding of [6,7-3H]TA when preincubated with unbound receptors. Aphidicolin, another DNA polymerase alpha inhibitor, failed to inhibit any of the glucocorticoid-receptor functions tested. Two specific anti-DNA polymerase alpha IgGs interfered with glucocorticoid receptor functions as measured by their ability to inhibit the binding of [6,7-3H]TA to unbound receptors (85% maximal inhibition) and, to a lesser extent, to inhibit the binding of activated [6,7-3H]TA receptor complexes to DNA-cellulose (50% maximal inhibition). The anti-DNA polymerase alpha IgG and beta-lapachone failed to affect the binding of tritiated estradiol, progesterone, or 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone to their receptors in appropriate rat target tissues or the binding of [1,2-3H]hydrocortisone to serum transcortin. The most obvious interpretation of these data is that cytoplasmic glucocorticoid receptors and DNA polymerase alpha share antigenic determinants. An alternative interpretation is that the polyclonal anti-DNA polymerase alpha antibody contains IgG molecules raised against calf thymus cytoplasmic activated glucocorticoid-receptor complexes that copurified with DNA polymerase alpha used as the antigen. Taken collectively, however, the antibody and inhibitor data suggest a relationship between DNA polymerase alpha and the glucocorticoid receptor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atger M., Milgrom E. Chromatographic separation on phosphocellulose of activated and nonactivated forms of steroid-receptor complex. Purification of the activated complex. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 21;15(19):4298–4304. doi: 10.1021/bi00664a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrack E. R., Coffey D. S. The specific binding of estrogens and androgens to the nuclear matrix of sex hormone responsive tissues. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7265–7275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Specific cytoplasmic glucocorticoid hormone receptors in hepatoma tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):932–937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Bollum F. J., Chang L. M. Intracellular localization of DNA polymerase alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3049–3052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cake M. H., DiSorbo D. M., Litwack G. Effect of pyridoxal phosphate on the DNA binding site of activated hepatic glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):4886–4891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Bollum F. J. A comparison of associated enzyme activities in various deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3398–3404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. M., Bollum F. J. Immunological reagents for comparisons of DNA polymerase-alpha and DNA polymerase-beta. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):494–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christmann J. L., Dahmus M. E. Monoclonal antibody specific for calf thymus RNA polymerases IIO and IIA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11798–11803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCioccio R. A., Srivastava B. I. Inhibition of deoxynucleotide-polymerizing enzyme activities of human cells and of simian sarcoma virus by heparin. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2401–2407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H. J., Schleenbaker R. E., Simons S. S., Jr Affinity labeling of the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor with dexamethasone 21-mesylate. Identification of covalently labeled receptor by immunochemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12920–12925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Chen J. T., Korn D. Enzymological characterization of KB cell DNA polymerase-alpha. Regulation of template binding by nucleic acid base composition. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):133–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Abrell J. W., Robert M. S., Yang S. S., Smith R. G. Reverse transciptase from Mason-Pfizer monkey tumor virus, avian myeloblastosis virus, and Rauscher leukemia virus and its response to rifamycin derivatives. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Apr;48(4):1185–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard G. F., Gurgo C., Grandgenett D. P., Green M. Rifamycin derivatives: specific inhibitors of nucleic acid polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 2;53(1):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91419-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson I. C., Fischel R. E., Loeb J. N. Suppression of liver DNA synthesis by cortisone. Endocrinology. 1971 Jun;88(6):1471–1476. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-6-1471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes A. M., Hesslewood I. P., Johnston I. R. Evidence that DNA polymerase-alpha of calf thymus contains a subunit of molecular weight 155000. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 16;62(2):229–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A. New views of the biochemistry of eucaryotic DNA replication revealed by aphidicolin, an unusual inhibitor of DNA polymerase alpha. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):647–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90426-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami S., Taguchi T., Ohashi M., Oguro M., Nagano H., Mano Y. Aphidicolin prevents mitotic cell division by interfering with the activity of DNA polymerase-alpha. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):458–460. doi: 10.1038/275458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John J. K., Moudgil V. K. Activation of glucocorticoid receptor by ATP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Oct 29;90(4):1242–1248. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimi M., Colman P., Feigelson P. The "activated" hepatic glucocorticoid-receptor complex. Its generation and properties. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 10;250(3):1080–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimi M., Love K. Role of chemical reagents in the activation of rat hepatic glucocorticoid-receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4687–4690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Loeb J. N. Differential sensitivity of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA synthesis to suppression by cortisone treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 24;246(3):412–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90777-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W., McGOVERN A. P., MARGESON K. B. Changes in the distribution of polymerase activity during DNA synthesis in mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jan 15;49:102–107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.1.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamothe P., Baril B., Chi A., Lee L., Baril E. Accessory proteins for DNA polymerase alpha activity with single-strand DNA templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4723–4727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmar P. H., Toft D. O. Inhibition of the binding of progesterone receptor to nuclei: effects of o-phenanthroline and rifamycin AF/013. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):8–15. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longiaru M., Ikeda J. E., Jarkovsky Z., Horwitz S. B., Horwitz M. S. The effect of aphidicolin on adenovirus DNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3369–3386. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall L. E., Graham D. R., Reich K. A., Sigman D. S. Cleavage of deoxyribonucleic acid by the 1,10-phenanthroline-cuprous complex. Hydrogen peroxide requirement and primary and secondary structure specificity. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):244–250. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moudgil V. K., Toft D. O. ATP-PPi exchange activity of progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3443–3447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen C. J., Sando J. J., Pratt W. B. Evidence that dephosphorylation inactivates glucocorticoid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman M. R., Thompson E. B. Characterization of a glucocorticoid-sensitive human lymphoid cell line. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3785–3791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguro M., Nagano H., Mano Y. The mode of inhibitory action by pyridoxal 5-phosphate on DNA polymerase-alpha and -beta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):727–734. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oguro M., Suzuki-Hori C., Nagano H., Mano Y., Ikegami S. The mode of inhibitory action by aphidicolin on eukaryotic DNA polymerase alpha. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;97(2):603–607. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B., Coffey D. S. A fixed site of DNA replication in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Tomkins G. M. Effect of inhibitors of nucleic acid synthesis on steroid-mediated induction of tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Nov 28;30(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A. M., Bell P. A. The involvement of receptro sulphydryl groups in the binding of steroids to the cytoplasmic glucocorticoid receptor from rat thymus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 10;411(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisher S., Rutman R. J., Erhan S. Phosphorylation of DNA polymerase. Cytobios. 1975;12(45):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando J. J., La Forest A. C., Pratt W. B. ATP-dependent activation of L cell glucocorticoid receptors to the steroid binding form. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4772–4778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. J., Sekula B. C., Litwack G. The effects of 1,10-phenanthroline on the binding of activated rat hepatic glucocorticoid-receptor complexes to deoxyribonucleic acid-cellulose. Endocrinology. 1981 Sep;109(3):803–812. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-3-803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuerch A. R., Wehrli W. beta-Lapachone, an inhibitor of oncornavirus reverse transcriptase and eukaryotic DNA polymerase-alpha. Inhibitory effect, thiol dependence and specificity. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar;84(1):197–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater J. P., Mildvan A. S., Loeb L. A. Zinc in DNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 2;44(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80155-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft D., Moudgil V., Lohmar P., Miller J. Binding of ATP to progesterone receptors: properties and functional significance of this interaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 11;286:29–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb29403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. J., Saunders G. F. Action of rifamycin derivatives on RNA polymerase of human leukemic lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissbach A., Baltimore D., Bollum F., Gallo R., Korn D. Nomenclature of eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):1–2. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. Purification of the glucocorticoid receptor from rat liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9284–9290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


