Abstract
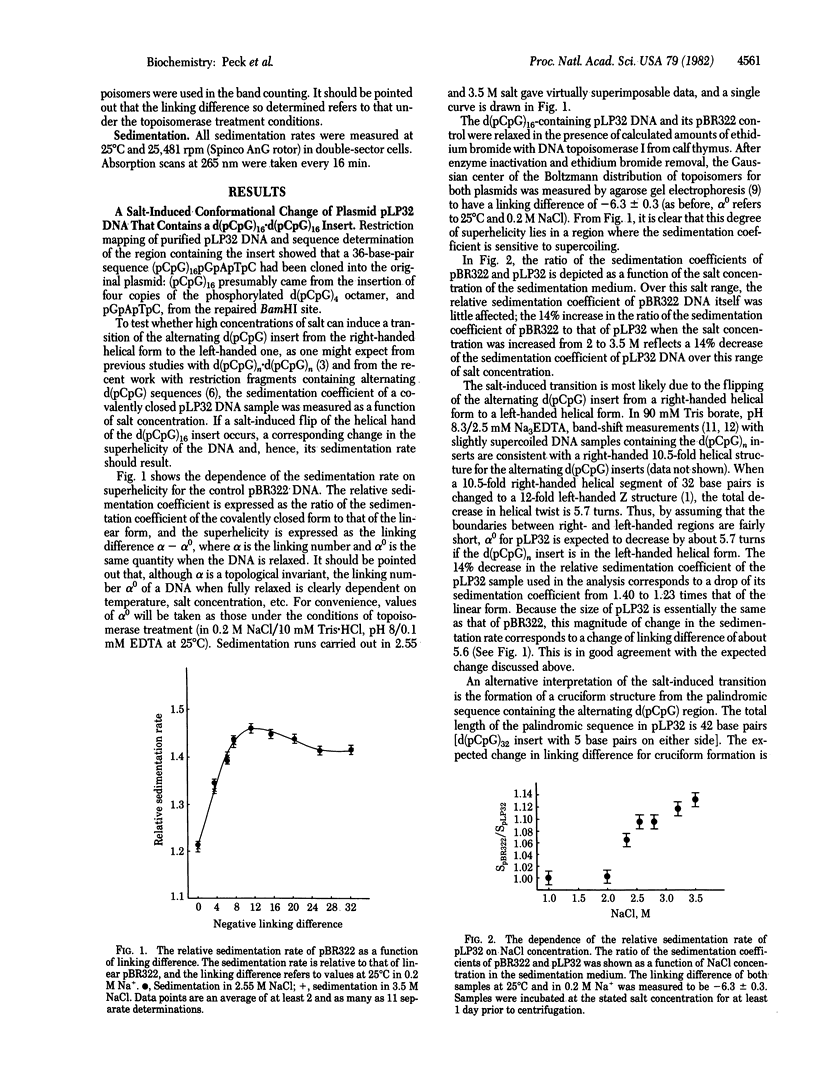
Negative supercoiling of plasmid DNAs containing 24--42 base pairs of alternating d(pCpG) inserts is shown to cause the flipping of the helical hand of the inserts from right to left under physiological conditions. For a negatively supercoiled DNA with a fixed linking number, this flipping reduces its superhelicity and, therefore, is accompanied by a shift of its electrophoretic mobility in agarose gel. Quantitation of the mobility shifts indicates that essentially the whole stretch of contiguous alternating d(pCpG) flips to the left-handed helical form when the negative superhelical density (specific linking difference) is greatest than or equal to 0.03.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer W., Vinograd J. Interaction of closed circular DNA with intercalative dyes. II. The free energy of superhelix formation in SV40 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):419–435. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects of methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew D. E., Wang J. C. Conformational fluctuations of DNA helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H., Takano T., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. High-salt d(CpGpCpG), a left-handed Z' DNA double helix. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):567–573. doi: 10.1038/286567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F. B. The writhing number of a space curve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):815–819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Ohmori H., Tomizawa J. DNA gyrase and DNA supercoiling. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):35–40. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T. S., Wang J. C. Thermodynamic properties of superhelical DNAs. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):527–535. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kłysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Larson J. E., Hart P. A., Wells R. D. Left-handed DNA in restriction fragments and a recombinant plasmid. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):672–677. doi: 10.1038/290672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. The inverted repeat as a recognizable structural feature in supercoiled DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6468–6472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., Mizuuchi M., Gellert M. Cruciform structures in palindromic DNA are favored by DNA supercoiling. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayotatos N., Wells R. D. Cruciform structures in supercoiled DNA. Nature. 1981 Feb 5;289(5797):466–470. doi: 10.1038/289466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Canuel L. L., Pohl F. M. "Alternating B-DNA" conformation for the oligo(dG-dC) duplex in high-salt solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2508–2511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Sequence dependence of the helical repeat of DNA in solution. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):375–378. doi: 10.1038/292375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl F. M., Jovin T. M. Salt-induced co-operative conformational change of a synthetic DNA: equilibrium and kinetic studies with poly (dG-dC). J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):375–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Pulleyblank D. E., Vinograd J. The problems of eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA packaging and in vivo conformation posed by superhelix density heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1183–1205. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Carlson J. O., Pettijohn D. E. Torsional tension in the DNA double helix measured with trimethylpsoralen in living E. coli cells: analogous measurements in insect and human cells. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):773–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thamann T. J., Lord R. C., Wang A. H., Rich A. The high salt form of poly(dG-dC).poly(dG-dC) is left-handed Z-DNA: Raman spectra of crystals and solutions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5443–5457. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Lukashin A. V., Anshelevich V. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Fluctuations in superhelical DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Mar;6(3):967–982. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.3.967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Helical repeat of DNA in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):200–203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Interactions between twisted DNAs and enzymes: the effects of superhelical turns. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):797–816. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]