Abstract
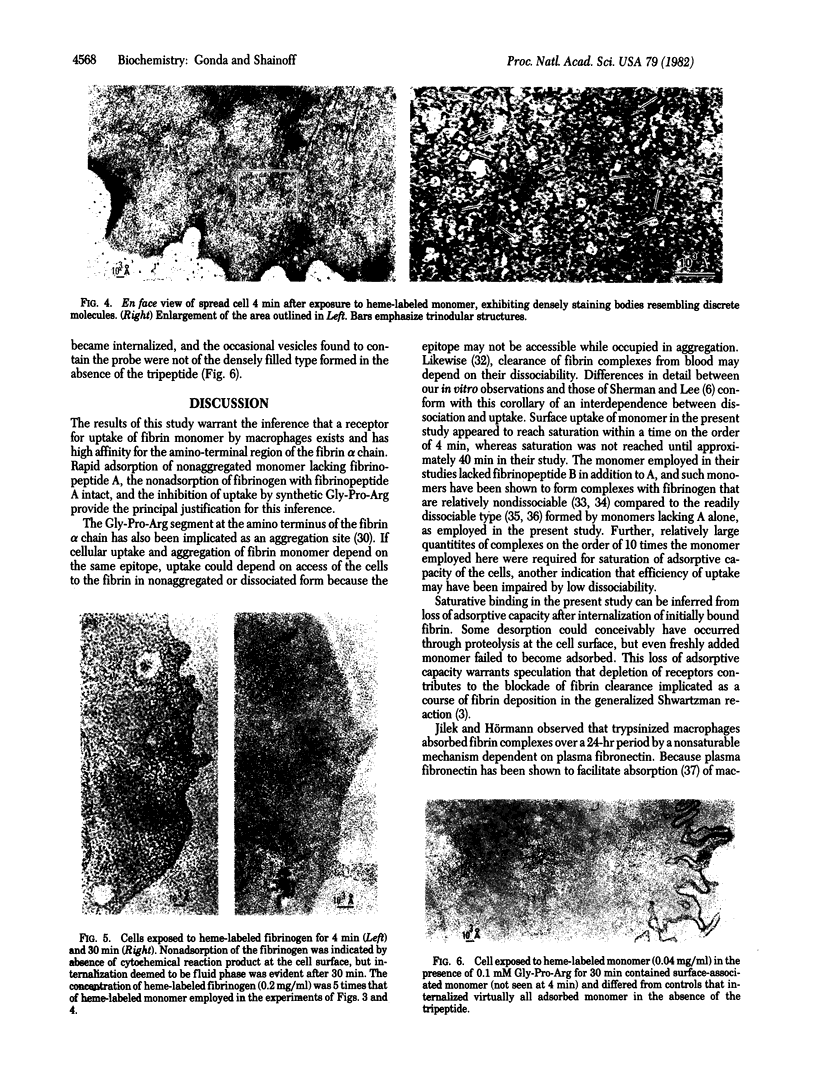
Human fibrinogen and fibrin monomer were labeled with heme-octapeptide for cytochemical examination of their interaction with rabbit peritoneal macrophages in vitro. Upon short exposure to labeled fibrin monomer in solution with unlabeled fibrinogen, the cells became covered with surface-adsorbed monomer in nonaggregated form and having a characteristic trinodular shape. Within 30 min, the adsorbed monomer became fully internalized by vesicular uptake, with much of it being incorporated into lysosomal bodies. A concomitant loss of adsorptive capacity of the cell surface for uptake of more monomer accompanied the internalization. By contrast, labeled fibrinogen was not adsorbed by the macrophage surface. Some internalization of fibrinogen by passive fluid-phase pinocytosis was evident, but it was not accompanied by loss of absorptive capacity for fibrin monomer. The active uptake of monomer may have depended on binding to the amino terminus that is blocked by fibrinopeptide A in fibrinogen, because addition of synthetic peptide corresponding to the terminal Gly-Pro-Arg segment inhibited both the adsorption and the internalization of monomer.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANG N. U., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. Pathogenesis of the coagulation defect developing during pathological plasma proteolytic ("fibrinolytic") states. III. Demonstration of abnormal clot structure by electron microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:935–948. doi: 10.1172/JCI104548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Amrani D., Mosesson M. W., Bianco C. Receptors for cold-insoluble globulin (plasma fibronectin) on human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):42–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Hessel B., Iwanaga S. Structure of N-terminal fragments of fibrinogen and specificity of thrombin. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1445–1448. doi: 10.1038/2151445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvin R. B., Dvorak H. F. Fibrinogen/fibrin on the surface of macrophages: detection, distribution, binding requirements, and possible role in macrophage adherence phenomena. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1377–1390. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardik B. N., Shainoff J. R. Crosslinking of monomeric fibrin by factor XIIIa. Thromb Haemost. 1979 Oct 31;42(3):864–872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar W., Prentice C. R. The effect of temperature on formation of fibrin complexes. Thromb Res. 1980 Jun 15;18(6):759–772. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90199-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., Lindeman J., Nieuwenhuizen W. Immunoenzyme histochemical localization of fibrin degradation products in tissues. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jun;103(3):337–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estis L. F., Haschemeyer R. H. Electron microscopy of negatively stained and unstained fibrinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3139–3143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler W. E., Erickson H. P. Trinodular structure of fibrinogen. Confirmation by both shadowing and negative stain electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda S. R., Shainoff J. R. Stabilization of plasma fibronectin following sulfhydryl blockade. Thromb Res. 1980 Dec 1;20(5-6):581–586. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL C. E., SLAYTER H. S. The fibrinogen molecule: its size, shape, and mode of polymerization. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Jan 25;5(1):11–16. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jilek F., Hörmann H. Fibronectin (cold-insoluble globulin), V[1]. Mediation of fibrin-monomer binding to macrophages. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Nov;359(11):1603–1605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaide H., Shainoff J. R. Cross-linking of fibrinogen and fibrin by fibrin-stablizing factor (factor XIIIa). J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):574–597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnovsky M. J. The ultrastructural basis of capillary permeability studied with peroxidase as a tracer. J Cell Biol. 1967 Oct;35(1):213–236. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierulf P., Abildgaard U. Studies on soluble fibrin in plasma. I. N-terminal analysis of a modified fraction I (Cohn) from normal and thrombin-incubated plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Oct;28(2):231–240. doi: 10.3109/00365517109086905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraehenbuhl J. P., Galardy R. E., Jamieson J. D. Preparation and characterization of an immuno-electron microscope tracer consisting of a heme-octapeptide coupled to fab. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):208–223. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudryk B. J., Collen D., Woods K. R., Blombäck B. Evidence for localization of polymerization sites in fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3322–3325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE L., McCLUSKEY R. T. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the reticuloendothelial clearance of circulating fibrin aggregates. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:611–618. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Doolittle R. F. Synthetic peptide derivatives that bind to fibrinogen and prevent the polymerization of fibrin monomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3085–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Berghaus G., Mahn I., Krell W. Formation and dissociation of soluble fibrin complexes in plasma at 20 degrees C and at 37 degrees C. Thromb Res. 1979;14(4-5):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Berghaus G., Mahn I., Köveker G., Maul F. D. In vivo behaviour of homologous urea-soluble 131I-fibrin and 125I-fibrinogen in rabbits: the effect of fibrinolysis inhibition. Br J Haematol. 1976 May;33(1):61–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00972.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plattner H., Wachter E., Gröbner P. A heme-nonapeptide tracer for electron microscopy. Preparation, characterization and comparison with other heme-tracers. Histochemistry. 1977 Aug 22;53(3):223–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00511078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAINOFF J. R., PAGE I. H. Significance of cryoprofibrin in fibrinogen-fibrin conversion. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:687–707. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shainoff J. R., Page I. H. Deposition of modified fibrinogen within the aortic intima. Atherosclerosis. 1972 Nov-Dec;16(3):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(72)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Harwig S., Lee J. In vitro formation and i vivo clearance of fibrinogen: fibrin complexes. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jul;86(1):100–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu N., Siminoescu M., Palade G. E. Permeability of muscle capillaries to small heme-peptides. Evidence for the existence of patent transendothelial channels. J Cell Biol. 1975 Mar;64(3):586–607. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.3.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Cohn Z. A. The interaction of soluble horseradish peroxidase with mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1972 Oct;55(1):186–204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tu A. T., Reinosa J. A., Hsiao Y. Y. Peroxidative activity of hemepeptides from horse heart cytochrome c. Experientia. 1968 Mar 15;24(3):219–221. doi: 10.1007/BF02152778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisel J. W., Phillips G. N., Jr, Cohen C. A model from electron microscopy for the molecular structure of fibrinogen and fibrin. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):263–267. doi: 10.1038/289263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissig S. L., Williams M. C. Permeability of muscle capillaries to microperoxidase. J Cell Biol. 1978 Feb;76(2):341–359. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]