Abstract
Carboxypeptidase N (kininase I, arginine carboxypeptidase; EC 3.4.17.3) cleaves COOH-terminal basic amino acids of kinins, anaphylatoxins, and other peptides. The tetrameric enzyme of Mr 280,000 was purified from human plasma by ion-exchange and arginine-Sepharose affinity chromatography. Treatment with 3 M guanidine dissociated the enzyme into subunits of 83,000 and 48,000 molecular weight, which were separated and purified by gel filtration or affinity chromatography. When tested with hippurylarginine, hippurylargininic acid, benzoylalanyllysine, or bradykinin, the Mr 48,000 subunit was as active as the intact enzyme and was easily distinguished from human pancreatic carboxypeptidase B (EC 3.4.17.2). However, the Mr 48,000 subunit was less stable at acid pH or at 37 degrees C than the intact enzyme was. The carbohydrate-containing Mr 83,000 subunit was enzymatically inactive but stabilized the Mr 48,000 subunit at 37 degrees C. Trypsin, plasmin, and plasma or urinary kallikrein cleaved carboxypeptidase N into lower molecular weight active fragments, which were unstable at 37 degrees C. Cleavage of the Mr 48,000 subunit with the same enzymes increased activity and yielded fragments of Mr 29,000 or less. Antibodies to the Mr 83,000 of Mr 48,000 subunits crossreacted with the intact enzyme, and antibody to carboxypeptidase N also recognized both subunits. However, antibody to the Mr 83,000 subunit did not recognize Mr 48,000 subunit and antibody to the Mr 48,000 subunit did not crossreact with the Mr 83,000 subunit. Thus, this study indicates that carboxypeptidase N is composed of two immunologically distinct subunits, a Mr 48,000 subunit that is responsible for the enzymatic activity and a Mr 83,000 subunit that may stabilize the enzyme in blood.
Full text
PDF
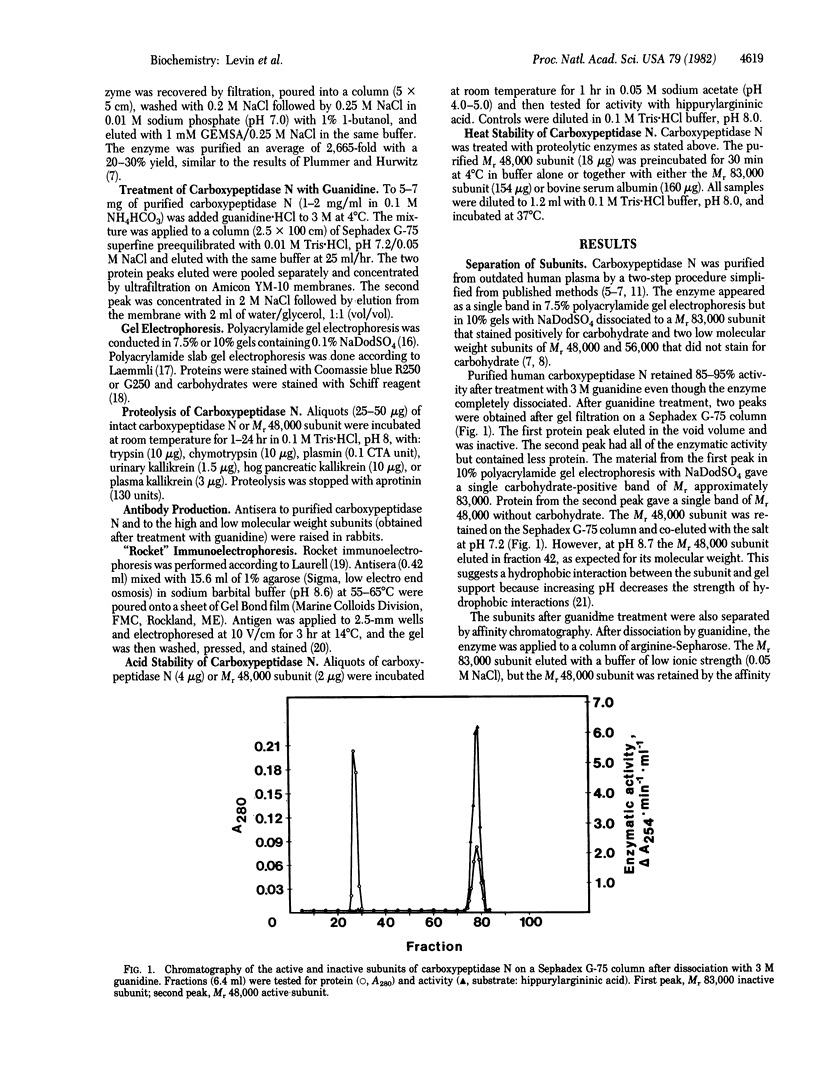
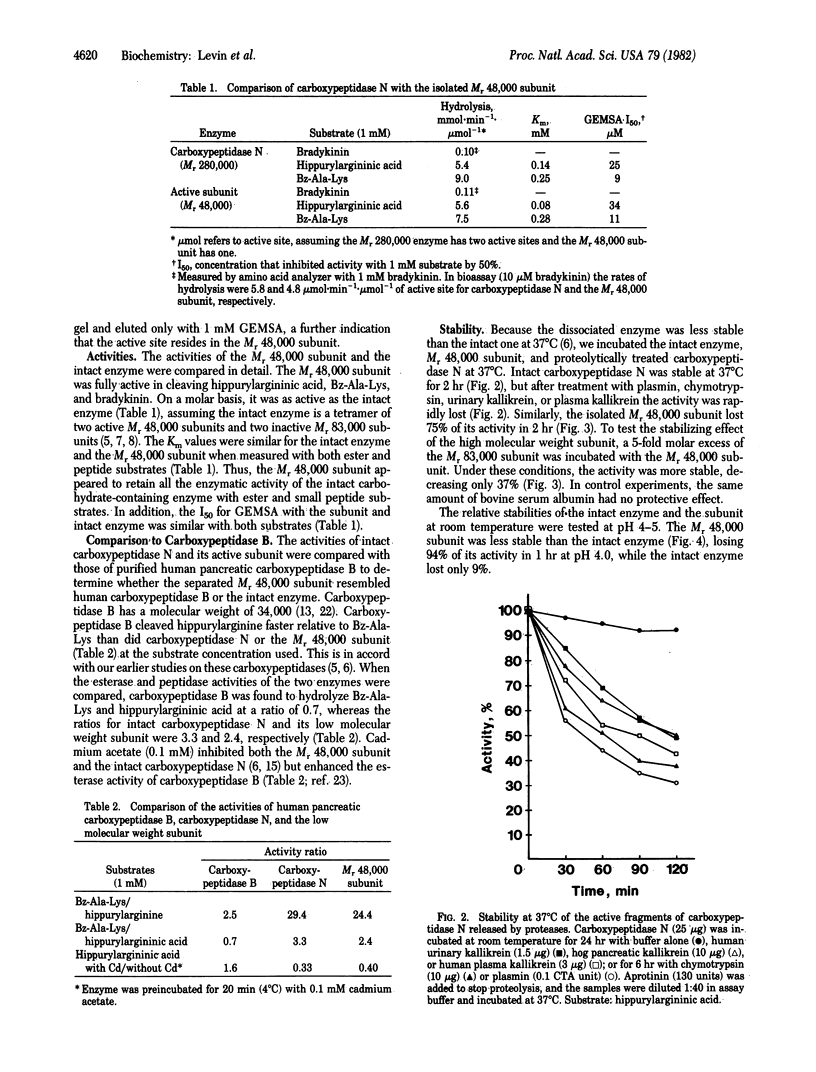
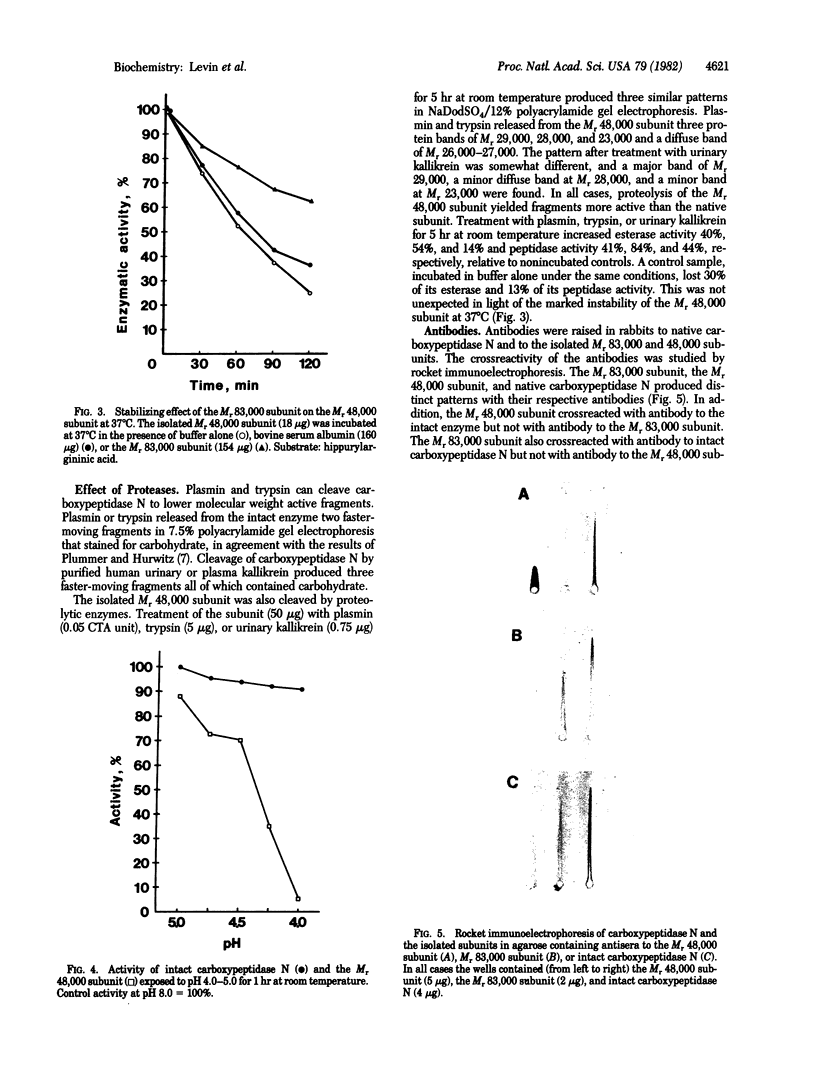

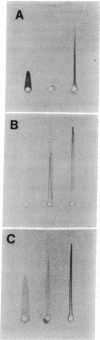
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bokisch V. A., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxin inactivator of human plasma: its isolation and characterization as a carboxypeptidase. J Clin Invest. 1970 Dec;49(12):2427–2436. doi: 10.1172/JCI106462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin N. C., Hugli T. E., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Serum carboxypeptidase B: a spectrophotometric assay using protamine as substrate. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 21;73(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Yang H. Y., Tague L. L., Manning N. Carboxypeptidase in blood and other fluids. 3. The esterase activity of the enzyme. Biochem Pharmacol. 1967 Jul 7;16(7):1287–1297. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(67)90159-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLK J. E., GLADNER J. A. Influence of cobalt and cadmium on the peptidase and esterase activities of carboxypeptidase B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Mar 18;48:139–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90524-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLK J. E., PIEZ K. A., CARROLL W. R., GLADNER J. A. Carboxy-peptidase B. 4. Purification and characterization of the porcine enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2272–2277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanneret L., Roth M., Bargetzi J. P. Carboxypeptidase N from pig serum. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Jun;357(6):867–872. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.1.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapitany R. A., Zebrowski E. J. A high resolution PAS stain for polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney W. C. An improved staining technique for precipitin bands in agar or agarose gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 16;96(3):1123–1127. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovic D. V., Marinkovic J. N., Erdös E. G., Robinson C. J. Purification of carboxypeptidase B from human pancreas. Biochem J. 1977 May 1;163(2):253–260. doi: 10.1042/bj1630253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay T. J., Phelan A. W., Plummer T. H., Jr Comparative studies on human carboxypeptidases B and N. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Oct 15;197(2):487–492. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90271-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay T. J., Plummer T. H., Jr By-product analogues for bovine carboxypeptidase B. Biochemistry. 1978 Feb 7;17(3):401–405. doi: 10.1021/bi00596a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshima G., Kato J., Erdös E. G. Plasma carboxypeptidase N, subunits and characteristics. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Sep;170(1):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr, Erdös E. G. Human plasma carboxypeptidase N. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):442–449. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer T. H., Jr, Hurwitz M. Y. Human plasma carboxypeptidase N. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3907–3912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Fornstedt N. Group fractionation of plasma proteins on dipolar ion exchangers. J Chromatogr. 1970 Sep 23;51(3):479–489. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96895-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF E. C., SCHIRMER E. W., FOLK J. E. The kinetics of carboxypeptidase B activity. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3094–3099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]