Abstract
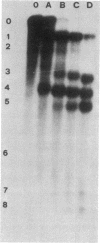
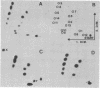
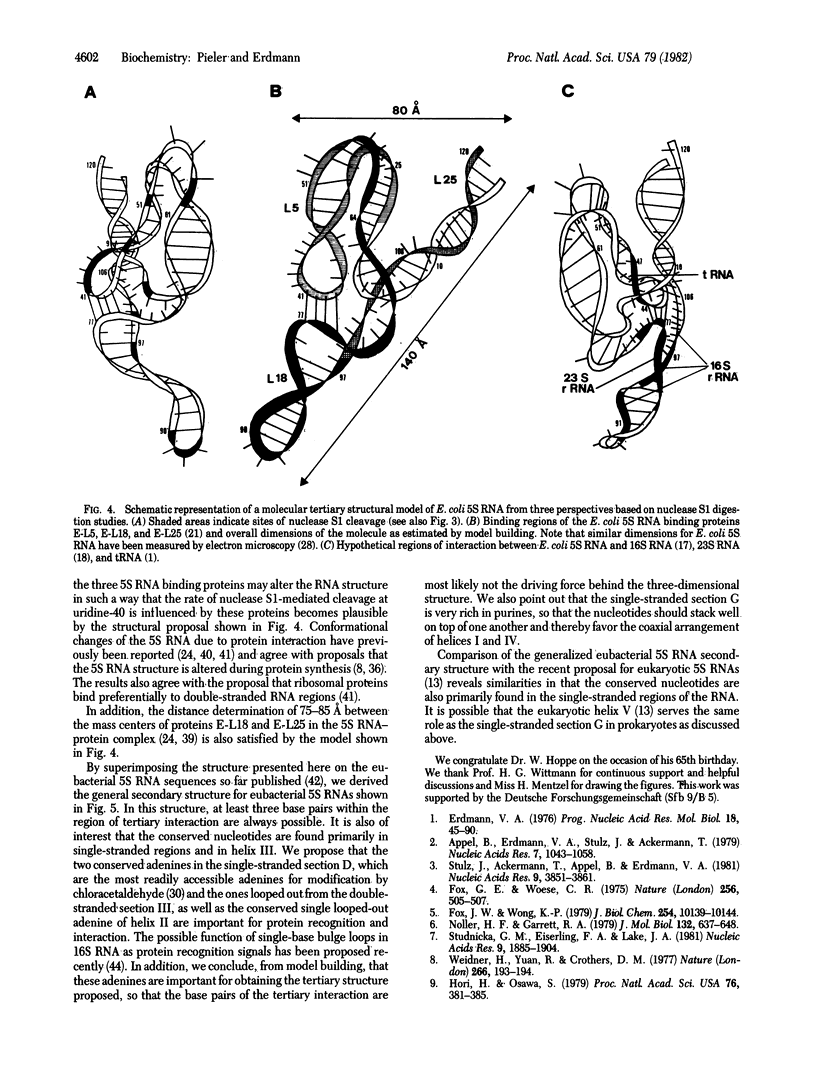
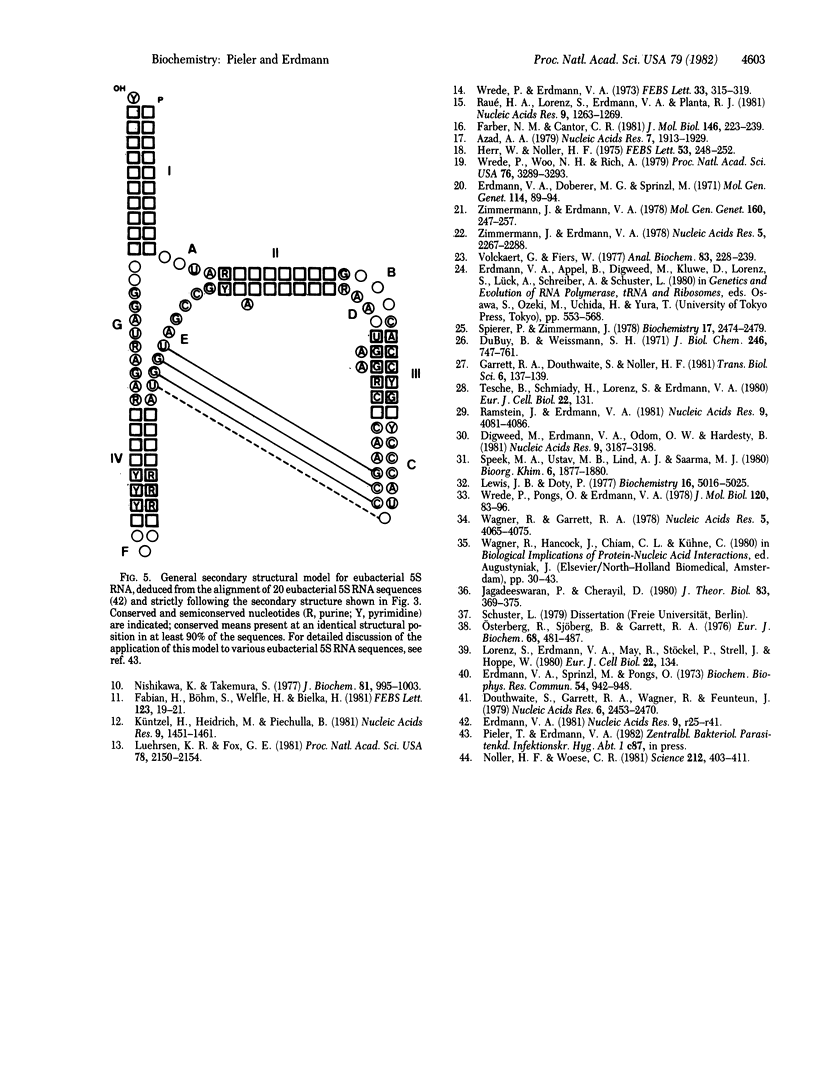
Escherichia coli 5S RNA and its specific protein complexes were hydrolyzed with the single-strand-specific nuclease S1. Based on the results, a tertiary structural model for E. coli 5S RNA is proposed in which ribosomal proteins E-L5, E-L18, and E-L25 influence the conformation of the RNA. This may be of significance for ribosomal function. Comparison of the proposed E. coli 5S RNA structure with those of 18 other prokaryotic 5S RNAs led to a generalized eubacterial 5S RNA tertiary structure in which the majority of the conserved nucleotides are in non-base-paired regions and several conserved "looped-out" adenines (in E. coli, adenines -52, -53, -57, -58, and -66) are implied to be important for protein recognition or interaction or both.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel B., Erdmann V. A., Stulz J., Ackerman T. Determination of base pairing in Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus 5S RNAs by infrared spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 25;7(4):1043–1057. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.4.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azad A. A. Intermolecular base-paired interaction between complementary sequences present near the 3' ends of 5S rRNA and 18S (16S) rRNA might be involved in the reversible association of ribosomal subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1913–1929. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Digweed M., Erdmann V. A., Odom O. W., Hardesty B. Fluorescence modification of Escherichia coli 5S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3187–3198. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douthwaite S., Garrett R. A., Wagner R., Feunteun J. A ribonuclease-resistant region of 5S RNA and its relation to the RNA binding sites of proteins L18 and L25. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2453–2470. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBuy B., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence of Pseudomonas fluorescens 5 S ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):747–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S RNA sequences and their precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r25–r42. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Doberer H. G. Structure and function of 5S RNA: the role of the 3' terminus in 5S RNA function. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(2):89–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00332779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Sprinzl M., Pongs O. The involvement of 5S RNA in the binding of tRNA to ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):942–948. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90785-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Structure and function of 5S and 5.8 S RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;18:45–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian H., Böhm S., Welfle H., Reich P., Bielka H. Laser Raman studies of rat liver ribosomal 5 S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 12;123(1):19–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber N. M., Cantor C. R. A slow tritium exchange study of the solution structure of Escherichia coli 5 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 25;146(2):223–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. 5S RNA secondary structure. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):505–507. doi: 10.1038/256505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett R. A., Noller H. F. Structures of complexes of 5S RNA with ribosomal proteins L5, L18 and L25 from Escherichia coli: identification of kethoxal-reactive sites on the 5S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Noller H. F. A fragment of 23S RNA containing a nucleotide sequence complementary to a region of 5S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 1;53(2):248–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80030-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S. Evolutionary change in 5S RNA secondary structure and a phylogenic tree of 54 5S RNA species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Cherayil J. D. A general model for the conformational switch in 5S RNA during protein synthesis. J Theor Biol. 1980 Mar 21;83(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(80)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küntzel H., Heidrich M., Piechulla B. Phylogenetic tree derived from bacterial, cytosol and organelle 5S rRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1451–1461. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Doty P. Identification of the single-strand regions in Escherichia coli 5S RNA, native and A forms, by the binding of oligonucleotides. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5016–5025. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luehrsen K. R., Fox G. E. Secondary structure of eukaryotic cytoplasmic 5S ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2150–2154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Takemura S. Structure and function of 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid from Torulopsis utilis. III. Detection of single-stranded regions by digestion with nuclease S1. J Biochem. 1977 Apr;81(4):995–1003. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Woese C. R. Secondary structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):403–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6163215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterberg R., Sjöberg B., Garrett R. A. Molecular model for 5-S RNA. A small-angle x-ray scattering study of native, denatured and aggregated 5-S RNA from Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):481–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramstein J., Erdmann V. A. A hydrogen exchange study of Escherichia coli 5S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4081–4086. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Lorenz S., Erdmann V. A., Planta R. J. Reconstitution of biologically active 50S ribosomal subunits with artificial 5S RNA molecules carrying disturbances in the base pairing within the molecular stalk. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1263–1269. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spierer P., Zimmermann R. A. Stoichiometry, cooperativity, and stability of interactions between 5S RNA and proteins L5, L18, and L25 from the 50S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 27;17(13):2474–2479. doi: 10.1021/bi00606a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studnicka G. M., Eiserling F. A., Lake J. A. A unique secondary folding pattern for 5S RNA corresponds to the lowest energy homologous secondary structure in 17 different prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 24;9(8):1885–1904. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.8.1885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stulz J., Ackermann T., Appel B., Erdmann V. A. Determination of base pairing in yeast 5S and 5.8S RNA infrared spectroscopy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3851–3861. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volckaert G., Fiers W. Micro thin-layer techniques for rapid sequence analysis of 32P-labeled RNA: double digestion and pancreatic ribonuclease analyses. Anal Biochem. 1977 Nov;83(1):228–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90531-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R., Garrett R. A. A new RNA-RNA crosslinking reagent and its application to ribosomal 5S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Nov;5(11):4065–4075. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.11.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner H., Yuan R., Crothers D. M. Does 5S RNA function by a switch between two secondary structures? Nature. 1977 Mar 10;266(5598):193–194. doi: 10.1038/266193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Erdmann V. A. Activities of B. stearothermophilus 50 S ribosomes reconstituted with prokaryotic and eukaryotic 5 S RNA. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jul 15;33(3):315–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Pongs O., Erdmann V. A. Binding oligonucleotides to Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus 5 S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):83–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90296-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Woo N. H., Rich A. Initiator tRNAs have a unique anticodon loop conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3289–3293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann J., Erdmann V. A. Binding sites of E. coli and B. stearothermophilus ribosomal proteins on B stearothermophilus 5S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2267–2288. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann J., Erdmann V. A. Identification of Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus ribosomal protein binding sites on Escherichia coli 5S RNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 17;160(3):247–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00332968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]